The recently announced Retirement Income Review terms of reference detail the three pillars on which Australia’s retirement income system is based – age pensions, compulsory superannuation and voluntary savings. This paper focuses on the second pillar, superannuation.
There are three key outcomes that can be met by the Retirement Income Review:
- Further develop the risk adjusted returns disclosure arrangements criteria to assist retirees in understanding the risks inherent in retirement income products.
- Encourage the development of a variety of risk management approaches with the objective of improving risk adjusted returns for retirees.
- Develop guidelines for ‘alternative – conservative’ and ‘alternative – growth’ asset classifications, based upon the risk level rating and in particular the product’s ability to address sequencing risk.
1. Risk adjusted returns disclosure
The December 2018 Australian Government Actuary Paper ‘Retirement Income Risk Measure’, discusses a range of standard metrics to help consumers make decisions about the most appropriate retirement income product for their own circumstances.
It is noted that:-
“…behavioural economists commonly point out that individuals are more averse to downside variation than upside variation. Intuitively this would apply to retirement incomes. For this reason, I have chosen to focus on quantifying downside risk and using that to measure the relative ‘income risk’ of various products.”
The Actuary’s advice says on page 6:-
“The proposed presentation for the fact sheet is a scale of one to seven referencing ‘income security’. A high number on the scale would indicate expected income is stable and reliable, higher risk products would equate to a low level of security, so a lower number on the scale ...
The income security measure takes account of inflation, longevity and market risk. For consumers these risks may be of different values. For example, a consumer who is concerned about whether their income varies due to market forces may want to know whether the product protects them from this particular risk.”
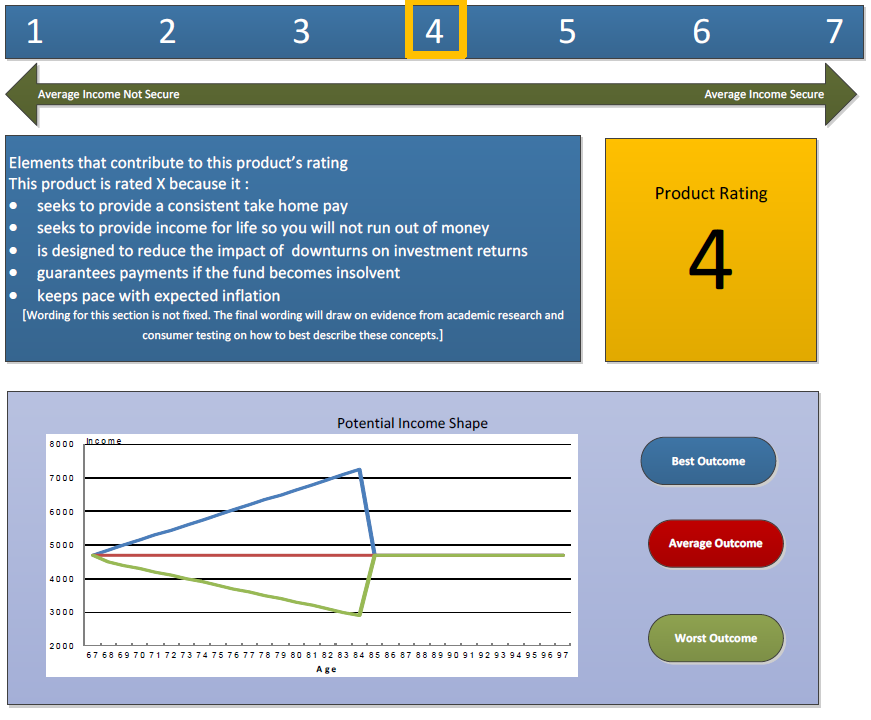
The much-discussed 'Comprehensive Iincome Product in Retirement' (CIPR) would provide a complete solution that balances a number of competing objectives. The three key retirement objectives are to maximise income, ensure income is provided for life and provide flexibility to access capital.
The Review provides the opportunity for industry to critically review the Treasury analysis of CIPR and observations on the proposed risk objectives (including any suggestions on how the approach could be improved). This process may enhance the risk metrics ratings products will receive on their ability to address longevity risk, market risk, sequencing risk and inflation risk.
2. Encourage the development of a variety of risk management approaches
There are a variety of investment risk management approaches with the objective to meet the equity income needs of retirees and defend against losses in declining markets.
Typically, the investment generates dividends from a diversified portfolio of Australian shares with an investment risk management overlay that aims to reduce the volatility of returns, in particular defending against losses in declining markets.
A brief summary of the approaches is as follows:
- Vary asset allocation between stocks and bonds (diversification)
- Buy underlying asset, write call options (buy-write income funds)
- Long/short funds (market neutral, 130/30)
- Buy underlying asset with the ability to sell futures contracts
- Buy put options and hold cash
- Buy underlying assets, buy put options (always include a ‘hard’ risk parameter)
These approaches are adopted by Russell Investments, State Street and Gyrostat (amongst others).
By developing clear evaluation criteria, industry will likely continue to develop innovative risk-managed investment approaches. It is likely that through the combination of these approaches, retiree solutions that maximise risk adjusted returns can be developed, with external providers becoming a component part of the retirement product if these are ‘best of class’ addressing a particular component of risk.
3. ‘Alternative – defensive’ and ‘alternative – growth’ classification criteria
For a product to be classified as ‘alternative – defensive’ it must address sequencing risk. Sequencing risk is the risk that the order and timing of investment returns in unfavourable, resulting in less money for retirement. If the benchmark used by a fund has experienced significant drawdowns, it does not address sequencing risk, and would be an ‘alternative – growth’ classification with a lower risk rating.
The marketing literature of many funds attracting retiree investors typically show:
- Income feature
- Return feature over specific time periods
- Relative performance versus selected index over specific time periods
Rarely do they report the maximum capital drawdown since inception. Given that the fund’s objective is to outperform a chosen index, the underlying investment may be exposed to large losses in the event of a major market correction. The protection element is reflected in the fund's maximum capital draw-down.
Many doubt the Review will focus on such definitions, as the super industry has struggled to deliver consistent standards to define growth or defensive assets.
Conclusion
The desirable retirement income product features combine protection, returns and regular income through all stages of the investment cycle, including large market falls. The Retirement Income Review can make positive contributions towards this objective and ultimately meet the policy objective to enable retirees to maintain their standards of living when they retire from the paid workforce or reach the retirement age.
Craig Racine is Managing Director of Gyrostat Capital Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.