Remember in 2011 when Netflix raised prices by dividing its streaming subscriptions from its DVD service? The announcement sparked an uproar that forced the company to issue an apology and hammered the stock price.
Today the world is in a very different place, and so is Netflix. The company is now a dominant streaming service and a megahit-making machine with more than 213 million subscribers worldwide. Its latest breakout, 'Squid Game' — a Korean drama about children’s games played with deadly consequences — captivated some 142 million households, making it the most viewed show in Netflix history.
This rising popularity has empowered the company to boost its prices. It has increased subscription rates in the U.S. four times since 2014, a period of robust subscriber growth globally. This is an example of pricing power, the ability to increase prices without losing customers.
Pricing power can be an antidote for inflation
Pricing power, always a positive for companies that can sustain it, may be a crucial competitive advantage in the year ahead. Inflation has surfaced across many global economies, and there are signs that it could linger in the coming months. The annual inflation rate in the U.S., as measured by the consumer price index, rose to 5.4% in September, its highest level in 13 years. Rising costs can erode a company’s profit margins and, ultimately, investor returns. But companies with clear, sustainable pricing power can protect their profit margins by passing those costs along to customers.
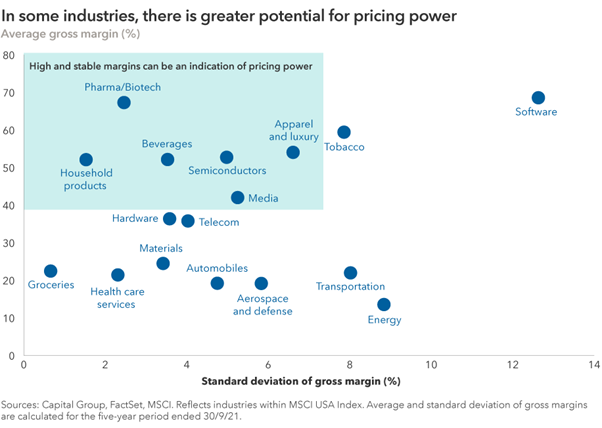
With growth slowing and inflation pressures building, I am focused on investing in companies with proven pricing power that are also the beneficiaries of secular growth trends.
Health care services: A prescription for inflation’s ills
High medical costs are a perennial ‘hot button’ issue for the government, and for good reason. Over the last 20 years, health care costs have risen at about 2.5 times the rate of broad inflation, as measured by the PCE inflation rate followed by the U.S. Federal Reserve.
Historically, health insurance companies have had pricing power and passed on rising health care costs to their customers through higher premiums. Today, companies like UnitedHealth Group are no longer mere toll collectors on the freeway of rising health care costs. They actually manage care. It is focused on helping governments and health care providers reduce spending and improve outcomes for patients. The company has been investing in predictive analytics and care delivery to reduce inefficiencies in the U.S. health care system.
They determined that the most powerful person in the care delivery ecosystem is the primary care doctor, who represents 3 cents of every dollar we spend on health care but determines where another 85 cents is spent. By getting primary care doctors involved earlier in decisions about care, UnitedHealth is seeking to keep members healthy and get more value for every dollar spent. By delivering more value, UnitedHealth can maintain its pricing power while helping to tackle a long-term problem in the US.
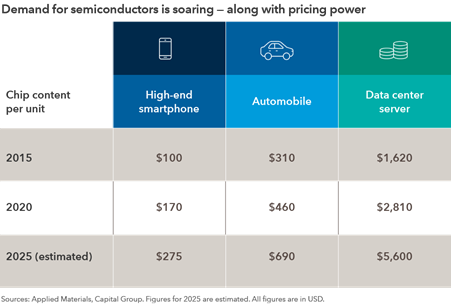
Semiconductors: Everywhere, in everything
The story of pricing power in the semiconductor industry is simple: Soaring demand meets limited supply. Today semiconductors can be found not only in mobile phones and laptops but also in everyday household products like refrigerators and ovens. New cars can require as many as 100 chips. Indeed, the auto industry has felt the brunt of the global shortage in semiconductor supply.
The rollout of new technologies, like 5G, artificial intelligence and cloud computing have further fuelled the world’s appetite for chips. In August, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing disclosed that it would raise chip prices by as much as 20%.
Consolidation in the semiconductor industry has transformed the competitive landscape, leaving a few dominant players with potential pricing power in specialized areas of the market. For example, companies with proprietary chip designs, like Broadcom, or Dutch chip-equipment manufacturer ASML, could raise their prices in an inflationary environment.
Beverages: Thirsty for leading brands
The ability to raise prices without serious backlash not only varies across industries but also within them. In the food and beverage industry, drink companies tend to pass along higher costs to consumers better than many food companies. That’s because the beverage industry is dominated by a few players with strong brand recognition.
One example is Keurig Dr Pepper, the producer of sodas and single serving coffee pods. The company has a history of pricing power, particularly for its most popular soft drinks, which include Canada Dry, Snapple and, of course, Dr Pepper.
Video games: Not just child’s play
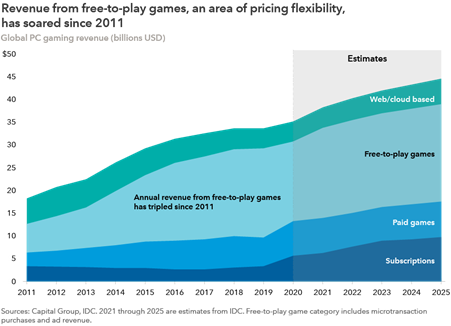
Once considered a minor niche in the entertainment industry, video games have soared in popularity and now represent the fastest growing segment of the world’s media entertainment industry. The global gaming industry is expected to grow to $225 billion in annual revenue by 2025.
Manufacturers have recently been flexing their power to raise prices. With Microsoft and Sony introducing updates to their Xbox and PlayStation consoles, respectively, game makers have disclosed plans to raise prices on console games to help account for the cost of creating more sophisticated games.
A prime example of pricing power potential in the industry is the annual revenue from free-to-play games like Apex Legends from Electronic Arts and Fortnite, published by Epic Games. Tencent has a 40% ownership stake in Epic. Activision owns King, the publisher of popular mobile game Candy Crush. Free-to-play games generate revenue through advertising, whose rates can be increased as costs go up and through in-game purchases.
Believe it or not, players spend real money on virtual clothing, weapons and other supplies for their gaming characters. Essentially, industry leaders can set the price for such items as they please.
The bottom line for investors: Focus on pricing power
I don’t think we are headed into a period of sustained inflation but I do believe rising costs are likely to linger in the coming months, making it the biggest risk investors will face in 2022.
With slowing growth, rising inflation and other uncertainties on the horizon, 2022 may seem a daunting environment for investors. But I’m optimistic that an active portfolio of select companies with strong pricing power can help investors thrive in the years ahead.
Diana Wagner is an Equity Portfolio Manager with Capital Group. Capital Group Australia is a sponsor of Firstlinks This article contains general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Please seek financial advice before acting on any investment as market circumstances can change.
For more articles and papers from Capital Group, click here.