An analysis of the performance of factors in the Australian share market reveals some valuable insights for equity investors. Contrary to conventional wisdom, large capitalisation stocks have consistently beaten small-cap companies.
While most investor portfolios have exposure to one or more factors, some factors tend to deliver better risk-adjusted returns than others over the longer term. Traditionally, it is believed that small caps outperform large caps because they are growing faster, a conclusion most famously promoted by academics Eugene Fama and Kenneth French. Their research found investors were rewarded for the greater risk in backing more volatile smaller companies.
A challenge to conventional wisdom
But our factor analysis reveals that over longer-term periods of 10 and 20 years, Australian large cap stocks outperformed small caps convincingly, as shown below to 30 June 2020.
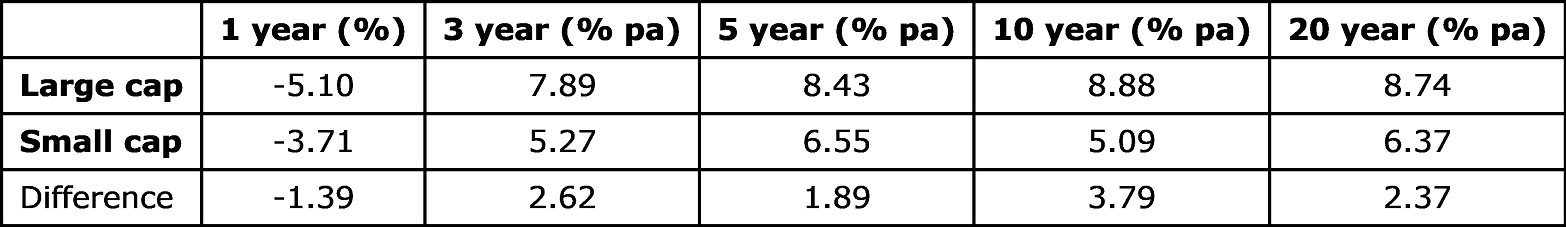
Source: Foresight Analytics and Refinitiv. Returns are measured by the Foresight Large Cap universe and Foresight Small Cap universe, which are represented by the top 90% market cap of companies in the Australian share market while the small caps are the bottom 10% of market cap.
The main reason is the concentration of the ASX200, where the weight of money, active and passive, has been directed to a few large offshore earners, the big banks, miners and healthcare. Example include miners BHP Billiton, Rio Tinto and Newcrest; financials Commonwealth Bank, Westpac and ANZ; healthcare names CSL, Sonic and Ramsay; IT heavyweights Computershare, REA and Carsales. This has entrenched the gains of large caps over small caps over the longer term.
Top performing sectors within large cap world
Within the large cap world, some sectors stand out in consistently delivering high returns over the past decade, such as healthcare, industrials, technology, consumer cyclicals and financials. The laggards over the past decade include energy, utilities and telecom.
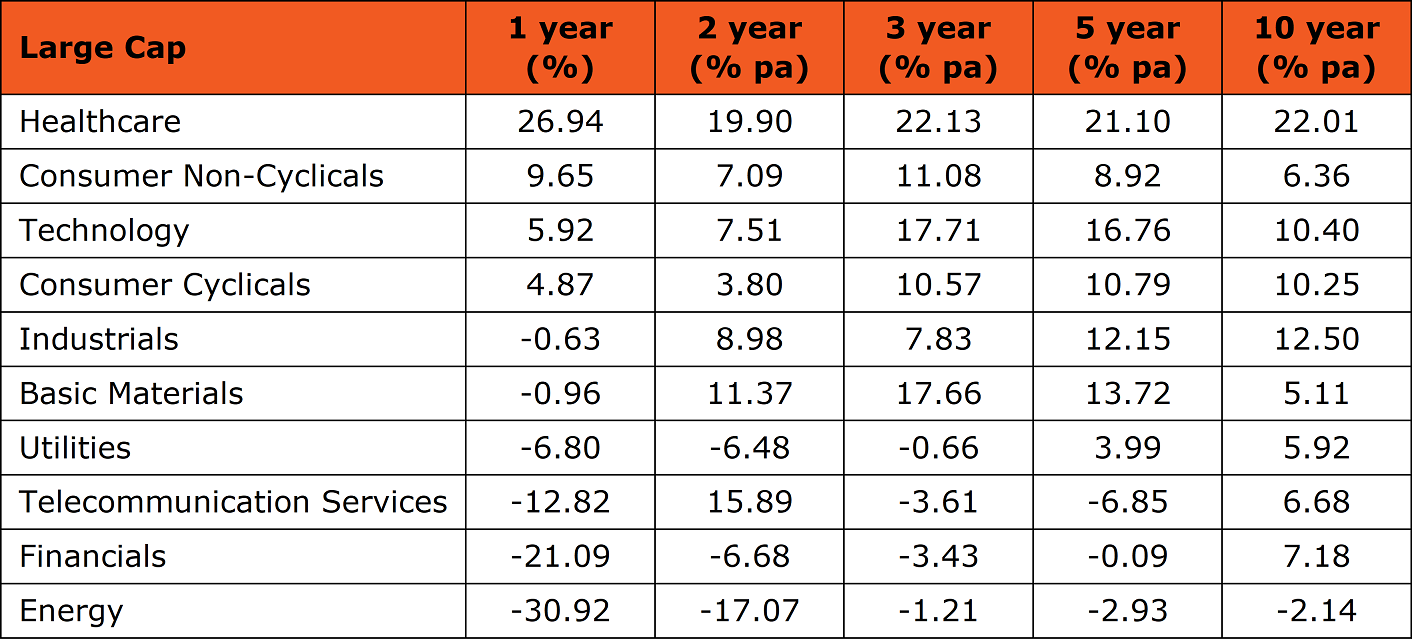
Note: Returns are as at 30 June 2020. Thomson Reuters Business Classification (TRBC) is used for industry sectors.
Data source: Foresight Analytics Global Investment Database
High-performing stocks from the mining industry have been boosted lately by gold’s stellar performance and an uptick in other commodity prices such as iron ore. Large cap consumer non-cyclical stocks are well represented by Domino’s Pizza, whose fortunes are continuing to rise with more eating at home due to COVID-19 restrictions.
Size performance over the short term
Over the shorter periods, the story is not dissimilar and large caps outperform. Money tends to flow into particular types of assets – most notably quality stocks – during a crisis, but we found that large caps consistently outperformed small caps across all major financial market crises.
This is exactly what happened in the first month of the COVID-19 crisis, though small caps rebounded strongly after the first 30 days of the crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in large cap, quality and growth factors delivering significant positive premiums. The impact of the pandemic on factor returns has been much more severe (in speed and depth) than the previous major crises, particularly during in the first 30 days. As a result, the coronavirus pandemic provided opportunities for generating alpha from managing factor exposure or pursuing factor rotation strategy.
However, unlike previous crisis, the value factor has underperformed growth while aggressive asset growth beat conservative asset growth. In addition, after a significant underperformance from small caps, we witnessed a strong recovery after the first 30 days. Momentum and quality premiums witnessed significant volatility after first 30 days of the current crisis as well, as the chart below shows.
Initial impact of COVID-19 crisis more severe than previous crises
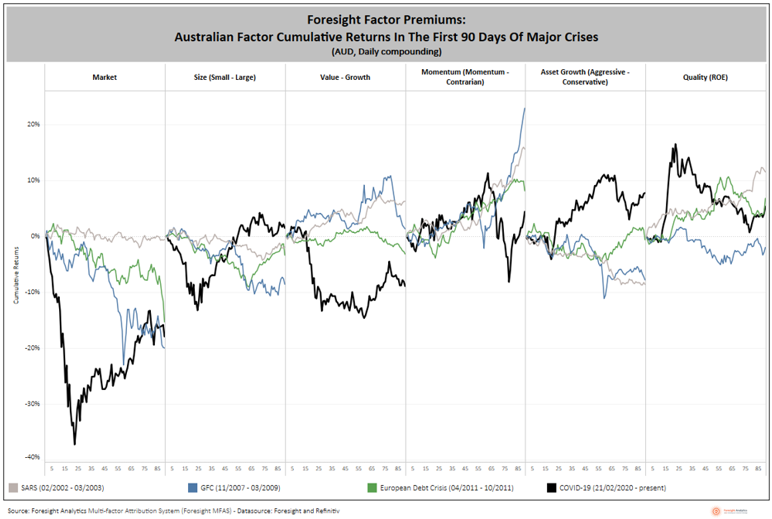
Given the pattern of the large cap performance behaviour during the previous three crises, investors can reasonably expect the large caps to outperform during future stock market crises.
Factor investing is often captured by active fund managers investing in assets with particular attributes such as value stocks or small caps, or ‘smart beta’ ETFs that track a rules-based index. For investors, it is important to understand how factors work when evaluating your investment’s performance and making any decisions to hire or fire a manager or invest in a particular investment product. Some factors give better risk-adjusted returns than others.
Despite the rhetoric from some investors, backing smaller, riskier stocks in the Australian share market will not necessarily give better returns than backing larger, less volatile stocks. Our share market is too concentrated for that.
Additionally, investors can manage the negative drag from size factor by avoiding passive and smart beta strategies that seek to maximise exposure to the size factor without paying any regard to other fundamentals. Investors would be better served by selecting skilled small cap active managers seeking to add value by picking fundamentally strong companies.
Jay Kumar is Founder and Managing Director at Foresight Analytics. This article contains general information only and does not consider your personal circumstances.