Historically, an allocation to the US large cap growth category of the equity asset class, as represented by the Russell 1000® Growth Index, has presented investors with a reasonable opportunity to gain exposure to mid cap stocks. For this analysis, we define US mid caps as companies with a market capitalisation between $2 billion and $25 billion1. The advantage of this inefficiency within the asset class is that it may help to diversify a portfolio, at least from a market capitalisation standpoint. However, due primarily to the strong performance of a handful of technology stocks (and their ensuing increase in market capitalisation) within the Russell 1000® Growth Index, today’s large-cap growth investor may be less able to gain mid cap exposure through the traditional large cap growth allocation (as shown in Exhibit 1).
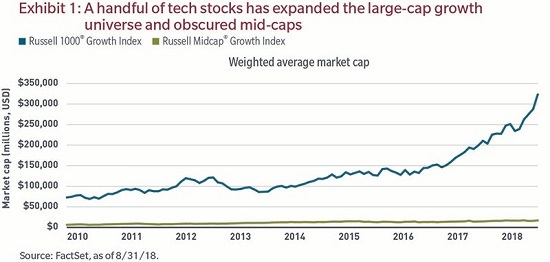
The increasing dominance of large caps
In our view, the dominance of the most influential large cap stocks can be better appreciated when viewed from the perspective of market-capitalisation buckets, as illustrated in Exhibit 2. Exposure to mid cap stocks in the Russell 1000® Growth Index has declined from 39% of that index in 2010 to just 14% as of 31 August 2018. Also worth noting is where this percentage change was reallocated. We have observed a significant increase in stocks with a market capitalisation greater than $300 billion in the index.
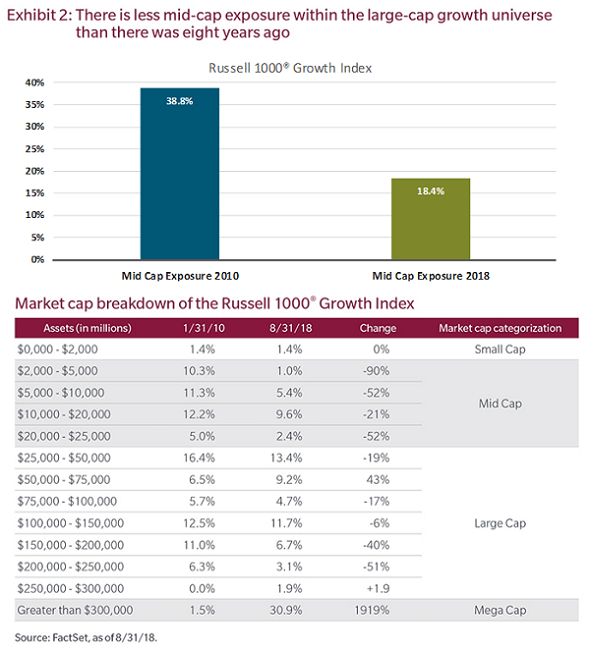
This one-dimensional shift in the market cap exposures has added an additional layer of concentration risk where over 30% of the Russell 1000® Growth Index is focused on those companies with a market valuation of over $300 billion.
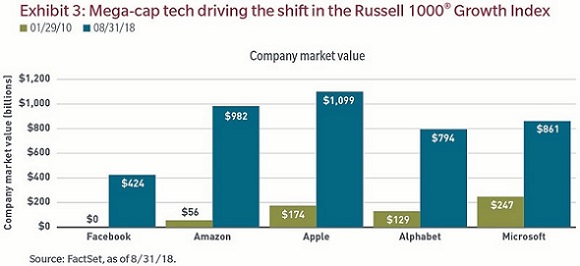
Exhibit 3 puts it in perspective. In 2010, Facebook was not even a publicly traded company (IPO: May 2012), but it’s currently the sixth-largest company in the index, behind only Apple, Alphabet, Amazon, Microsoft and Berkshire Hathaway.
Dedicated allocation to mid caps
While the market caps for the largest growth companies have accelerated dramatically since mid-2016, outpacing mid caps, how this trend is likely to progress is uncertain. However, an allocation to large cap growth today provides far less exposure to companies further down the capitalisation spectrum. A dedicated allocation to mid cap growth may prove a key component of a comprehensive asset allocation framework moving forward.
In any market environment, we strongly believe that investors should stay diversified across a variety of asset classes. By constructing your portfolio with the awareness of how these weights shift over time, you can help ensure that your portfolio is properly diversified and that your financial strategy supports your long-term goals, time horizon and tolerance for risk. Diversification does not guarantee a profit or protect against loss.
Nick Paul is Institutional Equity Portfolio Manager at MFS Investment Management, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. The views expressed in this commentary are those of the author and are subject to change at any time. These views should not be relied upon as investment advice, as securities recommendations, or as an indication of trading intent on behalf of any investment product.
For more articles and papers from MFS Investment Management, please click here.
Endnotes1 Companies with a market capitalization between $2 billion and $25 billion account for 80% of the constituents in the Russell Midcap® Growth Index, as of 8/31/18.
The Russell 1000 Growth Index® measures US large-cap growth stocks.
The Russell Midcap Growth Index® measures U.S. mid-cap growth stocks. It is not possible to invest directly in an index. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Frank Russell Company (“Russell”) is the source and owner of the trademarks, service marks and copyrights related to the Russell Indexes. Russell® is a trademark of Frank Russell Company. Neither Russell nor its licensors accept any liability for any errors or omissions in the Russell Indexes and/or Russell ratings or underlying data and no party may rely on any Russell Indexes and/ or Russell ratings and/or underlying data contained in this communication. No further distribution of Russell Data is permitted without Russell’s express written consent. Russell does not promote, sponsor or endorse the content of this communication.