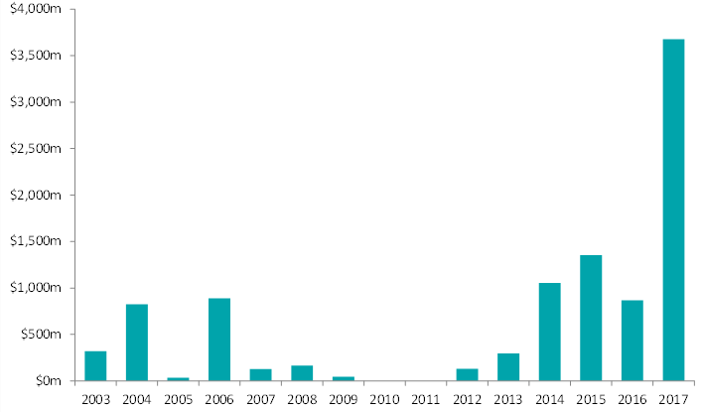
2017 was another big year for both Listed Investment Companies (LIC) and Listed Investment Trusts (LIT) with a record number of new and innovative entrants into the sector. LICs/LITs dominated capital raisings, bringing in $3.7 billion via Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) - accounting for more than half of the IPOs raisings for the year. And this was further supported by a number of secondary market raisings that saw $1.2 billion raised.
Money raised from LIC/LIT IPOs - 2003 to 2017
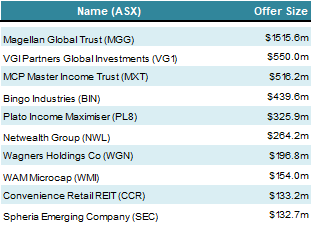
The largest 10 IPOs in 2017 of which 6 were LIC/LIT
Three reason for the growth
The growth rate of LICs was higher than managed funds in 2017, for three main reasons:
- Future of Financial Advice (FoFA) reforms: Since July 2013, commissions paid to financials planners by providers of managed fund have been banned. This has removed the incentive for financial planners to use managed funds over LICs or Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs).
- A competitive dividend yield in comparison to the ASX200: In July 2010, there was a significant change in the Corporations Act that paved the way for LICs to offer greater consistency in dividends. Previously, LICs could only pay a dividend if they had an accounting profit, which saw a number of LICs being unable to pay dividends through the GFC. However, following the introduction of the solvency test, LICs now have greater flexibility to offer sustainable dividend policies even with the absence of accounting profit. Many LICs offer a grossed-up yield higher than the Australian share market grossed up yield of 6.0%.
- Stronger demand from the SMSF market: An increasing number of investors are looking for greater control over their superannuation. The combination of rising property prices and prolonged low interest rate environment has resulted in a level playing field for alternative investment vehicles such as LICs and ETFs. SMSFs are a valuable investor base to cater for, as they now account for 28% of all superannuation assets in Australia and are growing.
We also saw two structural changes which we view as positive developments for LICs:
- IPO cost absorption: Historically, the cost of a LIC IPO - generally a fee of 2-3%- was transferred to the shareholder at listing. As a result, for example, a $1.10 IPO would see an opening Net Tangible Asset (NTA) of $1.06-$1.09. In late 2017, some LICs came to market with a proforma Net Tangible Assets (NTA) in line with its issue price. Managers of Magellan Global Trust (ASX:MGG), Spheria Emerging Companies (ASX:SEC) and VGI Partners Global Investments (ASX:VG1) absorbed the issue cost associated with its IPO, while MCP Master Income Trust (ASX:MXT) had its issue cost paid via a loan, which will be amortised by shareholders over the next 10 years. This enabled shareholders of MGG, MXT and VG1 to access these LICs at NTA on day one.
- Less bonus options: Bonus options issued at IPOs have generally been offered to investors to compensate for the issue cost reflected in the NTA. Investors who seek to purchase LICs in the secondary market must be cautious of the potential dilutionary impact on the NTA of in-the-money options, as options expiry nears. What is perhaps less understood is that the person who exercises these options is not diluted as they have received the benefit of a lower exercise price. As a result, bonus options were sometimes viewed negatively. With managers choosing to absorb the vast majority of the IPO cost, LICs no longer need to offer options as an IPO sweetener. Many LICs came to market without an option attached, removing the overhang that is cast around LICs close to option expiry.
Table 2: LIC/LIT IPO’s - 2017
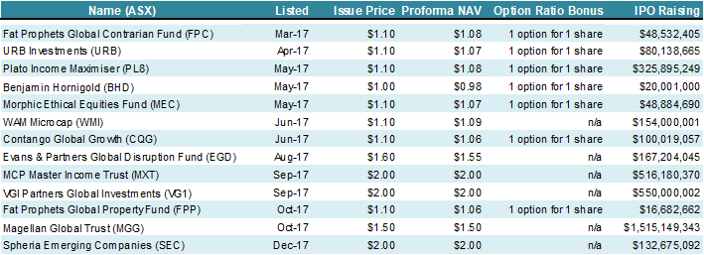 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
The focus for 2018
We anticipate these changes will drive further interest and larger capital raisings that are likely to tip through $500 million plus.
We also expect more growth in areas that are still under-represented in investment portfolios. Global equity-focussed products are likely to be a key beneficiary with an increase in both size and different styles of offering. We expect growth in products that offer high and sustainable income, as well as fixed interest products, which is a gap in the LIC sector. Although it has been a strong period of growth for the sector, we believe there are several drivers now in place to see this growth accelerate over the coming years.
Nathan Umapathy is Research Analyst at Bell Potter Securities. This document has been prepared without consideration of any specific investment objectives. For the latest Bell Potter Quarterly Report, click here, and for the Weekly NTA update, click here.