On the 22 March 2016, Mr Richard Elman, Founder and Chairman of the Noble Group Limited was quoted on Bloomberg as saying:
”We all know that commodities are cyclical, but predicting when that turning point comes is only possible with hindsight, especially with such excessive moves as are currently occurring. Those who come hoping for some kernel of wisdom leave disappointed when I tell them that I don’t know how all the different factors will play out - nor does anyone else.”
It is unusual for a high-profile executive to be so frank and explain how things really are. For someone like Elman who has been involved in building a large commodities business over five decades to admit that predicting turning points in commodity prices is impossible has consequences for all other market participants. If turning points are impossible for him to predict, then it follows that predicting turning points in resource companies is as difficult, if not more difficult. As Ed Seykota famously stated in an interview:
“Commodity trading is the purest form of trading in the world and resources companies are simply a leveraged version of this.”
Nobody rings a bell
Of course, resource journalists, researchers, newsletter writers and research analysts cannot admit this ‘simple truth’ otherwise their very reason for existing would be cast into doubt. Mr Elman has the luxury of having built up a large business and five decades of experience and is a major owner of a business that has experienced significant share price movement over long periods of time.
It follows from this logic that ‘no one rings the bell at the top of a resources cycle’ because it is impossible to predict. Similarly, ‘no one rings the bell at the bottom of the resources cycle’ because it is impossible to predict. It didn’t happen at the top of the last resources boom and it won’t happen at the bottom of the current resources downward trend.
What is extremely interesting, however, it that commodities and consequently resource companies do experience significant periods of trending. This brings us to how an investor actually makes money in resource companies. The short answer is by following the trend once it has been established and exiting the trend once it has ended.
Diagram 1: ASX200 Resources Index over last decade.
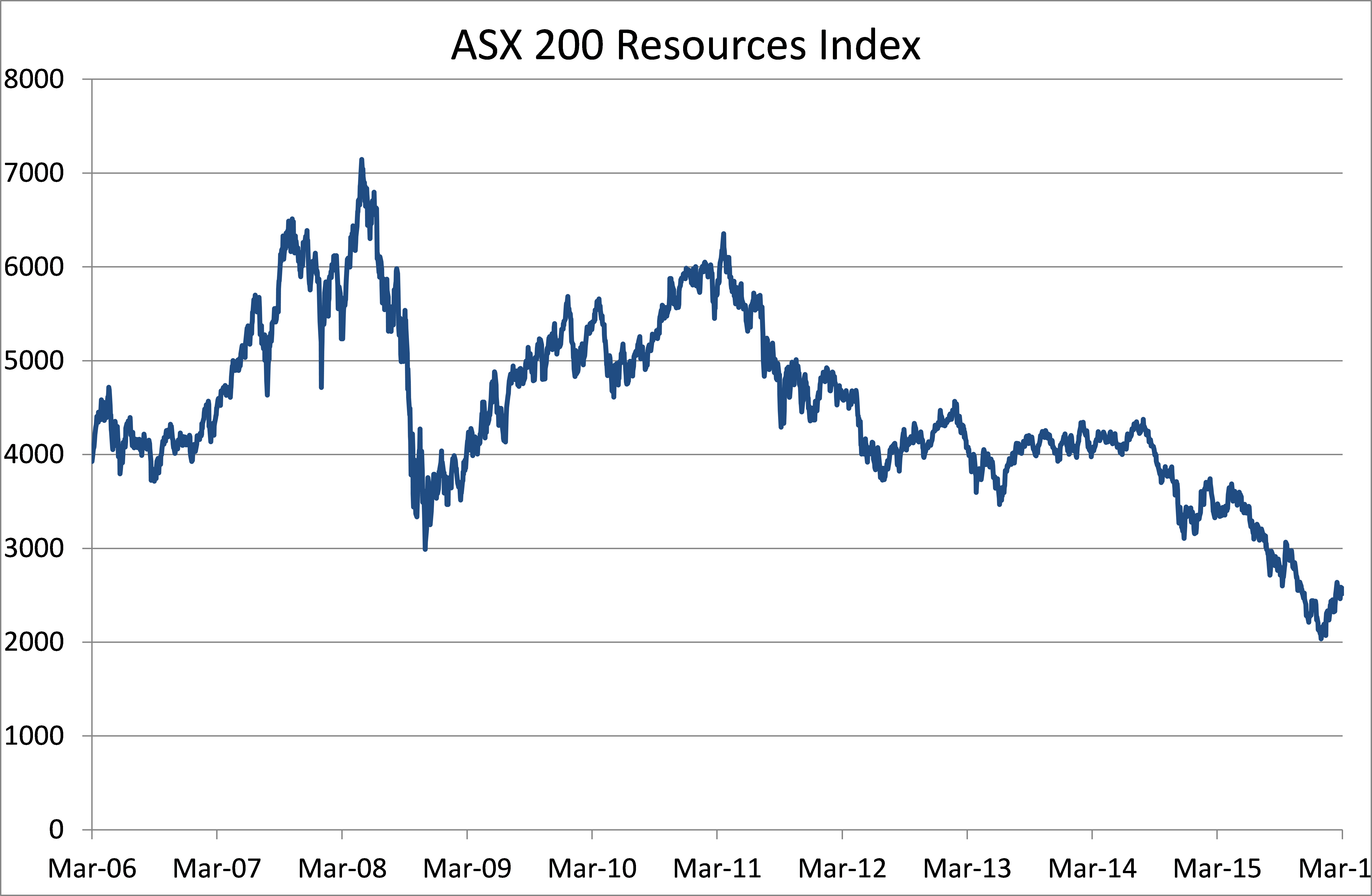
Diagram 1 is a ten-year chart of the S&P/ASX 200 Resources Index. We can see a period up to 2008 when the index was trending up strongly, then a severe sell off during the GFC and a strong recovery and trend until 2011. Since 2011 the resource index has been falling for five years. Only recently we have seen an ‘uptick’ in the resources index and many of the stocks that underlie this index. Clearly the longer-term trend is down but we may be seeing the first early signs of a recovering resources sector. However, as Mr Elman points out, this is impossible to tell, but will be easy in hindsight.
Closing shorts and entering longs
How do we deal with this set of circumstances at Cadence? Having been short a number of commodities over the past three to five years we find ourselves scaling out of these short positions a bit at a time. Diagram 2 illustrates our process of scaling out of (buying back) short positions.
Diagram 2: Exiting shorts
As we exit these short positions we may find that many resources stocks have become fundamentally cheap and are starting to trend up. This process then allows us to enter small long positions and potentially scale into a longer term recovering trend (Diagram 3 below).
Diagram 3: Entering longs
Should this prove not to be the case then we would simply exit these small positions with small losses. In this way we adopt a risk-adjusted approach to determine whether the resource decline has in fact ended and the market is entering a new trend. We believe this is the only way of establishing a position.
It is very difficult to predict turning points in any stocks but particularly difficult in resources stocks. However, once a trend has been established, trends tend to last for considerable periods of time, particularly in cyclical stocks and industries.
As we write this article we know that recent price movements have at a minimum tested long-term resource and energy price trends and may be indicating a longer term change in trend. Only time will tell, but our process for dealing with these trends is well-defined. We are not professing to ‘ring the bell at the bottom’ but the bell may currently be ringing.
Karl Siegling is the Managing Director of Cadence Capital Limited (ASX: CDM). CDM is a Listed Investment Company currently celebrating its 10-year anniversary. This article is for general education and does not consider the individual circumstances of any investor.