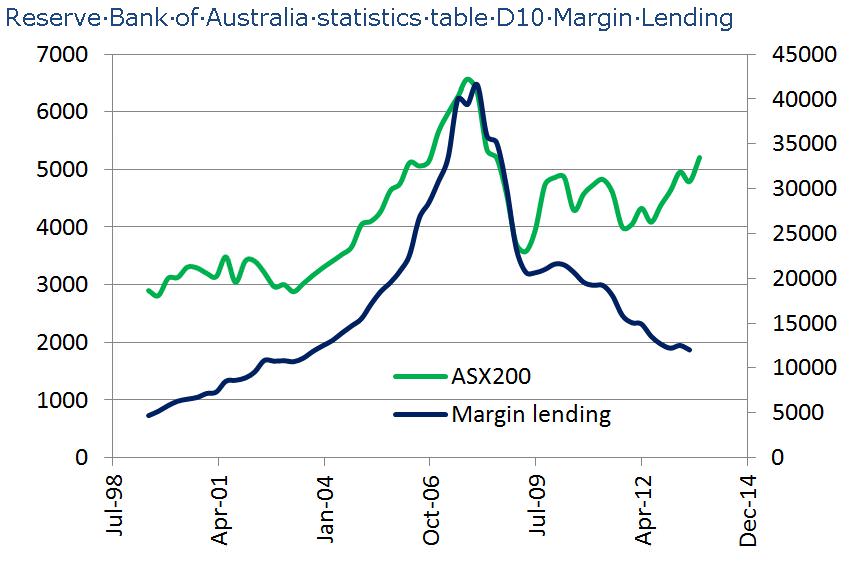
One of the features of the equity market bull run into 2007 was rapid growth in margin lending. Between January 2000 and September 2007, the total amount of outstanding margin loans in Australia grew from around $6 billion to over $40 billion. While this still did not represent a large fraction of the total capitalisation of the Australian market (around 3% of the total in 2007), it was a significant development for the retail end of the market.
When the equity market plunged during the GFC, so too did the volume of margin lending. In March 2009, total margin lending had shrunk to around $20 billion.
This makes intuitive sense. With the value of collateral sharply diminished, and confidence at reduced levels, it’s no surprise that margin lending levels fell sharply. What’s more interesting is what has happened since then.
As the chart below shows, since the bottom of the market in March 2009, equities have made good headway. While still not at pre-GFC levels, they have delivered healthy returns in recent years. Total margin lending, however, has continued to slide towards $10 billion, even as confidence has been returning to the market.
Chart 1. ASX200 and total margin loans outstanding
To our way of thinking, this is a healthy development. Some reasons to be wary of margin lending include:
- it tends to be an expensive form of funding. Margin lending only benefits the investor where the return on the equities exceeds the cost of the debt. With the long run average return on equities running at perhaps 11% per annum, there isn’t much room left after paying interest rates close to 8%
- this benefit disappears altogether if margin calls force you to sell at the wrong time. After a significant fall in share prices, the most successful investors tend to be the ones buying. Often, they are buying from margin borrowers, who have no choice but to sell
- debt funding of any sort tends to bring with it sleepless nights. A cool head is a prerequisite to good investment decisions, and when things get challenging, high levels of debt are a menace to good order.
At Montgomery, we sit in the far corner of the room. We use no leverage, and usually have a material part of our funds sitting in cash. We also avoid investing in companies that have material debt on their balance sheets. This absence of leverage helps foster a steady approach to our decision-making when market conditions become challenging, as they often do.
It is unlikely we will change our attitude towards debt any time soon, but if we were to wake up one day and decide that some leverage would be good, it is unlikely to be a margin loan.
It will be interesting to see what happens to the margin lending industry from here. We expect that having learned some of the above lessons the hard way, investors who do gear into shares are increasingly doing so by borrowing against residential property. Provided gearing levels are kept to prudent levels, this type of borrowing is likely to deliver a much better experience for borrowers. Nevertheless, if markets continue to rise, it is likely that investors will become more adventurous and margin lending may return, with its higher cost of borrowing.
Over time, of course, a new generation of investors will emerge. Without the benefit of first-hand experience of the GFC, they may embrace margin lending as a shortcut to wealth. When that happens, we will be checking our valuations closely, probably starting to count the rows to the nearest exit.
This cautious approach will no doubt cause some investors to miss out on heady gains. However, patience is a great virtue in investing. On the road to wealth there are many shortcuts that offer themselves to the unwary, and for long-term investors, it’s wise to think carefully about these shortcuts, or avoid them altogether.
Roger Montgomery is the founder and Chief Investment Officer at The Montgomery Fund, and author of the bestseller 'Value.able'