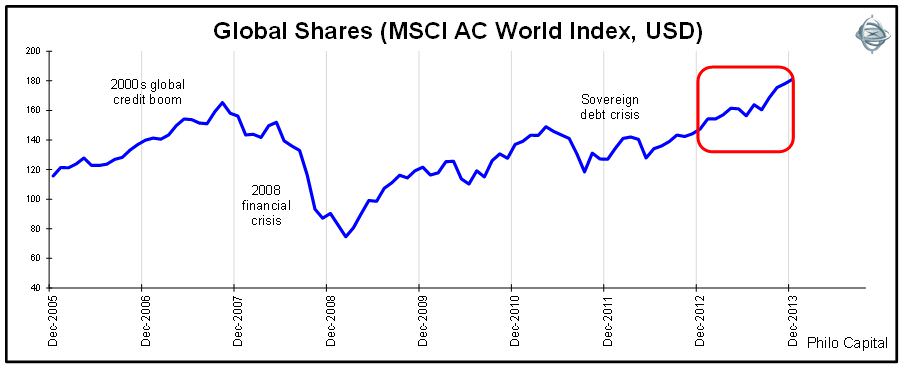
In 2013 stock markets around the world continued their rebound that began in late 2011 and early 2012, following the 2011 dip that was triggered by the European banking and debt crisis and the US credit downgrade. In 2013 the only minor dips for global stock markets were the Cyprus bank bailout crisis in March and the QE taper scare in May-June.
Our first chart shows the global total return index (including dividends) in US dollars since 2005:
The following charts show broad stock market indexes for the main global markets for 2012 and 2013:
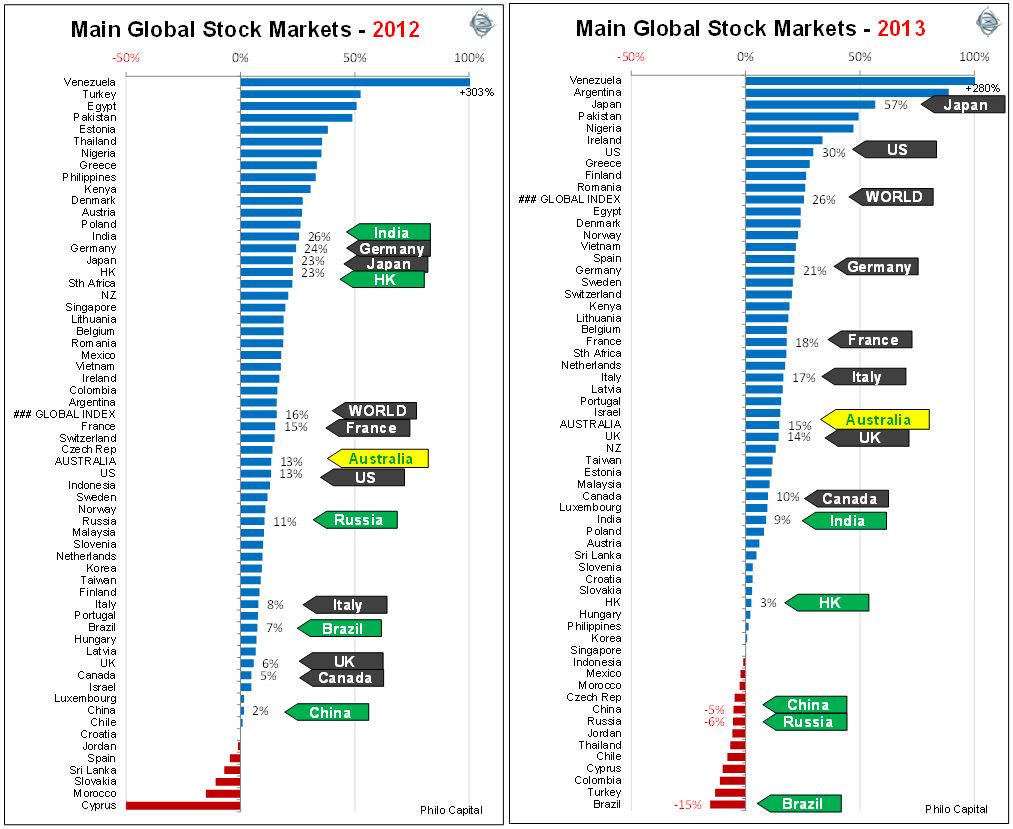
In 2011 earnings and dividends were up in most countries but stock market indexes were down almost everywhere.
In 2012 earnings were down in most markets and dividends were flat or down in most markets, but market indexes were up almost everywhere.
In 2013 almost all developed markets were up, although earnings were weak and their economies were still on life support in intensive care wards, supported by extremely loose fiscal and monetary policies. Meanwhile, the far more fiscally sound and faster growing large emerging markets were suffering the effects of domestic slowdowns, rising inflation and poor equity returns.
Developed Markets
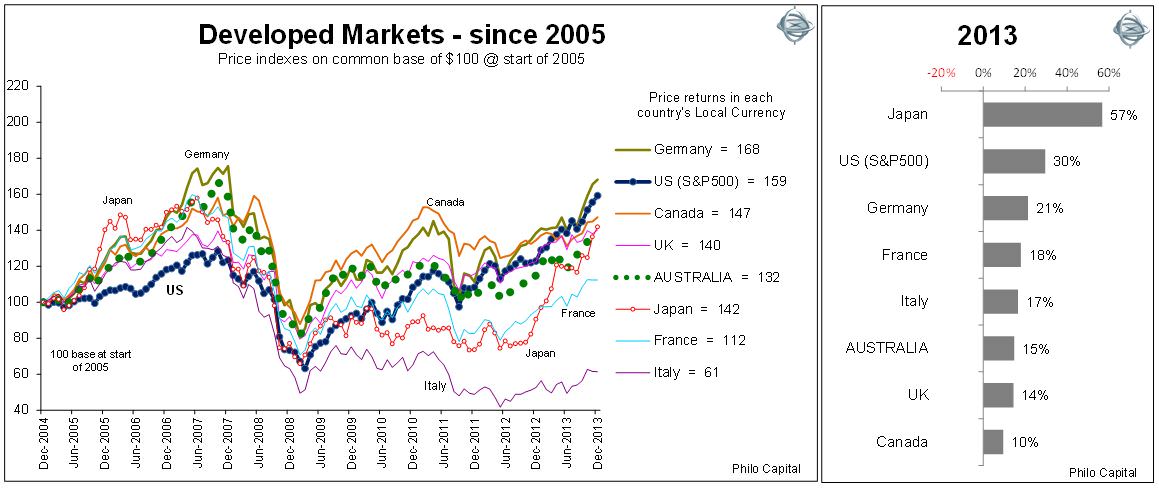
The 2012-2013 rally was led by the big industrial giants - US, Japan and Germany - driven in each market by cyclical companies such as industrials, retailers, media and banks.
European markets showed a pronounced divergence between the so-called ‘industrious’ north and the so-called ‘profligate’ south.
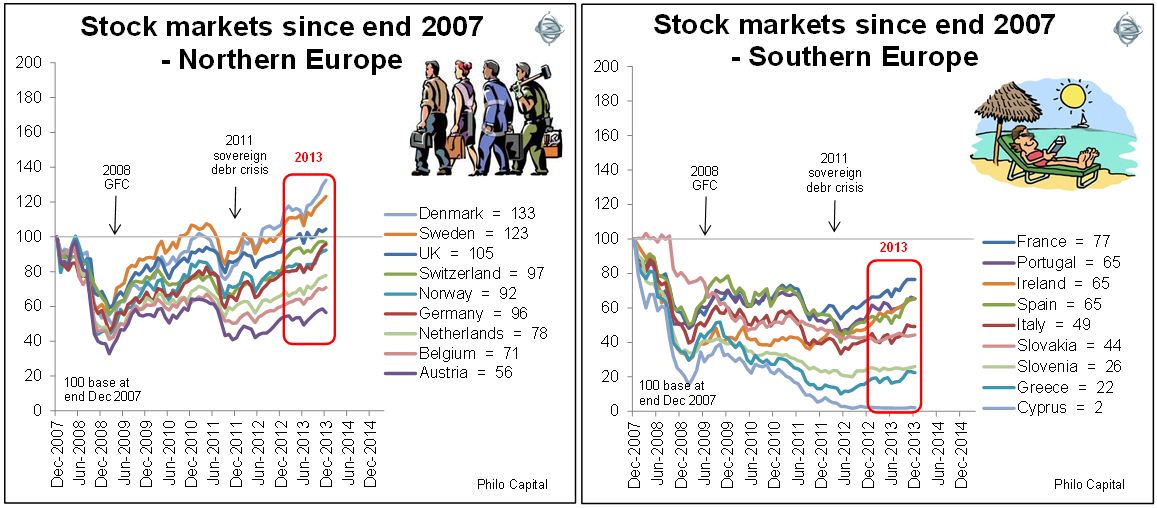
Despite this divergence, virtually all European markets rebounded strongly in 2013 (apart from Cyprus and Slovenia with their banking crises). Even Greece has rebounded strongly since its first and second bailout, as it heads for yet another bailout.
Emerging Markets
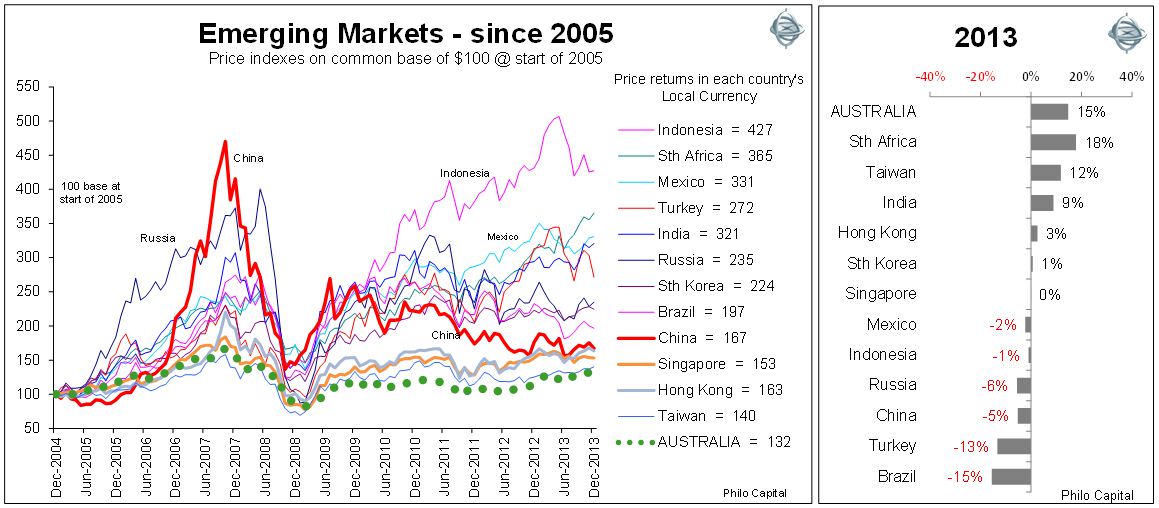
(Note the vertical scales on the charts for developed markets and emerging markets are very different in order to show the much larger swings in the emerging markets. All emerging markets except Taiwan have outperformed the developed markets and Australia by big margins through the pre-GFC boom, through the GFC itself, and in the post-GFC recovery.)
The worst of the main emerging markets have generated similar returns to the best of the main developed markets over the period, so if all markets were shown on the same chart, all of the emerging markets (aside from Taiwan) would appear above the best of the developed markets.
Emerging markets have been much more volatile and have been very vulnerable to the ‘hot money’ effect as money rushes in and out of global markets in ‘risk on/risk off’ swings. We saw this in the capital flight in the wake of the May-June 2013 Bernanke QE scare, and again in December as the QE taper plan was finally announced.
The south-eastern Asian markets were hit hard in the global capital flight due to the QE taper scare but most are far better placed now than they were when the 1997 Asian currency crisis hit.
As in Europe, there is a diversion between north Asian markets (driven largely by China) and South-East Asian markets (which are less reliant on the China supply chain). This is very evident in the following pair of charts:
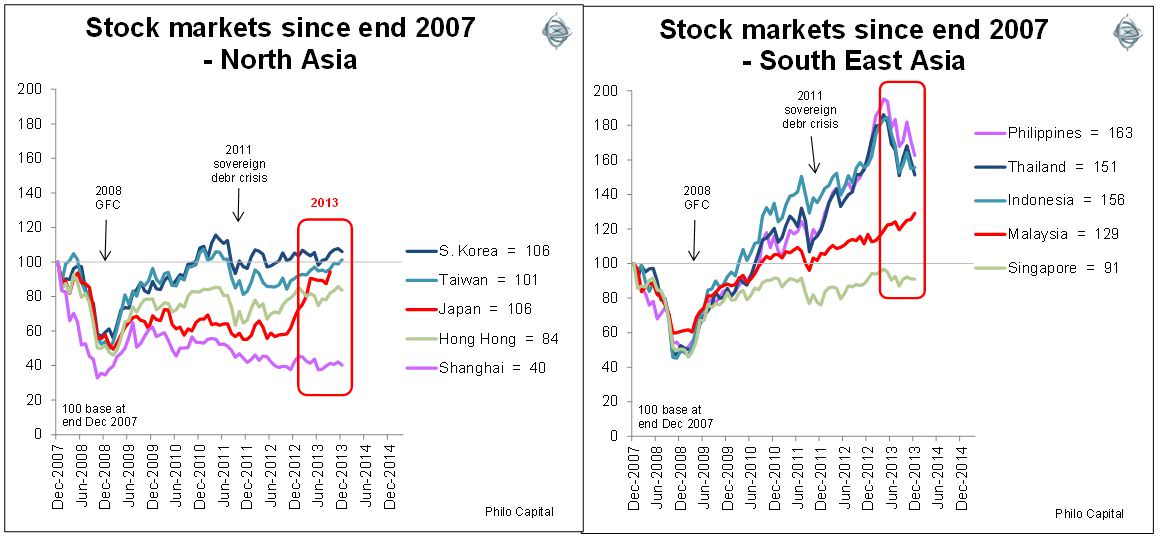
In 2013, as in the past few years, the BRICs (Brazil, Russia, India and China) were the laggards, with their slowing economies, inflation problems and highly concentrated stock markets dominated by state-controlled enterprises.
The term ‘BRIC’ was a brilliant marketing gimmick invented by Goldman Sachs ten years ago to sell stocks and consulting services. However the BRIC markets have generally been a disaster for investors. As investors, we see the BRIC phenomenon more in line with the J P Morgan term: ‘BRIC: Bloody Ridiculous Investment Concept’.
Our consistent advice for investors over the past several years has been: “The further away from China you are the better”.
Ashley Owen is Joint Chief Executive Officer of Philo Capital Advisers and a director and adviser to the Third Link Growth Fund.