Not many investors realise that a decent chunk of their US equities and fixed-income performance over the last 20 years has come from the benefit of hedging, and had nothing to do with the assets' underlying returns.
According to CBA research, hedging your US shares or bonds into Aussie dollars increased your returns by 4% per annum over this period. That is to say, you were paid to hedge, rather than hedging imposing a cost. For lower yielding asset-classes like fixed income, this made a big difference to the realised outcomes.
Between 1999 and 2018, US treasury bonds yielded only 3%, but by hedging into Aussie dollars, the yield increased to 7% while also reducing realised volatility significantly.
Tailwind becomes a headwind
Now the big deal is that this tailwind, which reflected the fact that the RBA’s cash rate was historically situated well above the Fed’s cash rate, has reversed as the Fed has embarked on its hiking cycle.
The chart below shows precisely how this dynamic has changed since 2011. The lower black line is the annualised yield on a US treasury bond while the upper grey line shows the same asset hedged back into Aussie dollars. Observe that in 2011, a US treasury yielding 2.5% morphed into a nearly 7% yield for hedged Aussie investors. The red dotted line represents the benefit or cost from hedging at any point in time.
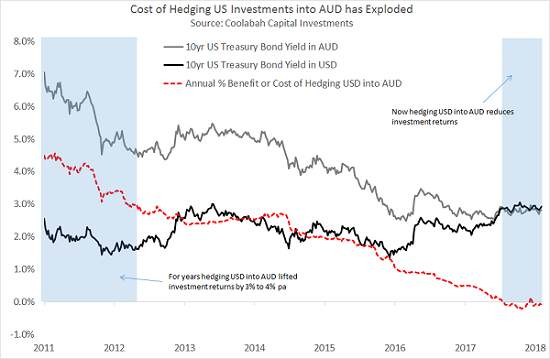
Click to enlarge
Whereas in 2011 local investors picked-up a return uplift of as much as 4.5% hedging US assets into Aussie dollars, that advantage has fallen away over time to the point now where the red dotted line is slightly negative. In 2018, a 2.94% yielding US treasury paid only 2.86% in Aussie dollars.
Understand the cost or benefit of a hedge
This comes back to the principle known as 'covered interest parity'. If you own a US asset and want to hedge it back into Aussie dollars, the cost will normally reflect the interest rate differential between the two countries for the relevant maturity. For example, if the RBA’s cash rate is above the Fed’s, you should receive additional returns and vice versa.
In practice this relationship can be distorted if there is excess demand or supply for either currency, which can generate a cross-currency 'basis' under which you receive or pay more for the hedge than covered interest parity would otherwise imply.
The Reserve Bank of Australia has been capitalising on this dynamic for years, hedging billions of dollars worth of Japanese government bonds into local currency. While the Japanese bonds have carried a negative yield, hedged into Aussie dollars they deliver a handsome return above many other government bonds because of both the local interest rate differentials and the attractive cross-currency basis the RBA has earned.
It becomes important to recognise this when undertaking long-term performance analysis. I recently saw a presentation for a new, predominantly US high-yield fund that contained historical yields and returns hedged into Aussie dollars over the last five years. The annual yield enhancement from hedging US dollars into our currency over this period was about 1.4%, which is no longer present.
With this benefit the US high yield product outperformed Aussie high yield by 1.3% in total return terms, albeit that US high yield had much higher volatility (4.7% versus 2.8%). But this might not be true going forward as the Fed’s cash rate has risen above the RBA’s equivalent.
Something that appears superficially attractive might be a hedging mirage that has subsequently evaporated. This is, of course, a generalised statement and one should evaluate every investment on its merits on a case-by-case basis and ideally seek the counsel of trusted advisers.
And it is not just about outright returns. Many asset classes, including US high yield, can play a valuable role in portfolios if they are less than perfectly correlated with your existing assets and therefore furnish diversification gains.
Christopher Joye is a Portfolio Manager with Coolabah Capital Investments, which invests in fixed income securities including those discussed by this article. This article does not address the individual circumstances of any investor.