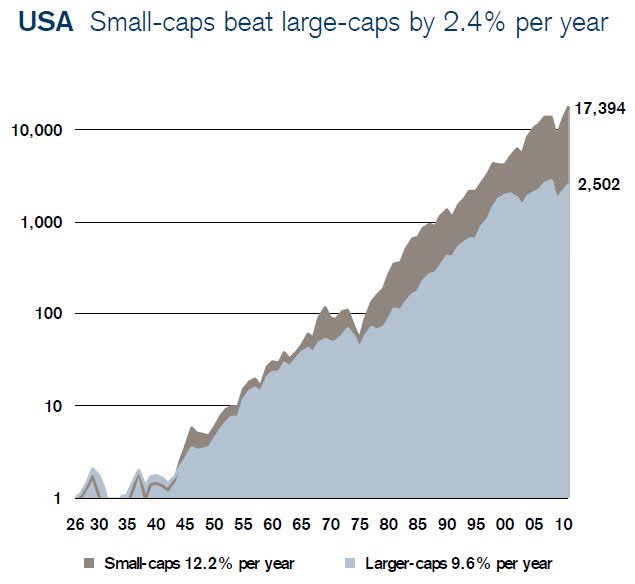
In Cuffelinks Edition 4, Chris Cuffe’s article mentioned that over long time periods, companies with small market capitalisation (‘small caps’) have outperformed large caps. The pioneering academic work most often cited is from Fama and French in the United States, and their work has been further developed by Elroy Dimson and colleagues from the London Business School, who provide these return metrics looking back since the 1920’s:
We should note however that this phenomenon has diverged in recent times in Australia. The following chart for the last decade shows that at various times both small and large caps have had their times in the sun.
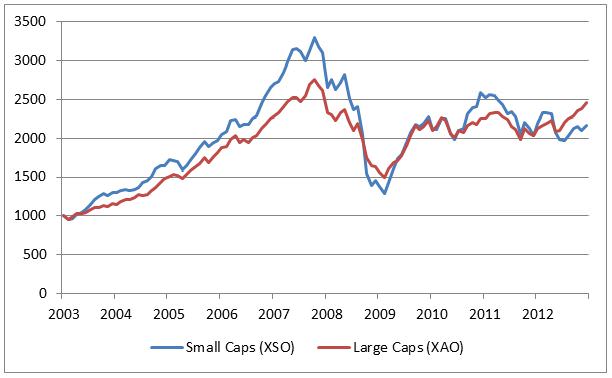
The dominant factor in relative performance is the market’s appetite for risk. In the mid 2000’s bull market, appetite for risk saw small caps surge and outperform sharply until about 2008. Since the GFC, the insatiable investor appetite for defensive yields has seen larger companies do well. It should also be noted that the small resources stocks which represent around 40% of the small cap index have been on a slide for the last two years, dragging the averages down in Australia, something not so much relevant when looking at offshore small cap outperformance.
Why small caps traditionally outperform
Smaller companies in Australia are defined as stocks outside the ASX100 Index. The Small Ordinaries Accumulation Index is what most small cap managers focus on which represents around 7% of the Australian market’s capitalisation. These companies are generally higher growth businesses in their infancy looking to become the next big household name in Australia. A large portion of the top 100 companies in Australia are in the mature phase of their life cycle, and growth rates of 5% are commonplace. These types of returns would be considered measly in the smaller end of town. As investors, we generally find that earnings growth has the highest correlation to share price movements overtime. This partly explains why small caps have outperformed large caps over such a long time period.
Smaller companies are under-researched, which creates the opportunity. Fund managers and stockbrokers scour this part of the market far less than with large companies. Over time, smaller companies that succeed become more noticed by analysts. When fund managers and the market ‘discover the stock’ this creates natural buying and pushes the price and rating up. This can be a good point to take profits given this point of the stock’s rerating generally comes with an expansion of its price to earnings ratio, a dangerous indicator to watch for.
A key part of small cap investing is having access to the senior management of the company. This is critical in understanding the dynamics of the business and what makes the leaders of the business tick. On the other hand, it’s incredibly hard for the majority of investors to contact Ian Narev, the CEO of the largest bank in Australia, Commonwealth Bank.
As an aside, a piece of advice which rings true when interrogating a company’s CEO is would you be happy to introduce that executive as your parent. As an investor in that company you are giving your money to the CEO to manage on your behalf.
The ideal small cap investment would have the following characteristics:
- strong free cash flow
- net cash on the balance sheet
- strong management team
- strong industry position
- low price to earnings ratio
- earnings growth at 1.5-2x price to earnings ratio
- a catalyst or event that will rerate the share price
- no other fund managers on the share register
One other advantage of small cap investing is the higher propensity for merger and acquisition activity. A few examples of this in recent years are Count Financial (acquired by CBA), Crane Group (acquired by Fletcher Building) and conglomerate Alesco (acquired by Dulux Group). Smaller companies are more likely to have targets on their backs. If successful, they attract the attention of their larger listed peers who are looking to generate earnings per share growth via acquisitions, when organic growth in their existing business can be anaemic. This can be a boon for investors providing excellent returns in the right circumstances.
Small cap prices are more volatile
Small caps are more volatile and less liquid in trading and are generally higher risk investments. They usually have more focused business lines compared with their larger counterparts, and therefore have a less diversified revenue stream.
The higher risk can be seen when things go wrong with the business, such as profit downgrades or a structural change in the industry. Recent examples of this include the ‘old media’ businesses such as Fairfax and APN News and Media. These companies have been too slow to adapt to the new digital age and have experienced rapid declines in their share prices when compared to the overall market’s return. Negative news flow in small caps generally creates a much higher level of volatility. An earnings downgrade from a company can see a stock fall in excess of 20% when the equivalent for a larger company may see a 5-10% move. This impact generally holds true on the upside with positive news. Higher risk, higher reward.
Large cap investments can provide a more steady return in the form of fully franked dividends. Generally these mature businesses are expected to pay back to shareholders each year a portion of their earnings. A smaller company which is going through a growth phase can require ongoing capital investment. Investors are generally happy for a smaller company to retain capital and invest given the superior return it can potentially generate. As companies grow and become more mature, they can then be expected to provide more income growth. Capital growth on the other hand is generally higher in small caps given the increased propensity to provide larger earnings growth.
Overall small caps have provided a higher return over the long term compared with their larger peers. While they come with added risk, they are an important part of a portfolio allocation decision and selecting the correct small cap investments can provide many happy returns over time.
Chris Stott is Chief Investment Officer and Portfolio Manager at Wilson Asset Management.