For many years, The Economist and other commentators have claimed there is a 'housing bubble' in Australia. The property sector and Australia’s banks say there’s not. Given the implications for property and for investors in the banks that are themselves heavily exposed to property, it is an important debate. We briefly lay out both sides of the argument, and then show the impact on other asset classes should there be a correction.
Case against the housing bubble: supply not keeping up with demand
Chart 1: House prices, Australia 1987-2014, compared to changes in supply and demand
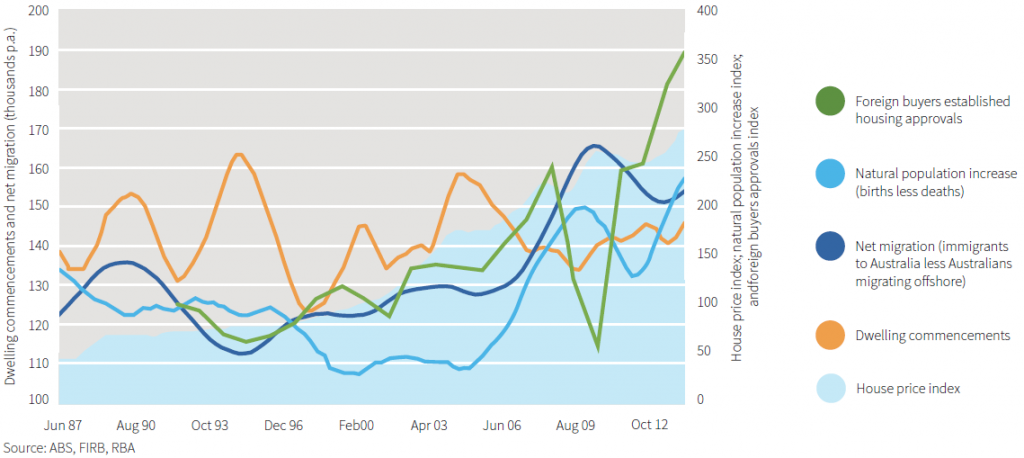
Several compounding factors can be blamed for the housing price increases:
- Net migration has been more than double the long-term average since 2005
- Foreign investment has also doubled
- Annual increase in population due to births less deaths shifted to new records from 2005
- Supply inflexibility as dwelling commencements have not increased since the 1980s.
Case for the housing bubble: fundamentals out of whack
Chart 2: Price/ rent index, various countries, 1975-2014
(higher the ratio, the more expensive the capital values compared to rental income)
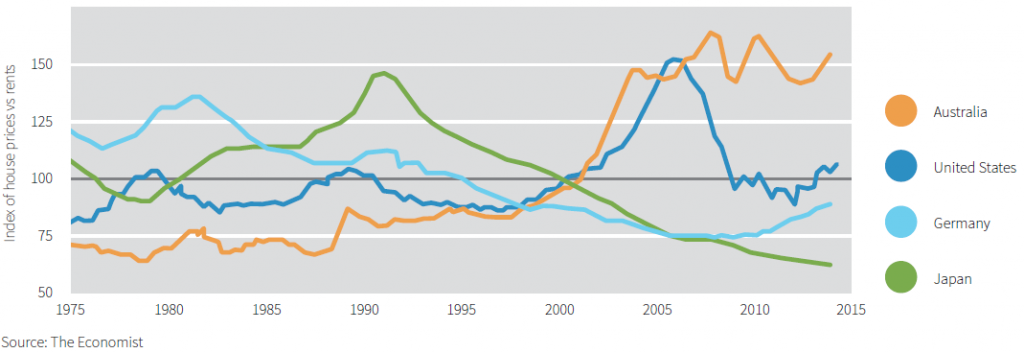
The case against relies more on the idea that Australian housing should comply with some global benchmarks such as those shown above. Regardless of which of these fundamental ratios are used, Australia comes across as one of the most expensive housing markets in the world:
- Rental yield vs long-term averages – Only Britain and Canada are further from long-term averages than Australia. China is far below Australia on this measure.
- Inflation-adjusted price increases – ‘Real’ prices in Australia are up 2.8 times since 1975, compared to the US at 1.3 times.
Of course no-one knows whether residential property is due for a strong correction. All you can do is be prepared and not over-exposed to the risk of a bubble, while not over-reacting, putting all your cash in the bank and potentially reducing your income. The key is to ensure you have the means to ride out any downturns without being forced to sell.
What impact would such a correction have on other asset prices?
Australians are heavily invested in residential property and so the impact of a property crash is obvious for those assets. But the impact on other investments is just as important to understand. Australia’s banks have around 61% of their loan books exposed to residential property, and banks now represent 32% of the ASX 300 and are the top four holdings in the average SMSF portfolio.
Table 1: Shock to Australia’s home values: potential impact on other asset values from a material (eg 20%) fall in home prices
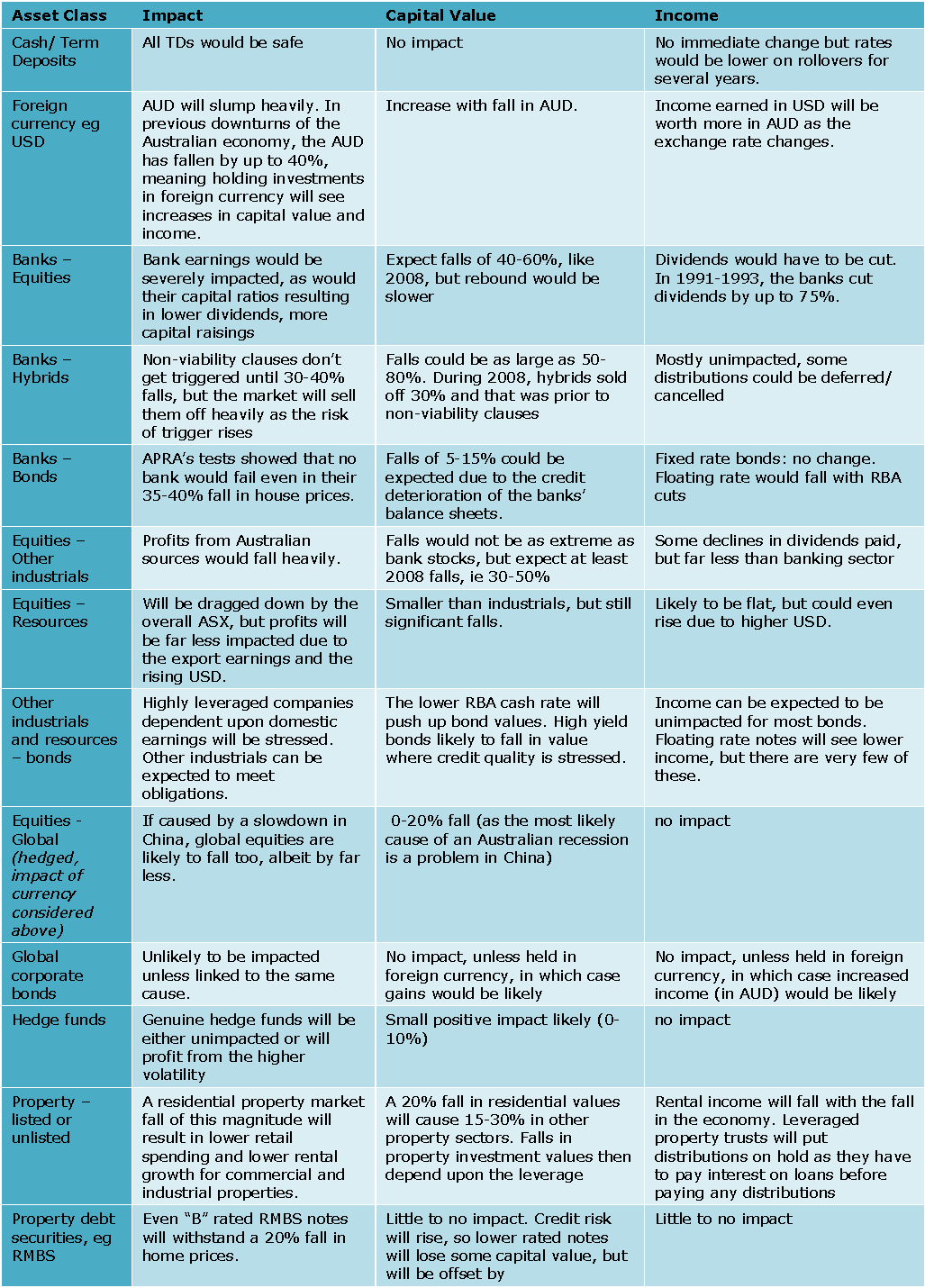
Views on the direction of Australia’s property market are mixed. Fundamentals should point to a fall in prices in the medium term, but Australia’s unique geography and high immigration constantly defy economic fundamentals. In the face of such uncertainty, it is prudent to stay the course but ensure that you are prepared for the unlikely scenario of, say, a 20% fall in real house prices and that this won’t have a material impact on your lifestyle.
Craig Swanger is Head of Markets at FIIG Securities Limited. This article is for general education purposes and does not address the specific circumstances of any individual.