An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is an open-ended managed fund listed on a recognised stock exchange. Investors in ETFs own interests in the pooled assets of a managed fund. Open-ended means the funds continue unless terminated.
EY research survey
EY conducted research into the prospects for ETFs, based on interviews with ETF market makers, service providers and promoters who collectively manage 85% of global ETF assets. The results are available in the report titled Global ETF Research 2017: Reshaping around the investor.
The headline finding is: Global ETF assets which were US$417 billion in 2005, reached US$4.4 trillion by the end of September 2017. That is an imposing cumulative annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 21% per annum.
EY expects the trend to continue. The forecast is a level of US$7.6 trillion by the end of 2020, with between 15-25% of inflows coming from new investors. Two-thirds of respondents believe that most fund managers will have an ETF offering in the next five years.
These growth numbers, incessant already for 12 years, projected for at least another three, should make us ask how and why.
It's undeniable that passive investments are winning market share by securing more inflows than active strategies. Says EY: “There is a growing view that, after costs, very few active strategies consistently outperform index-based investments.”
Initially, ETFs benefited because they provided index replication at a lower cost. According to EY, other trends that have worked in favour of ETFs are the shift to self-directed retirement saving, low yields, regulation, and digital distribution.
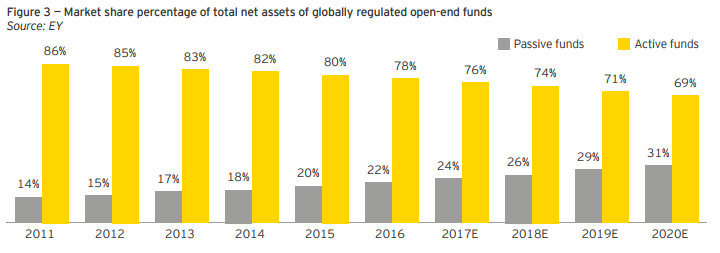
However, as unlisted index providers find ways to cut costs, index-based ETFs will also need to trim theirs to stay competitive. EY research suggests that passive funds will exceed active funds by 2027. In the US, says EY, “the ‘shift to passive’ has now been at work for 10 years.” Market participants nevertheless concede that both active and passive strategies can create value. Active houses are now focusing on illiquid assets that ETF providers cannot easily replicate. They are lowering fees or shifting fee structures to a larger performance-based component. Many managers are issuing ETFs themselves, as well as offering innovations such as offering both listed and unlisted classes of capital. Figure 3 from the Report shows passive gaining market share.
Industry response
The positive outlook for ETFs assumes that the industry will be responsive to such challenges.
Most ETFs have been equity based, but even active institutional investors in search of better but stable yields could look toward fixed-income ETFs. “Active investors are even supplementing portfolios of individual issues with bond ETFs in order to quickly capitalise on investment opportunities,” says BlackRock’s Brett Olsen.
The area of socially responsible investment (SRI)-themed ETFs could be primed for growth as demand for environmental, social and governance (ESG)-screened investing increases.
The growing economic engine of Asia also makes it a target. The EY report quotes:
“In Korea, an active equity ETF drew the largest inflows in the first half of 2017, and Hong Kong’s approval of leveraged and inverse (L&I) funds led the number of Asian L&I ETFs to jump from 79 to 163 in the year to September.”
The survey participants stress that the industry must adapt continually to regulation, retail and institutional investors’ needs, and to competition from traditional funds even as their managers embrace the product.
Outlook for Australia
EY’s Antoinette Elias says,
“In Australia, we continue to experience significant growth, with the ETF market capitalisation increasing by 39% in the last 12 months to $33.3 billion as at 31 October 2017. The local ETF market is taking a growing share of the traditional managed funds space and continues to be retail investor driven, rather than institutional.”
Thus, the Australian growth story is no less spectacular than the worldwide trend, although it has started later.
Other research corroborates the EY view, such as the CFA Institute Research Foundation release called, “A Comprehensive Guide to Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)”. Their take:
“… on any given day, ETFs typically represent between 25% and 40% of the total dollar volume traded on US exchanges. In short, in just over two decades, these innovative financial products have gone from an afterthought to one of the most important forces shaping how investors invest and how the market itself functions.”
Brief pros and cons for investors
Retail investors need to keep in mind the essential pros and cons of ETFs, including:
Pros
- Investors can usually buy and sell an ETF on an exchange at very close to the Net Asset Value, often at a cheaper cost than unlisted managed funds.
- Through ETFs, retail investors can access investment strategies normally reserved for large or institutional investors, such as shorting, long/short bullion or commodity prices, and other riskier investments.
- Investors can sometimes short an ETF, thereby creating the inverse outcome of the ETF itself.
- ETFs make it feasible to get exposure to multiple overseas markets and complex investment strategies with a relatively small amount of money.
Cons
- Having an instrument listed is no guarantee of sufficient liquidity, such as where the market in the underlying securities is disrupted (high yield bonds are a good candidate). Exits could be harder, or costlier, than from a managed fund during volatile market conditions.
- Set rules define and calculate repurchase values in managed funds, but ETF share values depend on market sentiment and the activities of market makers.
- An ETF does not make the underlying investment any less risky. Some retail investors may lose sight of this.
It’s the last of the cons that is worth repeating. Listing an asset class does not change its investment outcomes.
Vinay Kolhatkar is a freelance journalist, novelist, and finance professional. This article is for general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.