One of the most difficult aspects of investing is learning how to remove emotion from the decision-making process and just focus on the facts. Investors need to resist the temptation to get caught up in the hype of the daily news and noise, and to have the courage to go against the herd if that is what the facts dictate.
Investors who follow the herd invariably end up buying at or near the tops of booms when everybody else is buying and when the media and the so-called ‘experts’ are most euphoric. Then they often end up selling when everybody else is selling, when the media is most pessimistic at the bottom of the busts.
One of Warren Buffett’s simplest but hardest to follow gems of wisdom is to be greedy when others are fearful and to be fearful when others are greedy. This is much easier said than done!
Most investors seek reassurance
The first step is to learn to ignore the popular media, and especially the so-called financial media, and all the well-meaning advice or hot tips from friends, family and neighbours over the back fence. That is difficult enough, but it is even more difficult to go to the next to step and actually go against the herd and sell in booms and buy in busts. This goes completely against human nature. Humans are social animals who constantly seek reassurance from the herd, and are prone to follow the weight of popular opinion.
As a result, most investors (individuals and institutions) buy high and sell low - ie they are bullish and buy (or worse still, gear up and buy) at or near the tops of booms, and then they are bearish and sell (or worse still, are forced to sell by their margin lender) at or near the bottom of busts.
Two prime examples of this I saw first-hand were the crazy bursts of share buying and gearing up fuelled by the introduction of franking credits in 1987, and a similar crazy burst of share buying and gearing up in the months leading up to the closing of the $1 million super contributions window in June 2007. On both occasions, investors everywhere sold other assets (incurring tax on capital gains) and threw the money at the stock market in the media frenzy, only to see their money halve in value in the crashes that followed immediately after. If they used gearing they lost more than half and many thousands of people were wiped out completely. The extra flood of money and debt accelerated the market rises in 1987 and 2007, and so markets had further to fall when they collapsed.
I have used the following chart hundreds of times in presentations. It always gets a laugh, whether the audience is first time individual investors or experienced fund managers.
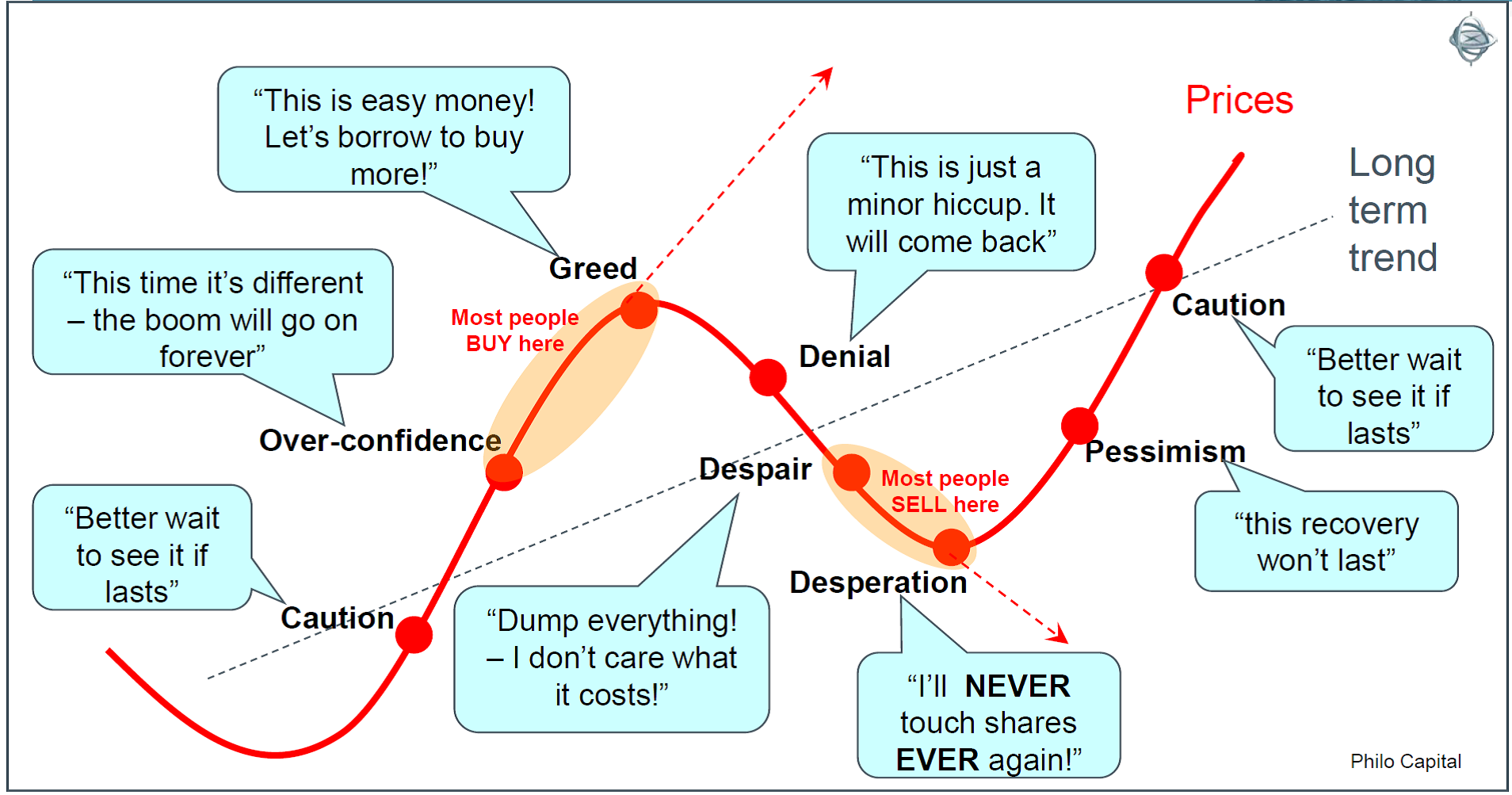
They laugh mostly because they know it is true but also because they know that humans are almost powerless to avoid the traps because it happens in every cycle.
Buying more as prices rise
Investors like to see prices (of shares or any other investment) rising. The longer prices keep rising, the more assurance they have that ‘this time it’s different’ and that prices will keep on rising in the future. Often they sit cautiously on the sidelines waiting and watching the market rise for several years before they finally pluck up the courage to take the plunge - inevitably right at the top before the fall.
Conversely, when prices are falling it is very easy to succumb to the general market and media pessimism and start believing that prices will keep on falling in future. Investors who bought in the boom hang on grimly, watching the market keep falling, hoping it will miraculously bounce back. Then finally, after all hope is lost and when the media are most pessimistic, they sell out in despair - often right at the bottom just before the rebound.
Individuals follow this pattern because they’re humans. Fund managers end up falling into the same trap because the majority of them are index-huggers. In the booms most of them know they shouldn’t be buying shares when they are over-priced but they still grit their teeth and keep buying anyway, because they are terrified of falling too far behind the general market index. Likewise in the busts they know they shouldn’t be selling shares cheaply but they have no choice but to sell because they have to meet fund redemptions as investors withdraw their funds in the panic. The end result is the same as for individuals - they buy high and sell low.
The above chart is a fun caricature and we should test the theory that people really are most bullish at the top of booms right before the busts, and they really are most bearish at the bottom of busts right before the market rebounds.
In Part 2 next week, we look at consumer sentiment measures in Australia as an indication of investor optimism. You may be surprised just how closely investors in the real world follow this simple pattern of behaviour in every stock market cycle.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.