Just as we seemed to be passing peak inflation, the recent attack by Russian forces on Ukraine has resulted in another spike in commodity prices. Along with heavy western sanctions, any thought of near-term inflation subsiding now appears to be on the backburner.
So, the big news – as it has been for the past few months – remains inflation, its (increasingly not so) transitory nature and the rising expectation that US interest rates will soon rise (and by how much). At the same time bond yields have been steadily rising, with the US 10-year recently reaching 2%, while US real yields have also been trending up from a low of -1.2% in November last year to -0.5% today.
Year to date, listed global real estate is down 8.7% (in Australian dollar terms). Is this an opportunity or a risk? To help answer this, we looked at past periods to see if we can draw any inference for the future.
Fed Funds rate and a look at the past
Fed Funds futures are implying lift-off for the first-rate hike at the March meeting – and between now and this next time next year, up to a total of seven 0.25% rate hikes. For those who view listed real estate as a yield play, and expect rising rates to be a headwind, if the past is any indicator for the future the opposite may hold true.
The two charts below show the performance of global listed real estate and global equities (indexed to 100) during each of the past 2 rising rate periods. In either period, neither global listed real estate nor global equities delivered negative returns, albeit back in 2004-06 global listed real estate was a significant outperformer.
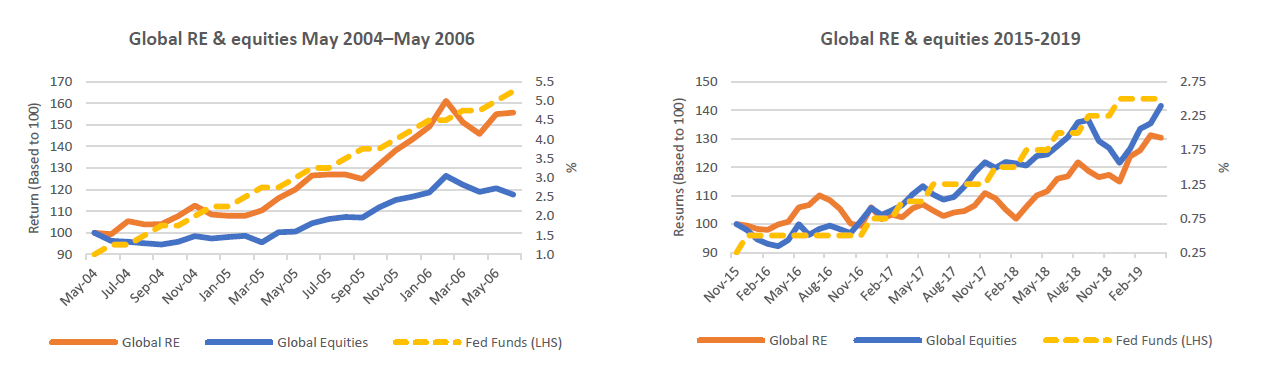
Source: Bloomberg
In 2004–06, the US consumer price index (CPI) started at 2.9% and peaked at 4.1%, whereas in 2015–19, US CPI was more benign – starting at 0.4% and rising to 1.9%. In today’s higher inflation environment, the relative returns of 2004-06 may be a better guide for today, which is also the conclusion we arrived at last year when we analysed listed real estate returns during periods of high inflation.
Wage inflation can be significantly more damaging for equities
It is worth considering that wage growth is also ticking up, which may not be great for the relative returns of equities.
According to the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, the three-month moving average median wage growth in the US is currently at +5.1% and at levels not seen in 20 years.
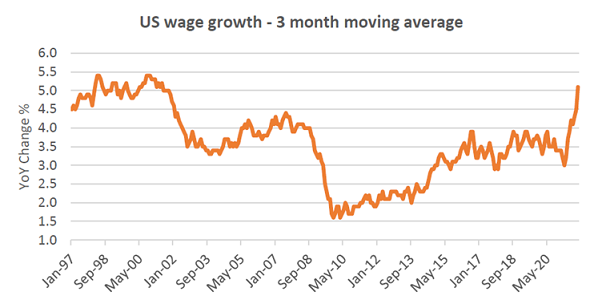
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta
This is important because increasing wage share can detract from corporate profits. One wonders how much of the strong tailwinds for US (and global) equity performance since 2009 and until the start of the pandemic were because of the ongoing weakness in labour markets. The combination of top-line growth from strong economic growth combined with decreasing unit labour costs was a likely contributor to significant margin expansion.
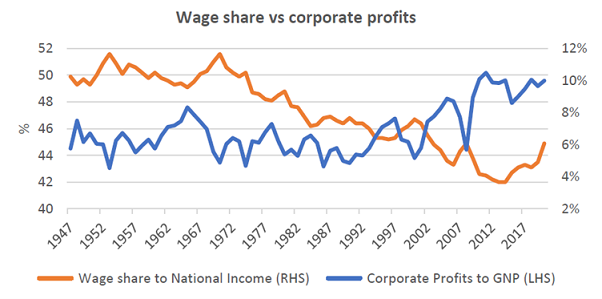
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis
As we have previously argued, if this reverses the downside may not be insignificant. Employees will seek higher wages to offset inflation, and in the absence of further fiscal support this will need to come out of corporate profits. If profit share moves from its current position of 10% to 8% (which is still high by historical standards) due to improving wages claims, this would represent a fall of 20% relative to gross national product. This could mean flat nominal growth for an extended period in the face of rising rates.
Compare this risk to real estate. Most real estate has low labour intensity, but high capital intensity. Rising labour costs are not much of a headwind for operating margins but can lift replacement costs significantly.
What about bonds?
While US 10-year bond yields have been steadily rising, it is the front end that has been rising the fastest. That is, the yield curve (measured as 10-year less 2-year treasury yields) has been flattening. Anecdotally, and indeed historically, this has generally been regarded as constructive for listed real estate returns as highlighted by the dotted circles in the chart below.
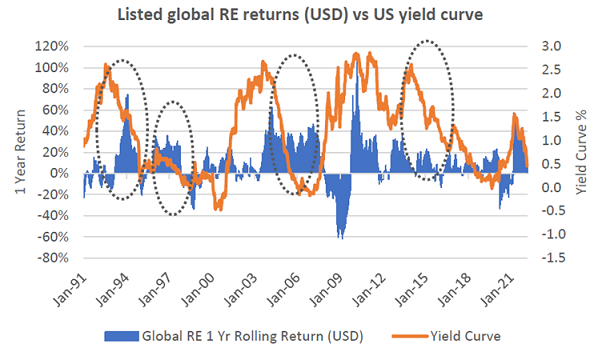
Source: Bloomberg, FRED
In fact, our own analysis shows that while in the short term the correlation to changes in bond yields against global listed real estate returns varies, in the long term there is very little correlation.
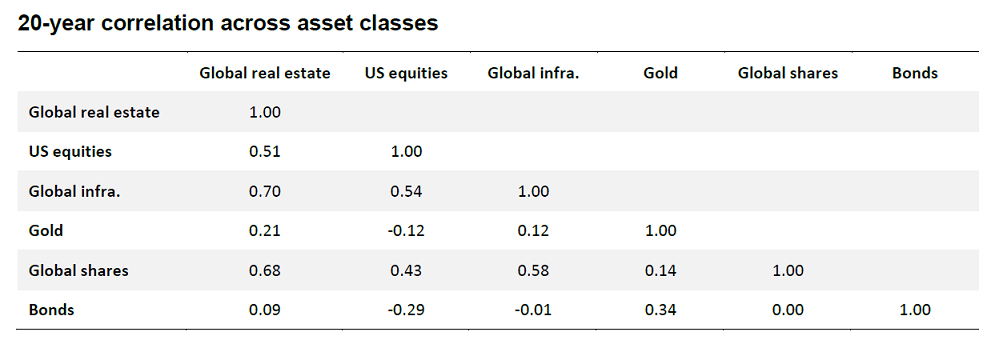
Source: Bloomberg, Quay
What about real yields?
If we run the same correlation analysis in the table above but substitute nominal for real bonds, the correlation is, surprisingly, still almost zero at only -0.06. Said another way, there is almost no long-term correlation between change in real bond yields and global listed real estate returns either. However, short-term observations can paint a different picture.
If we revisit the period April 2013 to July 2013, real bond yields spiked by +1.2% from -0.6% to +0.6%, driven by a sell-off in nominal bond yields in response to an anticipated reduction in the Federal Reserve bond-buying program, or the ‘taper tantrum’ as it is now known. Returns from global listed real estate suffered, with the index falling almost -20% over the same period (in USD terms) and then trading sideways for the rest of the year, only to regain +20% over the calendar year 2014 and then onwards and upwards. Back then, US CPI was ranging between 1-2% (and actually trended to zero over the course of 2014) and implied inflation was hovering around 2.5%.
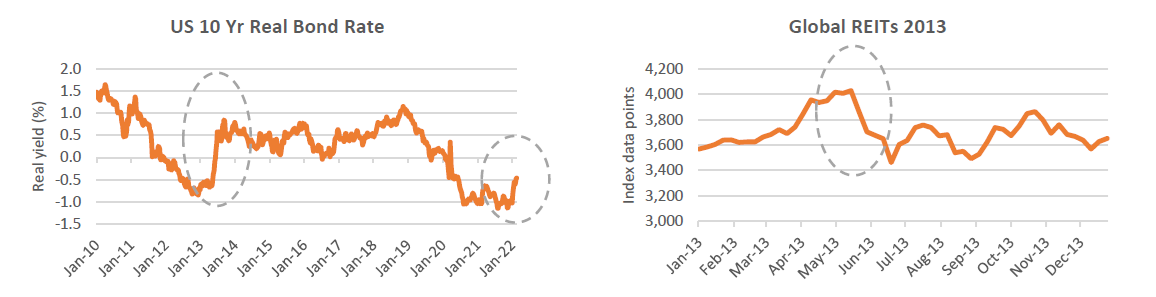
Source: Bloomberg
Of course, we now know this sell-off in listed real estate was an over-reaction by an inefficient market.
Lately, the real bond yield has crept up by around 70bps, now at -0.5% from a low of -1.2%. With implied long-term inflation now at 2.6% (10 yr nominal less 10 yr real bond yield) from a rate of 2.3% over the same period, long-term inflation expectations haven’t really changed that much either.
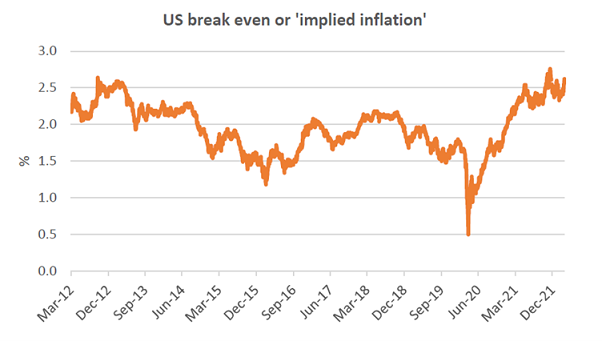
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis
Maybe real yields require watching? However, in the meantime, negative yields are still very accommodative for total returns.
Concluding thoughts
Analysing the impact of interest rates, bond yields and real yields on historical returns is interesting and can be useful to understand how the past may impact the future. However, when we step back, it really is difficult to be conclusive based on this analysis. Yes, global listed real estate has historically performed well when rates have been rising, but there are always other variables at play. What was the supply and demand environment like, what is the outlook like and what is the value proposition?
We don’t stay awake at night worrying about macro inputs we can’t control but do try and understand what (if any) risks they may present. What we have learnt over the past 8 years is the best way to minimise the risk to our investors is to spend our time focused on understanding the fundamentals of what we are investing in. It is our opinion that long-term returns have nothing to do with rates, but everything to do with the fundamentals of our investees.
Justin Blaess is a Principal and Portfolio Manager at Quay Global Investors. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.