For the past six years, the Legg Mason Global Investment Survey has revealed investor sentiment and behaviour across 17 countries, including Australia. In 2018, almost 17,000 people with at least €10,000 (in local equivalent, or US$50,000 in the US) to invest in the next year were in the survey, including 1,000 in Australia.
The timing of the fieldwork is important, as it took place in July and August 2018, before the recent market falls (but the market also fell in February 2018). Nevertheless, the optimism about equity markets shown in the results may not be as strong if the survey was taken now.
Key global findings
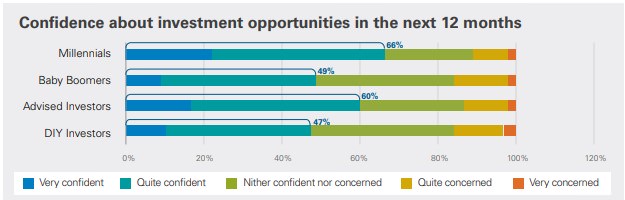
At the time of the survey, as shown below, most investors were optimistic about investment opportunities in next 12 months with only 14% being concerned. Millennials (18 to 36 years old) in particular were more bullish than Baby Boomers (50 to 71 years old).
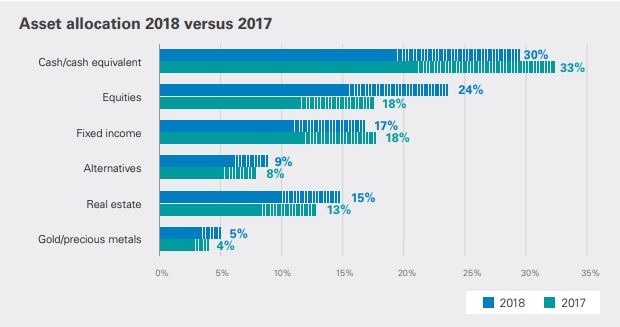
There was a marked expectation of allocating more to equities and real estate and less to cash in 2018 compared with 2017. It will be interesting to see if investors have a reality check if the equity sell-off seen in October to early December 2018 continues.
Generally, in the global survey results, investors think technology will not replace human interaction in financial advice and customer service. Twice as many investors feel volatility can have a positive effect on portfolios if managed correctly, compared to those who worry about the risk. Using a financial adviser helps investors to be more diversified. Almost half of investors choose funds allowing for ESG considerations. Millennials feel increasingly confident about a comfortable life in retirement, yet they only have 21% of their portfolio in equities.
Millennials are approaching investing differently than their parents. They are more willing to embrace risk and use a financial adviser than Baby Boomers, are open to alternative assets and are led and influenced by their ethics. While we are still some way away from full service automated robo advice, investors are looking for the same level of convenience in their investments as they expect in other parts of their lives. Investors want to discuss their options with an expert, but less than half say they often or always use a financial adviser when making decisions about their investments.
The internet remains the leading source of investment guidance for those investors who do not rely on a financial adviser. Ten years on from the global financial crisis, there remains a risk legacy. The risk concerns of many individual investors are macro-related, such as world economic instability, trade wars, global political instability and inflation.
About 77% of investors are saving and investing with specific goals in mind, a trend that is even higher with Millennial investors (80%) or Generation X – aged 37 to 50 years - (80%). Inevitably, these investment goals are both short-term and long-term, depending on the generation and life stage of the individual.
A focus on the Australian results
The full Legg Mason survey results for Australia, the world and other individual countries are linked here.
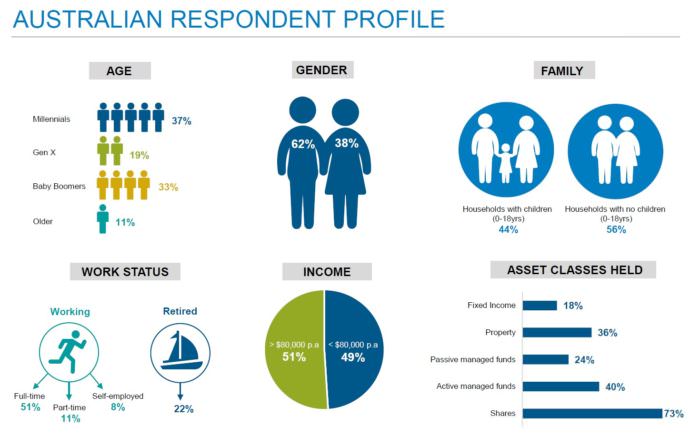
The findings for Australian and global investors in more detail start on page 68 onwards, and given the size of the global data set, the responses make fascinating reading. Here is a selection of five questions as an example.
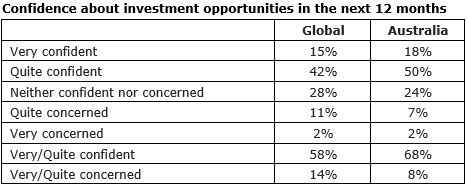
1. Australians more confident about future investment opportunities.
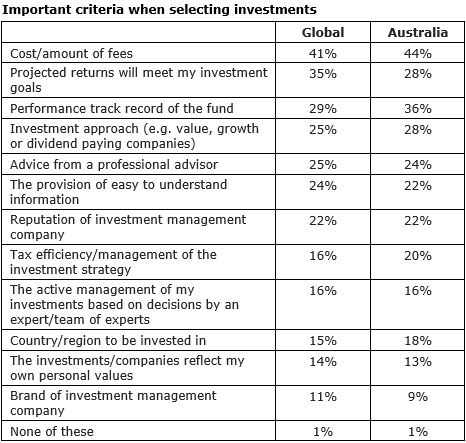
2. Australians more focussed on fees and past fund performance (up to three responses allowed).
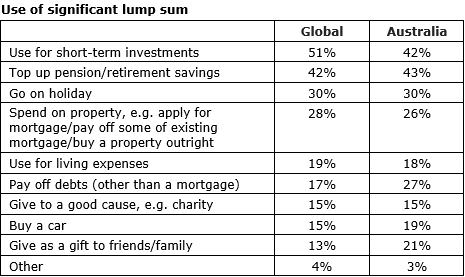
3. Australians less inclined to use a lump sum for short-term investments (up to three responses allowed).
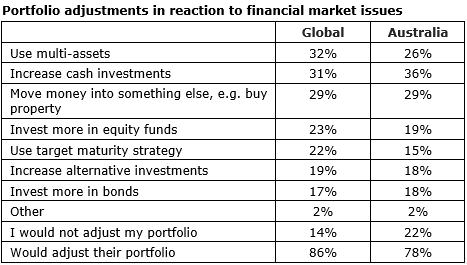
4. Australians will increase cash or not adjust a portfolio, rather than move to multi-asset funds (up to three responses allowed).
5. Australians more likely to buy dividend-paying stocks than bonds to produce income.
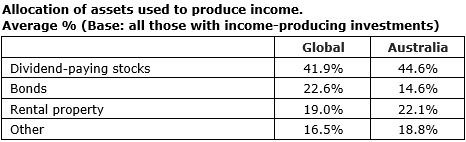
Another factor worth highlighting is that Australian investor bond allocations are low by global standards, and 58% of direct (unadvised) investors have no fixed income holdings. Conventional portfolio theory dictates that fixed interest should be part of a well-diversified portfolio and act as a foundation of a retirement savings pool. Only 12% of Australia’s self-directed super pool is allocated to domestic fixed interest, down from 14% per cent three years ago. Australians are more familiar with cash and term deposits. When these two are combined with domestic and global fixed income, the allocation is 31% compared with the average exposure for pension markets in OECD countries of 51%. Most portfolios would benefit from the protective and diversifying characteristics of high-quality fixed income.
Graham Hand is Managing Editor of Cuffelinks.
Legg Mason is a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is for general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual. For more articles and papers from Legg Mason, please click here.