Over the last year, volatility has remained stubbornly subdued, hitting new lows on a regular basis. This trend has been seen across many markets and asset classes, including the often unpredictable emerging markets. US equities led the way, shrugging off public policy uncertainty, the Fed’s rate hikes, and natural disasters.
How low can it go?
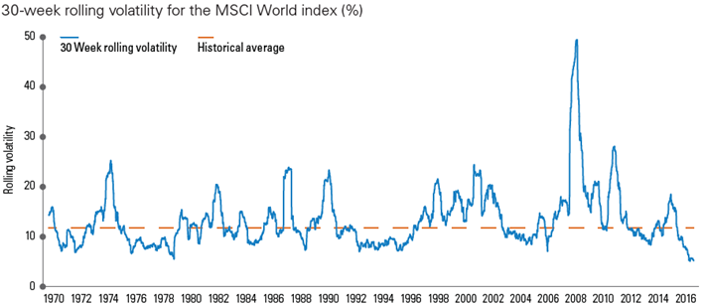
Source: Bloomberg. 1/12/17.
Looking ahead, several key risk factors could come into play. There is considerable uncertainty around key geopolitical relationships and the pace of monetary policy tightening. As global growth takes hold, central banks are beginning to rein in their unprecedented quantitative easing programs. Many countries also have a long way to go in implementing structural reforms. And bond and equity prices looking increasingly expensive, particularly in developed markets.
Can volatility remain this low indefinitely? Will interest rate normalisation put a spanner in the works? And, if volatility does pick up, how can investors not only manage the associated risks, but also take advantage of the opportunities presented?
Ready to revert?
Traditionally, volatility has been mean-reverting, returning to average levels over time. Analysis from Legg Mason’s global equity affiliate, Martin Currie, suggests volatility is now at 50+ year lows. Large declines in correlations between stocks, as well as a drop in the individual volatility of stocks themselves, are behind this phenomenon.
If tighter labor markets and higher inflation start to emerge due to sustained global growth, it could initially cause higher volatility in fixed income markets, which may then feed into equity markets. Equity volatility tends to lag changes in the yield curve by around 30 months, according to Legg Mason global equity affiliate ClearBridge Investments. In their view, while quantitative easing acted as a pacifier of volatility, quantitative tightening may act as an accelerant.
Fixed income as a leading indicator of volatility
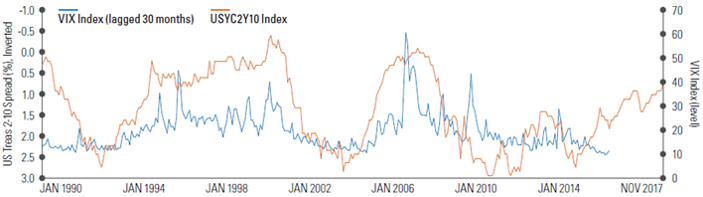
Source: Bloomberg, 1/12/17. Indexes are unmanaged and not available for direct investment. Index returns do not include fees or sales charges. This information is provided for illustrative purposes only and does not reflect the performance of an actual investment.
A prolonged period of low volatility can also act to increase the scale of volatility once it returns. Many risk models are built using measures of short-term historical volatility and may now be “increasingly underestimating the true level of risk in portfolios”, according to Martin Currie. A pick up in volatility could, therefore, lead to a more rapid market response as risk models adjust from their low base.
Furthermore, investors are expecting markets to continue to perform well as the economic environment remains benign. Hence, the risk of disappointment is skewed to the downside. A deviation from expectations could cause an outsized movement in asset prices.
What investors can do
The implications of higher volatility for portfolios are not always negative. What can investors do?
- Buy low-volatility stocks: One approach to the challenge of an uptick in equity volatility is to explicitly seek out stocks with properties that can minimise volatility, both individually and as components of an overall portfolio. A good example is companies with strong dividends that are sustained by the financial and business fundamentals of their underlying businesses. The overall financial characteristics of strong dividend payers can reduce a stock’s vulnerability to rapid market changes.
- Move fixed income away from benchmarks: A more flexible, unconstrained approach to fixed income may help manage risk, by allowing greater scope to access the full global bond landscape as well as individual security selection. By dynamically shifting allocations in line with market conditions, unconstrained managers can identify the most compelling, potentially undervalued bond markets and currencies — as well as regions, countries, or sectors that offer a better yield or where duration risk should be rewarded — while avoiding or even shorting areas of concern.
- Consider active management: As volatility feeds into equity markets, active management may also help to manage risk. For example, strategies designed to invest in stocks with a historical tendency to resist periods of volatility can help protect portfolios from the full scale of any downturns. Lower correlations among stocks and a higher dispersion of returns across the market also creates more winners and losers. As Martin Currie notes:
“We are conscious of increasing dispersion in returns within the asset class, and the consequent need for investors to be selective. This is best achieved through taking an active, fundamentally driven approach to investment, and a focused, stock-picking strategy is very well placed in this regard.”
Additional information, particularly around (ESG) environmental, social and governance issues, can increase a manager’s conviction in the sustainability of a company’s returns, even during periods of market volatility. An active manager with an ESG framework can also be an engaged investor, working with companies to create sustainable long-term returns.
Andy Sowerby is Managing Director at Legg Mason Australia, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. The opinions and views expressed herein are not intended to be relied upon as a prediction or forecast of actual future events or performance, guarantee of future results, recommendations or advice.