COVID-19 has had a major impact on all segments of real estate although performance to date has varied by type and sector. We expect this pattern to continue as we move through the recovery phase.
The latest MSCI Mercer Core Wholesale Property Fund Index shows that the 17 unlisted wholesale property funds in Australia worth a collective $101 billion generated a total return of -4.8% in the three months to 30 April 2020 and -0.8% over the year. Yet the 29 listed real estate securities (A-REITs) with a market capitalisation of $95 billion in the S&P/ASX300 A-REIT Index generated a total return of negative -29.7% in the three months to April, and negative -20.1% over the year (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Performance of Listed A-REITs and Unlisted Real Estate: April 2020
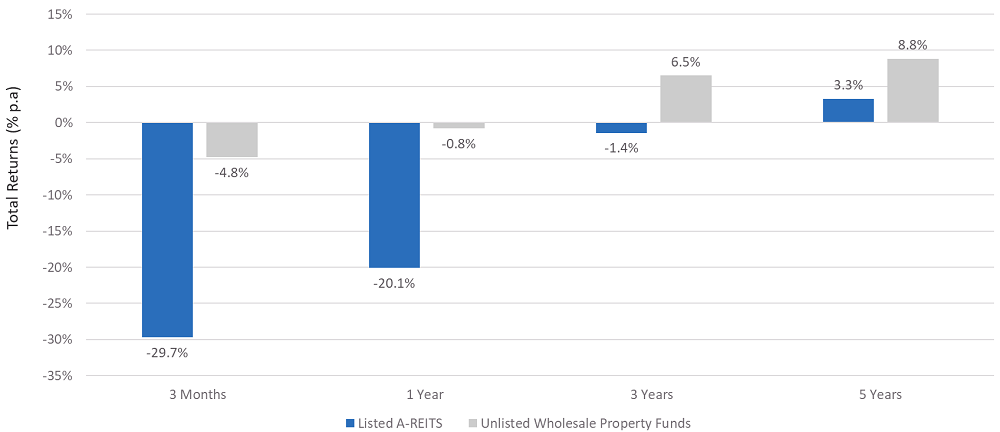
Source: UBS and MSCI
The velocity at which the listed A-REIT sector sold off in March and then rebounded in April was quite staggering. The S&P/ASX300 A-REIT Index generated a total return of -35.2% in March, the worst month on record for the A-REIT index, eclipsing October 2008 (-25%).
In April, the A-REITs retraced some of their losses following the unprecedented response from authorities to provide liquidity to credit markets and financial support to households and businesses. A-REITs generated a total return of 13.7% for the month, one of the best monthly performances on record.
Unlike in the GFC, A-REITs were in good shape coming into the COVID-19 pandemic, with significantly stronger balance sheets (lower gearing levels, diversified sources of, and longer duration, debt) and arguably better assets with minimal offshore exposure. Yet that wasn’t enough to offset the rapid sell-off in A-REITs.
Historically, listed real estate securities have tended to quickly overreact to unexpected macro events and overshoot to the downside relative to changes in the values of their real estate assets. The daily pricing of listed A-REITs exacerbates the sell-off.
In addition, a large proportion of the A-REIT investor base now comprises ETFs, index funds and equity funds which will buy or sell based on broader market conditions rather than implied cap rates (yields) or the earnings of the underlying real estate. So, while it was not unexpected that they would follow the sell-off in broader equities market, the magnitude of the sell-off and bounce back did surprise.
In response to dislocation in markets and economy, the managers of the 17 major unlisted wholesale property funds—AMP, Charter Hall, ISPT, Investa, GPT, Lend Lease and QIC—either revalued their assets at the end of March or April, or in the case of some funds, revalued at the end of both months. Figure 1 shows the returns versus the listed market were still markedly different.
Sector performance varies
Drilling down, the relative performance rankings of the sectors—diversified, retail, office and industrial real estate—are similar across the listed and unlisted real estate markets although the dispersion of performance between the two markets is wide. In other words, both markets have similar views on the sectors, it’s just the magnitude in pricing that differs.
Across both the listed and unlisted markets, retail was the worst performer and industrial the best performer over both the three months (Figure 2) and year to April 2020 (Figure 3). Yet in the three months to April 2020, the dispersion in performance between the listed retail A-REITs and unlisted retail funds was 22.6% and between industrial A-REITs and unlisted industrial funds it was 15.0%. Over the year, the dispersion was 17.3% and 11.4% respectively.
Figure 2: Performance of Listed A-REITs and Unlisted Real Estate: Three Months to April 2020
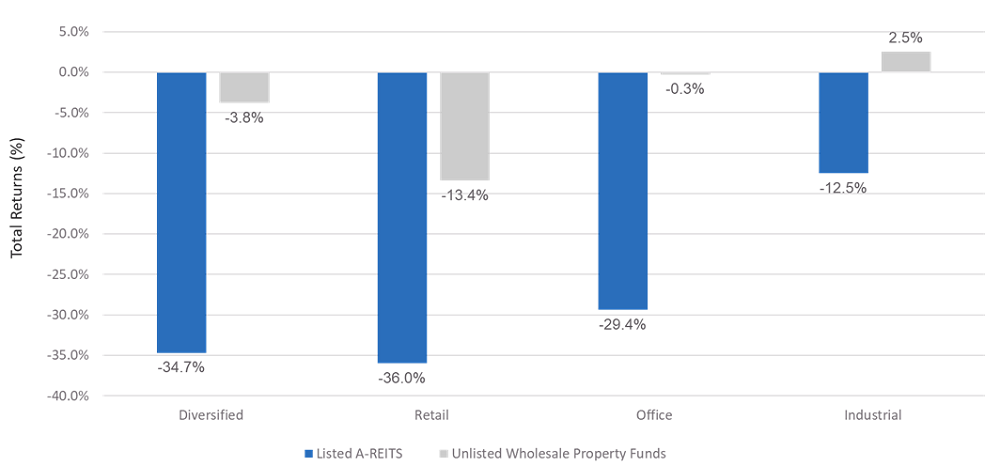
Source: UBS and MSCI
Figure 3: Performance of Listed A-REITs and Unlisted Real Estate: 12 Months to April 2020
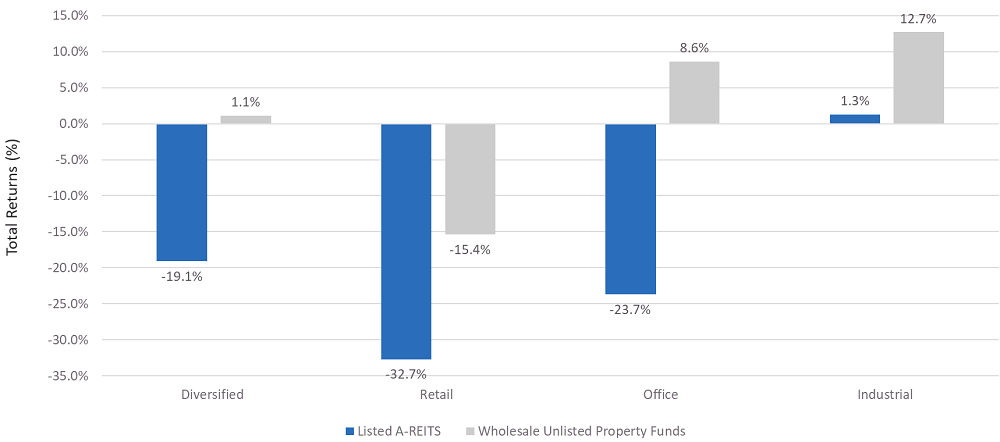
Source: UBS and MSCI
Retail faces structural headwinds
Retail, especially discretionary retail, was already facing strong headwinds. COVID-19 is expected to accelerate a cultural and structural shift in the way consumers purchase their goods, many of which had not shopped online before the pandemic. The ongoing challenge to bricks-and-mortar retail formats to remain relevant in a highly competitive marketplace will put further pressure on retailers and their landlords to adapt their offering. Large retail malls, once the staple of a core real estate portfolio, will struggle to outperform.
On the other hand, industrial and logistics real estate continues to benefit from low levels of vacancy and structural tailwinds. Recent events will super charge the growth in ecommerce. Also, the amount of inventory held in reserve ‘so called safety stock’ will increase to avoid companies becoming caught by future disruptions in their supply chains. Retailers, cold storage occupiers and transport and logistics providers will accelerate the optimisation of their supply chains and occupy purpose-built, high-quality technology filled facilities.
Coles’ recent pre-commit on long-term leases to two Charter Hall owned high-tech customer fulfilment centres (CFCs) in Sydney and Melbourne is testament to the changes under way in the industrial and logistics sector. Coles plans to use the UK-based Ocado’s leading edge automated single-pick fulfilment technology and home delivery solution in their CFCs. Commenting on the deal, Coles Group CEO Steven Cain said:
“Ocado’s online fulfilment solution, which also includes new website technology for Coles Online and Ocado’s delivery management technology to maximise transport efficiency, will transform the Coles Online experience for customers.”
Industrial and logistics to lead transaction activity
Real estate transaction activity is likely to be lower for the foreseeable future as investors and financiers take a wait-and-see approach to how the economy recovers. Yet the industrial and logistics sector is set to buck the trend. High quality industrial and logistics real estate is expected to show the greatest volume of transaction activity in the coming year.
At an institutional level, both domestic superannuation funds and global pension funds are underweight industrial and logistics assets. Given the thematic tailwinds driving the sector as noted above, capital will chase these assets. The sheer weight of capital could in turn push prime industrial cap rates (yields) below those of prime office for the first time.
Pricing in the listed and unlisted real estate markets will often diverge in the short-term, creating arbitrage opportunities. What has happened in recent months is not new although as noted earlier, the magnitude of the sell-off in A-REITs was unprecedented.
But looking through the lens of both the listed and unlisted real estate markets, it is clear that retail assets, particularly those focused on discretionary shopping, will continue to underperform and industrial and logistics assets will be the winners for the foreseeable future.
Adrian Harrington is Head of Capital and Product Development at Charter Hall, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
For more articles and papers from Charter Hall (and previously, Folkestone), please click here.