It’s amazing to think investors would ever stop caring whether a company was profitable or not, but it seems to happen every cycle, usually towards the latter stages of a long bull run. Companies with a history of reliable profits take a back seat to concept stocks, stocks with no profits but great stories and exciting visions. These stocks are usually early-stage technology companies, industry disruptors or exploratory miners.
Instead of focusing on the usual hard measurements like profit and competitive advantage to pull in investors, they typically market their massive mineral deposits, revenue growth, or the huge size of their TAM (total addressable market). TAM is a particularly spurious measure which in our view often means how much money a company thinks it might be able to make out of a group of people who it thinks might want to buy its product.
Investors get excited by the prospect of high growth and returns and when the market is buoyant it all works. In recent years, particularly, these kinds of stocks looked very appealing with interest rates at all-time lows and bonds returning negative yields. Then, when governments and central banks across the globe poured in trillions of dollars of liquidity during COVID, these unprofitable, high-risk stocks, went stratospheric.
Fund managers and cheer leaders of these concept stocks reached celebrity status (every cycle has them), while fundamental investors like us were left scratching our heads.
At some point while all of this was going on, the market quietly stopped caring whether a company made money or not. It cared about revenue growth, and it cared about the size of the TAM, but companies that made consistent profits were left behind.
Things are changing
Many of the more speculative companies have sold off heavily, and we’re seeing other types of companies attract the attention of the market – profitable companies.
A good example is a company we hold in our funds – Amcor. It’s a boring company. It doesn’t have any celebrity spokespeople, you won’t see it splashed across billboards, Elon Musk has probably never heard of it. It makes flexible packaging, as well as rigid containers and other receptacles for food, medicine and other essentials, things people buy in good times and bad. The other thing it makes is money, plenty of money. And not just revenue; Amcor is forecasting a profit of $1.2 billion this financial year.
We were watching the Amcor stock price last week, and suddenly it jumped close to 10%. We double-checked we hadn’t missed something. Had it forecast impressive growth? Signed a new deal? Sold off part of its business? No. Amcor had just released its quarterly results and shown, once again, that it was a solid, growing business with sound fundamentals. Yes, it had grown its revenues, as well as increasing its margins (as it was able to pass on higher input costs to its customers).
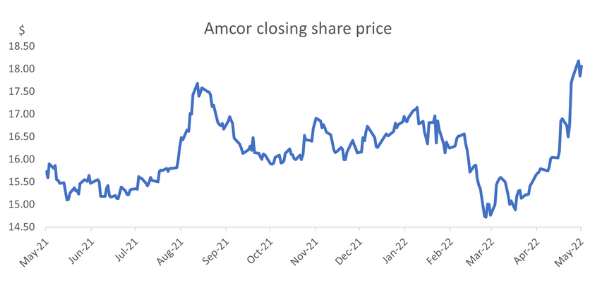
Source: FactSet; As at 12 May 2022
Nothing particularly different to the last few years, but this time the market noticed, and it acted. The market suddenly realised a global leader in packaging with growing revenues and profits was attractive on 15 times profits (not revenue). As you can see from this newspaper clipping from the '87 crash, this isn't the first time Amcor has performed well in a volatile market.

Source: Sydney Morning Herald Newspaper - 21 October 1987
Fundamentals again
We are seeing this happen across all our portfolios. Well established, quality businesses that are making a profit and have a competitive advantage, recurring earnings and sound management are performing substantially better than the market.
Here’s another example. We also own shares in a company called Aurizon. It’s Australia’s largest rail-freight company with assets and haulage operations around Australia.
We were at a conference recently and went to an Aurizon presentation. Unlike many other presentations we went to, it was almost deserted. Why? In short, because it’s another boring company. A boring company that provides an essential service and makes a good profit out of it.
One aspect that deters some potential investors is that hauling thermal coal is 30% of Aurizon’s haulage business. And thermal coal, long-term, is a dying industry. But Aurizon is well-placed to diversify out of coal. It also hauls copper, grain, nickel, iron ore, lithium and other commodities and is aiming to double its bulk haulage business by 2030, while reducing thermal coal to less than 20% of its business. It can also reuse excess thermal coal wagons to haul other commodities, so it doesn’t require much capital to diversify.
Another win is that while thermal coal is on the way out, rail itself has a bright future, particularly in goods transport. Once railways are built, they are a very economical, and environmentally sound, way of moving goods around the country.
Finally, all of Aurizon’s contracts are backed by CPI, so it’s well-placed to pass on any rising costs to its customers, weather the current market volatility and continue to do well. Despite the empty presentation room, it seems the market is starting to agree with us. Aurizon’s share price has risen 10% in the last three months. It still trades on a reasonable valuation of 13 times profits and pays a dividend yield close to 6%.
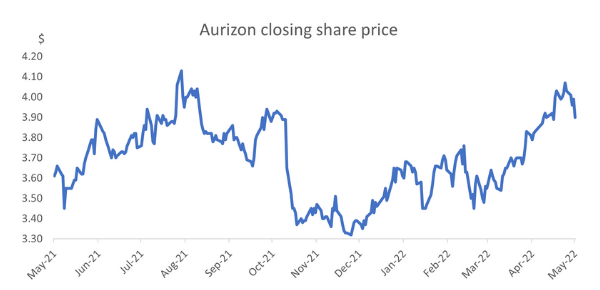
Source: FactSet; As at 12 May 2022
These are just two examples of a shift we’re seeing. A shift away from new, “exciting, visionary, ground-breaking companies” to boring, necessary, solid companies. A shift towards well-established, quality businesses, with resilient cash flows, that make good profits and have solid growth prospects.
While these types of companies haven’t been catching the market’s interest over the past few years, it seems like they are starting to again. It seems like old-fashioned concepts like quality and value, which we’ve always held on to, are becoming popular again.
We think that high-quality companies are always a good investment. While fads come and go, for us fundamentals never go out of fashion.
Daniel Moore is a portfolio manager for Australian equities fund manager Investors Mutual Limited. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only and is not intended to provide and should not be relied on for financial advice.