Two dominant investment styles are value versus growth. Value investors look for undervalued stocks while growth investors prefer companies with strong earnings growth potential. While value investing has outperformed over the long term, its underperformance in recent years, particularly in the recent selloff, has caused many to question when the promised value recovery will occur.
To shed some light on this, it is helpful to understand when value has outperformed in the past and the market conditions that led to this.
Where are the value stocks?
Value stocks are typically found in the more cyclical parts of the market such as the Financials, Resources and Consumer Discretionary sectors. These stocks are more sensitive to broader economic conditions, compared to defensive sectors such as Healthcare, Utilities, and Consumer Staples.
Value stocks tend to outperform when economic conditions are improving. In such an environment, the earnings growth outlook from the cyclical parts of the market improves relative to defensive sectors. This drives a rotation out of defensives and into cyclicals, leading to a period of relative outperformance by value.
The second point is that value stocks typically perform better in a rising interest rate environment. This is the result of two factors.
Firstly, rising interest rates usually correspond with improving economic conditions, which as mentioned above, generally favours value.
Secondly, rising interest rates increase the discount rate applied to future earnings and in general, ‘growthier’ stocks are more impacted as a greater proportion of their valuation is based on long-term future earnings. Therefore, a higher discount rate has a bigger impact on the valuation of growth stocks than it does on value stocks, which are more driven by nearer-term earnings and dividends.
In light of this, it’s easy to see why the past few years have been difficult for value investing, as global economic growth has been patchy, and we have been in a lower for longer interest rate environment.
The chart below shows how value stocks do better coming out of recessions, but how much growth has won in recent years.
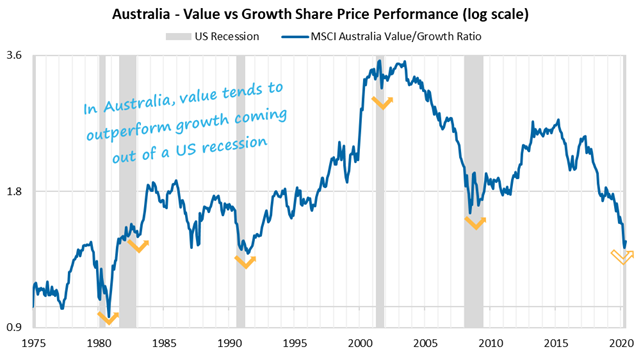
This environment has been very favourable to stocks offering perceived defensive characteristics, such as infrastructure, or strong organic growth, such as healthcare. Valuations of these types of stocks have pushed up to high levels, both in absolute terms and versus their own historical valuation metrics. At the same time, value stocks have lagged and the valuation gap between cheap and expensive stocks is currently at record levels.
Value fighting back
In the second half of 2019, it appeared there was some light at the end of the tunnel. Global growth was starting to pick up, led by the US, as trade tensions eased and the UK election saw a resolution of the Brexit impasse. Bond yields were starting to tick up and value began logging several months of outperformance.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic put a halt to this, seeing economic growth collapse, interest rates slashed, and investors taking flight to ‘safe haven’ stocks. These factors predictably saw value underperform during the sell-off.
Tellingly, however, since its bottom in late March, the market has rallied sharply, led by cyclicals, and value outperformed strongly in April and May. Over this period, the Perennial Value Australian Shares Trust (PVAST) delivered a return of 19.9% versus the 14.1% return of the benchmark S&P/ASX 300 index. We believe the fund’s ‘true to label’ value approach was an important driver of outperformance during the rally.
The key point is that value tends to outperform not when a crisis is unfolding, but rather, in its aftermath. This is when either the bubbles of euphoria that had been driving the market up may have burst, or the fears that had driven the market down have been realised and dealt with. At this point, investors form the conclusion that the economy will recover, and life will go on. They then seek out solid, reliable, reasonably priced businesses to invest in – in other words, they look to value stocks.
These periods have also shown that style rotation, when it occurs, can happen sharply. When valuation dispersion reaches extreme levels, such as we are seeing today, something usually gives and mean reversion kicks in, resulting in a period of strong outperformance for value investing.
If current trends continue, then the impacts from COVID-19 may be less severe than feared and economies may bounce back. If this is the case, we will have an improving economic outlook, interest rates already at extremely low levels and unlikely to go any lower, and valuation dispersion at record levels. In effect, all the preconditions would be in place for a rotation to value.
Not only does maintaining an exposure to value alongside other styles provide a form of diversification in a portfolio, but after a long period in the wilderness, the tide may be turning in value’s favour.
Stephen Bruce is a Director of Perennial Value Management and Portfolio Manager of the Perennial Value Australian Shares Trust. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.