Since the first publication of this article on 22 March 2020, both UniSuper and AustralianSuper have announced they will revalue their unlisted assets.
CEO Ian Silk said on 24 March 2020:
"The values of all investment portfolios have been adjusted to reflect the economic and financial market impacts of Covid-19. Unlisted assets have been reduced by 7.5% on average, which has resulted in a 2.2% reduction of the balanced option effective yesterday."
This means that members can no longer switch to cash and avoid the fall in price.
Most large superannuation funds have significant investments in unlisted assets. Many are telling you that these assets have not lost value despite sharemarkets falling 30%+ across the world. This gives rise to perverse incentives for superannuants:
- If you leave one of these funds now, you will get paid at the high prices for unlisted assets
- Anyone left behind bears the brunt of the losses when the revulation hits values.
Rough numbers? I suspect right now that the median superannuation fund will pay you about 7% to leave.
Disclosure: Some of this is probably sour grapes! I run a superannuation fund that only buys liquid assets in separately managed accounts. So, an investor's return is their return with all assets revaued at market prices. We can't rely on tax mingling, unlisted asset revaluations or accounting tricks that master trusts use.
Chant West gave us a preview of superannuation fund returns for March 2020:
"Growth funds, which is where most Australians have their superannuation invested, hold diversified portfolios that are spread across a wide range of growth and defensive asset sectors. This diversification works to cushion the blow during periods of share market weakness. So while Australian and international shares are down at least 27% since the end of January, the median growth fund's loss has been limited to about 13%."
Here's some quick maths on the likely impact
Chant West's definition of a growth fund is one that has 60-80% of its portfolio in 'growth' assets. Let's call it 70% exposure to shares, 5% cash and 25% to a composite bond fund.
If shares are down ‘at least’ 27%, cash is unchanged, and a composite bond fund is down about 5%, then the implied return is a loss of -20%.
Chant West says the loss is only 13%. There is 7% missing.
My calculation assumes that the 25% is in composite bonds, but it is more likely in higher-risk unlisted assets.
So where is the missing money?
Now, each super funds will obviously have different assets and performance. For example, own growth fund is only down 0.8% over the same time frame but we took aggressive derisking measures at the end of January.
The superannuation market is about $3 trillion. It is the market. If, somehow, almost every superannuation fund worked out the same thing we did and sold equities in January, the market would have fallen in January.
The answer is superannuation funds have unlisted assets that they are not writing down. In the February 2020 ASFA statitics on large fund assets, the average allocations to unlisted assets were property 5%, infrastructure 6% and equity 4%, a total of 15%, but some individual funds would be much higher.
For example, many retail funds hold assets with greater liquidity to meet redemptions, whereas industry funds rely more on continuous inflows of contributions for liquidity, allowing holdings of more illiquid assets.
They are pretending that the prices are mostly unchanged from January, but the world has changed since then.
Financial crisis comparison
A great example is unlisted property funds during the GFC. Unlisted property funds invest in effectively the same assets as listed property funds, the underlying properties are worth the same, the performance differs because of how it is reported and the revluation method.
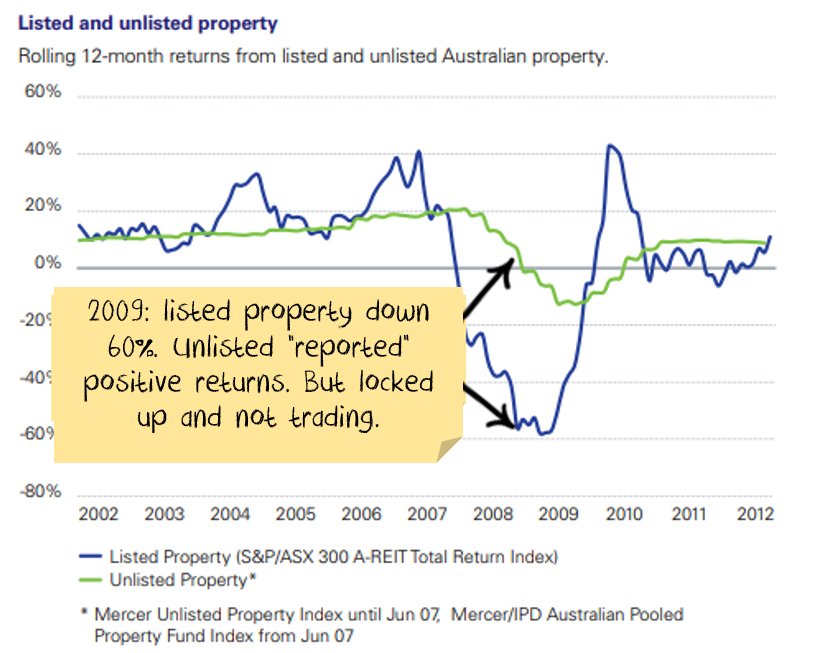
The perverse superannuation incentive
The problem is that if you invest in a fund that reports like this, you can be diluted if other investors leave. They receive the higher assumed price, and any new contributions you make now are at inflated prices.
To illustrate with an extreme example, let's say:
- You and I are the only investors in a super fund with $100 each invested
- The fund owns 50% in an unlisted asset and 50% in cash. So, the total value of the fund is $200 made up of $100 in the asset and $100 in cash
- The asset falls 60% ($60) in price, so our fund is now only worth $140 ($70 each), but the fund doesn't revalue the asset and so reports the fund still being worth $200
- I decide to redeem my holding in the fund
- The unlisted asset can't be easily sold, and so the fund pays me $100 cash being half of the $200 that the fund is still being officially valued at.
- This leaves you with $40 of unlisted assets – double the loss that you should have taken.
Adding insult to injury
The other problem with a typical superannuation fund (but not some of the newer ones that use a separately managed account structure) is your tax is mixed with other investors. Rodney Lay from IIR recently wrote:
" ... unit trust investors face another risk – being subject to the taxation implications of the trading activities of other investors. Net redemption requests may require the manager to sell underlying portfolio holdings which, in turn, may crystallise a capital gain ... During the GFC some investors had both (substantial) negative returns plus a tax bill on the fund’s crystallised gains. Good times!!!"
Net effect for loyalty
Not all super funds hold the same proportion of unlisted assets, but if you are a loyal soldier sticking with a superannuation fund that continues valuing unlisted assets at last year's prices then:
- You will probably absorb the losses of anyone that leaves
- You might even get an additional tax bill because the people that leave trigger a CGT event for you.
But at least your superannuation fund will be able to ‘report’ higher returns.
Damien Klassen is Head of Investments at the Macrobusiness Fund, which is powered by Nucleus Wealth. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.