The central bank policy of 'quantitative easiness' has morphed into simply ‘queasiness’. Certainly, that’s an apt feeling among investors following sharp falls in risk asset prices in the last quarter of 2018, again bringing into focus the question of asset allocation for the path ahead. While many of the surprise falls reversed, at least in part, through January 2019, it’s important to consider what may have driven the sharp declines. Are they symptomatic of a more prolonged malaise or a temporary setback?
It’s hard to ignore the secular shift in the comparable risk/reward metrics of major asset groups. Sharemarkets rewarded investors almost without missing a heartbeat in the entire post-GFC environment, buoyed by central bank monetary stimulus. The combination of a stable tiller and cheap money was an intoxicating mix. But now, perhaps if the initial US experience is anything to go by, we’re seeing for the first time in a long while the impact of having ‘the training wheels off’ and of borrowing costs moving back to a more normalised level, on a jittery equity market.
Fixed interest became relatively more interesting
What we are faced with today is a shifting set of relative market dynamics combined with a much less certain political landscape, with neither being especially ‘equity friendly’.
One thing that is arguably different now as we contemplate future asset allocations is the risk premia or simply the forecast return spread between cash and bonds, and equities. The ~1% cash rate return of the past decade was utopia for equities. Dividend yields of 4% or 5% made them the darling of any asset allocators tool kit. But now that cash rates in the US exceed 2%, the equity dividend yield return spread is less attractive.
And that’s before we factor in the tailwind that a rising rate environment ultimately brings to sovereign and credit yields. There may be some pain as rates rise if duration exposure is left unhedged, but the forward-looking returns from those bond assets today look more appealing. US 10-year Treasuries continue to oscillate around the 3% mark, and investment grade credit yields sit comfortably above 4% at the medium-to-long end of the curve.
The chart below illustrates the forward-looking benefit that the combination of sporadically widening spreads and rising rates - which characterized much of 2018 - provides to bond investors. They give higher yields across the maturity curve with no discernible elevation in the level of default risk. Suddenly, an equity dividend yield of even 5% doesn’t feel quite as rich, and certainly not on a risk- or volatility-adjusted basis.
Investment grade corporate bond yield curve
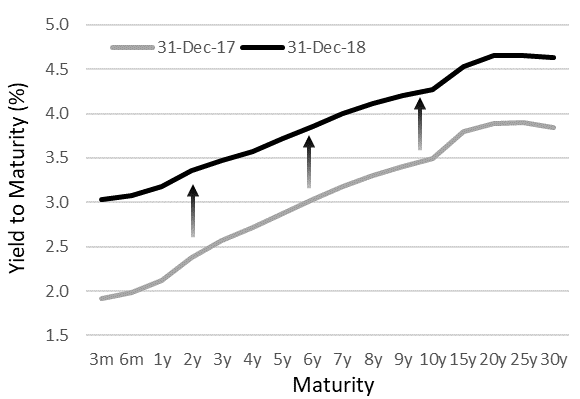
Source: Bloomberg as of 31/12/2018 using Bloomberg’s BVAL USD US Corporate Investment Grade Yield Curve. The yield curve is constructed using USD senior, unsecured fixed rate bonds issued by US investment grade companies.
All this in a climate of political instability brought about by populism and anti-globalism and protectionism with the power to materially disrupt global trade and harmony, and an increasingly embattled Donald Trump.
In 2018, defensive asset allocations won
After all the noise of 2018, those carrying the most defensive strategic asset allocations emerged victorious. It was a worthy reminder that through cycles there will always be periods where it pays to bias your objectives towards preserving money just as much as growing it. Regardless of whether risk asset volatility of the past couple of months proves to be temporary or more sustained, higher cash and bond yields signal a harder environment for equities to maintain the strong competitive edge that they have enjoyed over the past decade.
Chart 2: Short-term Treasuries top returns
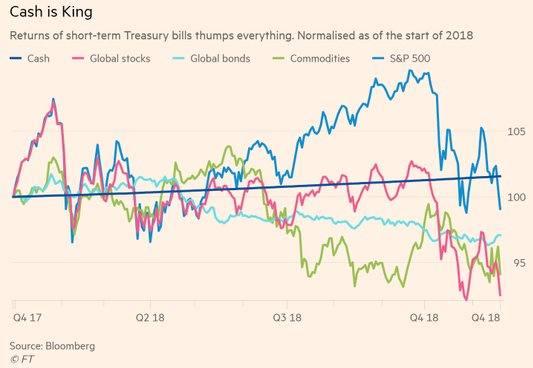
However, our responsibility as investors to those that entrust their money to us means that we cannot sit idly by. This environment has developed as one where optimal balancing between prudent defense and sensible return-seeking becomes paramount.
To borrow from Nat King Cole, while there may be trouble ahead, we must face the music and dance. But perhaps from a safer point on the dance floor not too far from the exit should a hasty retreat become necessary.
James Bloom is Managing Director, Investor Relations at Kapstream Capital, an affiliate of Fidante Partners. This article is for general information, not financial advice. It has been prepared without taking into account any person's objectives.
Fidante is a sponsor of Cuffelinks. For more articles and papers from Fidante, please click here.