The Reserve Bank Governor, Glenn Stevens, has drawn the line in the sand over the past six months, first by observing that entrepreneurial risk taking has been absent, then by imploring businesses to abandon their cost and capital discipline to embrace pro-growth strategies.
Analysts should therefore be looking for signs of a revival in the corporate sector's animal spirits as a guide to the date of lift-off in the Cash Rate. Regrettably, the recently released credit aggregates showed that business credit was flat in August and only 3% higher than a year earlier, confirming that the corporate sector remains reluctant to lift gearing against the backdrop of the new capital discipline.
The Governor's anxiety is understandable considering the imminent investment cliff in mining and energy over the next two years as the construction of LNG processing plants approach completion.
But does Mr Stevens seriously expect the non-mining sectors to ramp up their investment intentions at a time when they face persistent revenue headwinds? Unfortunately, the RBA continues to under-estimate the power of monetary policy to revive the corporate sector's animal spirits, to boost company revenues and lift expectations of growth in nominal GDP.
The ongoing weakness in consumer sentiment and the recently released August retail trade data suggest that the consumer's animal spirits also remain dormant. To put the retail trade survey in context, by excluding items such as services, petrol, motor vehicles and utilities, it accounts for less than one-third of total household sector spending.
Despite its narrowness, it represents an invaluable guide to consumer sentiment because it includes durable goods - such as PCs, washing machines etc - that households tend to buy when they are feeling optimistic and secure about their financial future.
I have further narrowed the survey to capture the three categories that listed discretionary retailers are most exposed to: household goods retailing; clothing, footwear & personal accessories; and department store sales. The chart below shows that discretionary spending across these three categories in aggregate has almost come to a standstill since the end of 2007 after growing at a strong compound annual rate of almost 7% in the preceding decade.
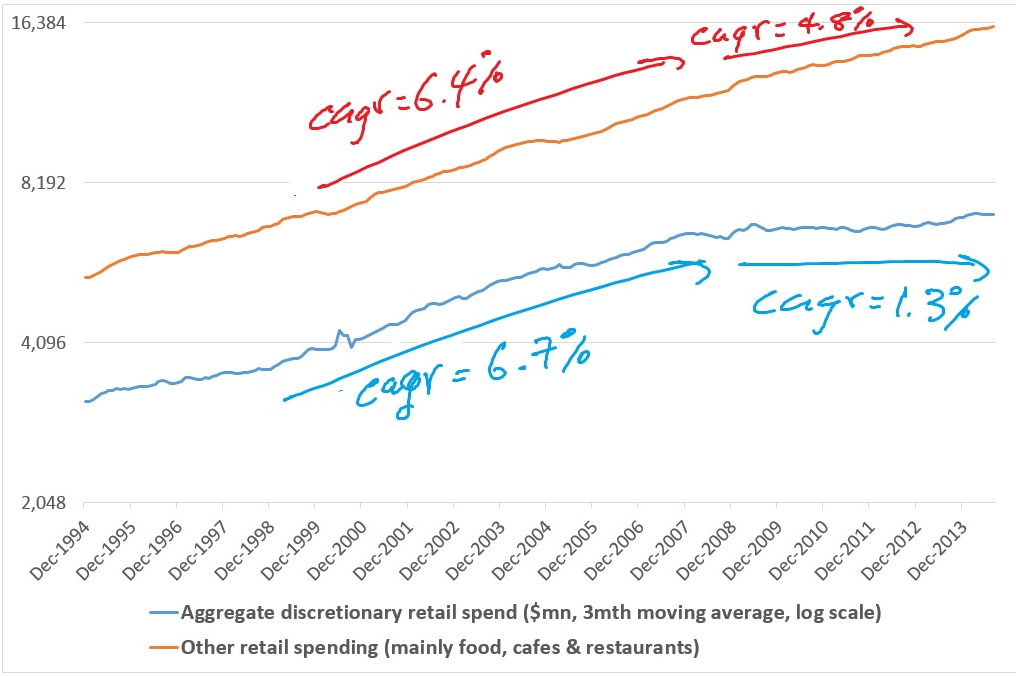
In contrast, the other components of the retail trade data - mainly spending on food as well as cafes & restaurants - has also slowed over the past seven years, but this has been more moderate. Clearly, discretionary retailers have been more exposed to revenue and competitive headwinds than consumer staples.
Persistently weak labour market conditions have not helped, with aggregate hours worked remaining stagnant for three years as companies continue to undertake restructuring and trim costs to offset anaemic revenue conditions.
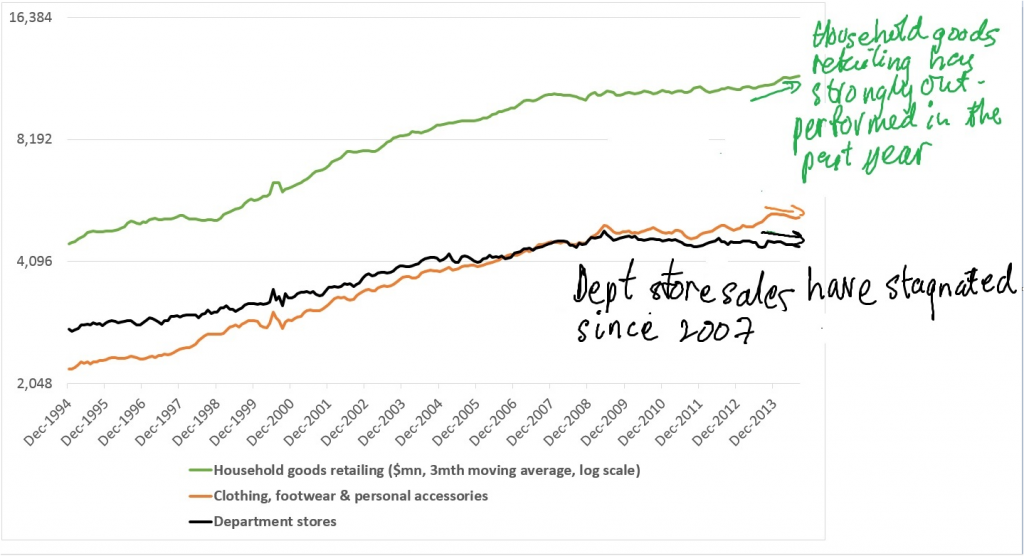
Growth in all three components of discretionary spending have materially slowed since the financial crisis, but department store sales has remained the laggard (see chart below). In the past year, household goods retailing has lifted at a time when department store sales and spending on clothing, footwear & personal accessories has gone backwards.
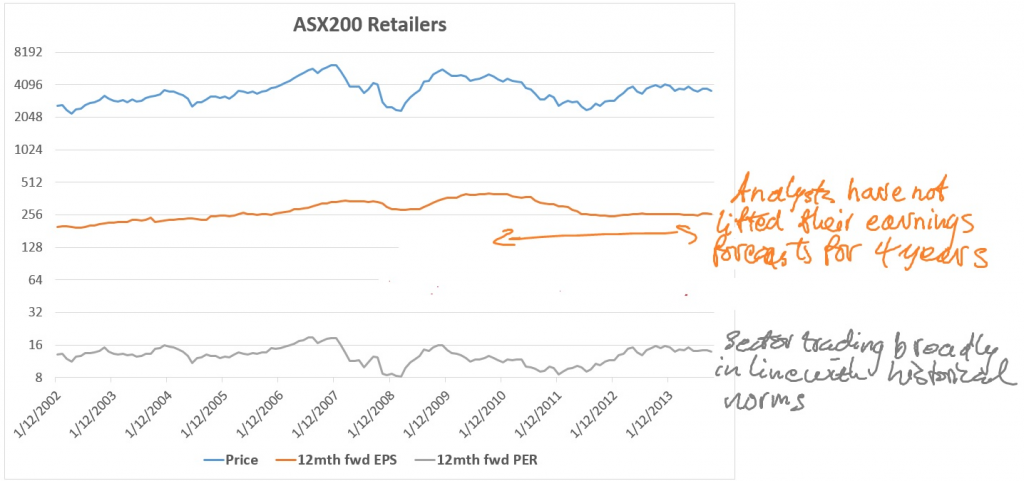
The consumer's dormant animal spirits and intense retail competition (particularly from e-tailers) are reflected in the fact that sell-side analysts have not lifted their EPS projections for the discretionary retail sector for over four years now (see chart below). Indeed, the sector's forecast profitability is at the same level it was in 2005. This has been the lost decade for Australia's discretionary retailers. Valuations are not compelling at current levels, with the sector trading slightly above its historical median of 13 times twelve month forward earnings.
The consumer environment has deteriorated in recent years thanks to weak labour market conditions and increased job insecurity. This has been reflected in a decline in permanent incomes due to a lift in the discount rates that households apply to their future income stream. Little surprise that households have undertaken balance sheet repair and lifted their savings rate.
The revenue headwinds that have beset discretionary retailers are unlikely to change given intense competition from e-tailers and the RBA's timid approach to monetary policy. As with its attitude towards entrepreneurial risk taking, the RBA continues to under-estimate the ability for monetary policy to revive the consumer's animal spirits.
Discretionary retailers need to accept that a cautious consumer represents the new normal for now, and that trimming costs, lifting productivity and consolidating without undermining their service offering represents the most effective way to offer better returns to their long suffering shareholders.
Sam Ferraro is founder and principal of the independent financial consulting firm, Evidente.