Certainly 2025 will go down as yet another year dominated by the growth of the major technology companies, with AI themed investments headlining a surge in equity and debt capital market activity. Much of this activity is funding burgeoning AI capital expenditures with further significant growth expected in coming years as the major technology players make an almost 5x increase in combined capital outlays over the 7 years to 2028 (refer Chart 1).
Chart 1. AI ‘Hyperscalers’ – Annual Capex Expenditures (Actuals and Estimates, $USbn)
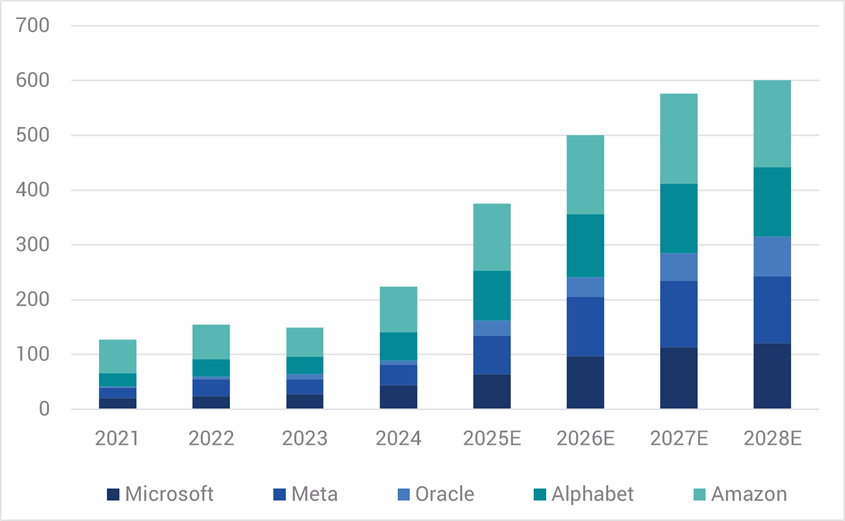
Source: Bloomberg/Yarra, Nov 2025.
Aside from growth in capital expenditure fuelling equity prices and underpinning US economic growth, the major global technology players are increasingly turning to debt markets for funding. Mega debt deals this year are already many multiples of previous annual totals, with the prospect of much more debt issuance to come (refer Chart 2).
Chart 2. AI Tech Giants – Borrowings (Bonds and Loans, $USbn)
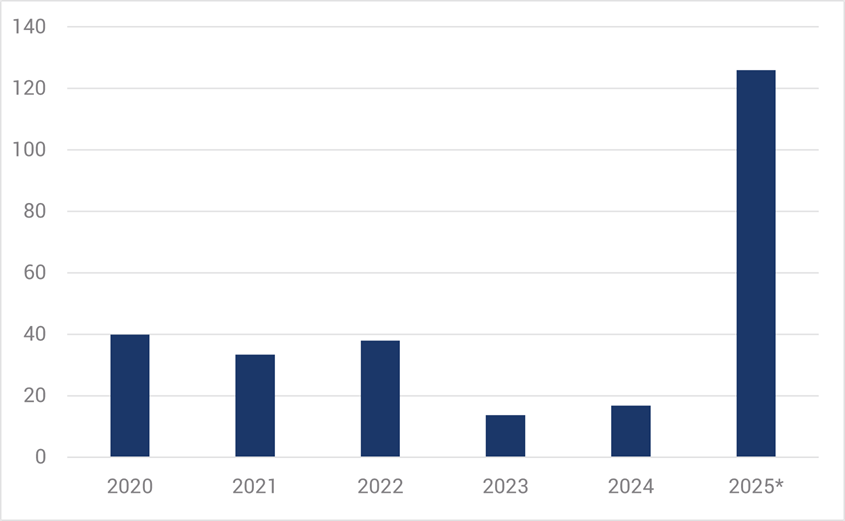
Source: Bank of America/Yarra, Nov 2025. * New borrowings to Oct 2025.
Renowned for their credit worthiness and strong cash flow generation, the AI hyperscalers appear very well placed to manage increased debt on their balance sheet. But everything, including even AI, has its limit. Given capital expenditures are expected to accelerate further over the outlook, we may very well reach the theoretical limits of debt funding in the years ahead without significant downgrades in credit quality, even for such illustrious names as Amazon, Google, Meta, and Microsoft etc.
To date, credit markets have absorbed large sums of new debt from AI companies, but higher Credit Default Swap (CDS) pricing is beginning to reflect some indigestion across the sector. This especially the case for triple B rated Oracle (refer Chart 3). Going forward, further debt capital issuance is likely to further pressure credit spreads.
Chart 3. CDS Spreads – US Technology Companies (bps)
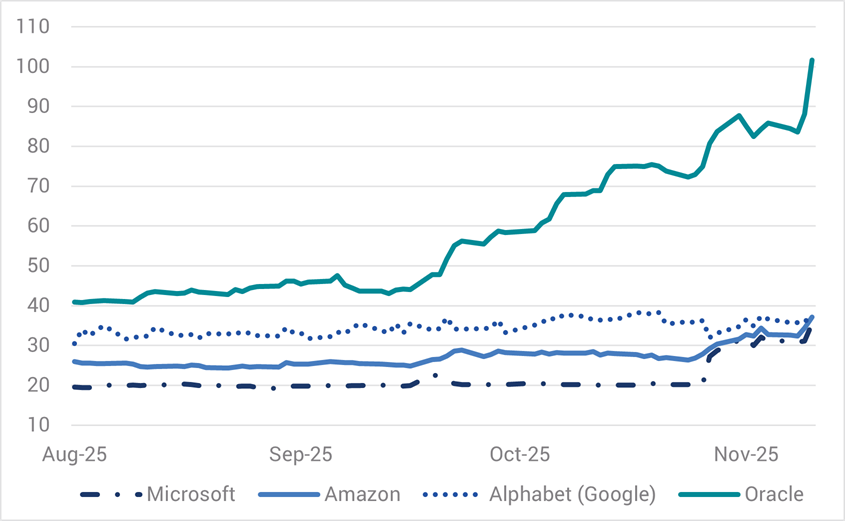
Source: Bloomberg/Yarra, Nov 2025.
For those of us in credit markets, major events can often be eerily similar to historical periods. From our perspective, highly rated AI companies increasingly tapping debt markets to fund burgeoning capital expenditures bears an uncanny resemblance to the early 2000s, where similarly rated European telcos (massively) overpaid for 3G spectrum licenses and associated infrastructure. In the second half of 2000, the likes of Deutsche Telekom (DT), Orange S.A. (France Telecom), British Telecom and Vodafone etc., used debt funding to pay European governments more than $US100 billion for 3G spectrum licenses on the lucrative early promise of the ‘Internet of Things’ (IOT) age.
As we now know, those roads to 3G riches were more potholed than expected, with associated debt issuance and lower-than-expected returns leading to significant negative credit migration and much higher credit spreads. For instance, the spreads of Credit Default Swap – insurance against default – for DT peaked at 400bps in 2002 (refer Chart 4) and its credit rating declined from a high of AA- in 2000 to a low of BBB+ in 2004. It still resides there some 20 years later.
Chart 4. CDS Spreads – CDS Spreads – European Telcos (bps)
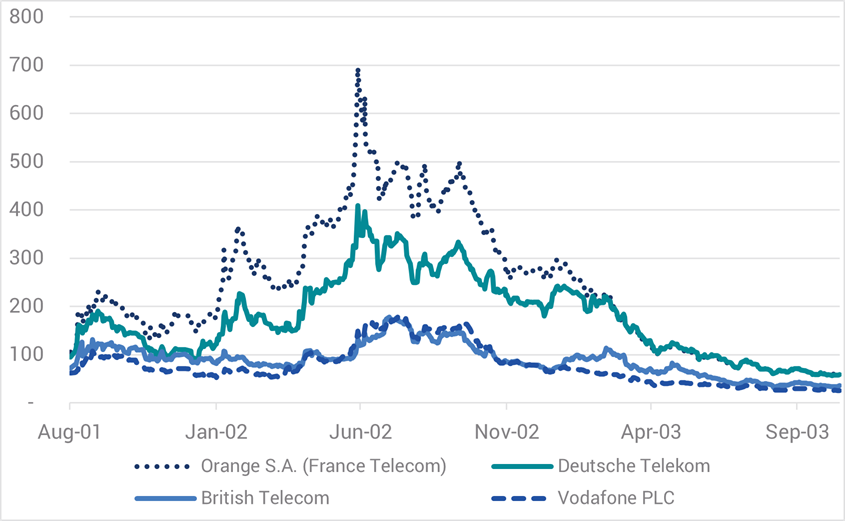
Source: Bloomberg/Yarra, Nov 2025.
The history books confirm that credit investors incurred significant marked-to-market losses funding Europe’s 3G capital expenditure binge in the 2000s, with a sense of Déjà vu now on the horizon for AI investors. While current credit quality – as assessed by S&P – for the likes of Meta (AA-), Amazon (AA), Alphabet (AA+) and Microsoft (AAA) is unquestionably pristine, if the past experience of the European telcos are anything to go by, their credit quality is unlikely to remain so. We believe the credit ratings of hyperscalers in the years ahead are likely to migrate down to single A and maybe even triple B categories.
Credit investors buying the bonds of hyperscalers should clearly be factoring in future credit migration risk into new issuance credit spreads, which for the most part does not appear to be occurring. For instance, Meta recently issued $US13bn (total) across 10 and 30-year tranches at Treasuries +78 and 98bps respectively. While you can debate whether the 10-year securities represent good value, we struggle to make any coherent argument in support of the relative value of the 30-year tranche, with any negative credit migration in the years ahead likely to lead to steep mark-to-market losses.
Phil Strano is Head of Australian Credit Research at Yarra Capital Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article contains general financial information only. It has been prepared without taking into account your personal objectives, financial situation or particular needs.
For more articles and papers from Yarra Capital, please click here.