'Abe-nomics' is the name given to the economic programme of Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, with another former PM Taro Aso as finance minister, since they were returned to power in the December 2012 election. This radical programme has important implications for Australian investment markets.
Japan’s boom and bust
Japan’s economy has been virtually stagnant since the great Japanese bubble burst at the start of the 1990s. Japan was the great ‘emerging market’ of the post WW2 era – much like China has been for the past two decades. Actually Japan was more of a ‘re-emerging’ market since it had previously ‘emerged’ from three centuries of isolation to become an industrial and military giant in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Japan grew literally out of the rubble of WW2 to become the richest country in the world by the 1970s and 1980s. It became the second largest economy in the world behind the US despite having only half the population of the US. Over the same period the US went from being the world’s largest creditor nation to the largest debtor while Japan became the largest creditor. In the late 1980s, the Japanese stock market even overtook the US market in total value.
But it all came crashing down when the bubble burst after peaking on the last day of the 1980s. The collapse triggered a massive banking crisis that still has not been fully resolved nearly 30 years later. Prices of Japanese shares and real estate have still not recovered their late 1980s peak values even today (so much for ‘buy and hold’ investing!). The economy stalled and has been drifting in and out of recession ever since. Even worse, deflation took hold, driving up the yen and hurting exports and tax revenues. Japan is now the world’s largest debtor and the largest creditor is China.
Abe-nomics
After more than two decades of stagnation and failed experiments, Japan needed a radical new plan. Shinzo Abe and Taro Aso’s radical 'Abe-nomics' programme has several aims: to stimulate growth by cutting interest rates and raising asset prices to encourage spending and investment; to depress the yen to assist exporters and protect local industries from imports; and to create inflation so people will spend rather than save.
The four arrows in the plan
There are four ‘arrows’ in the plan:
- Monetary policy, with low and now negative interest rates and QE and central bank buying of assets with newly printed money.
- Fiscal policy, with deficit-funded spending programs
- Structural reforms, such as in the labour market and in protected industries.
- (An unwritten but potentially very powerful fourth) Nationalism, aimed against China, since there is nothing like uniting a nation against a common enemy to spur confidence and spending.
There are also additional measures, including directing pension funds to invest more in shares and other ‘risky’ assets.
From late 2012 until mid-2015 Abe-nomics worked well on the yen and share prices but did nothing to revive economic growth or inflation. The yen fell 40% and the Nikkei 225 index of stock prices rose 140% in lock-step, as shown in the chart below.
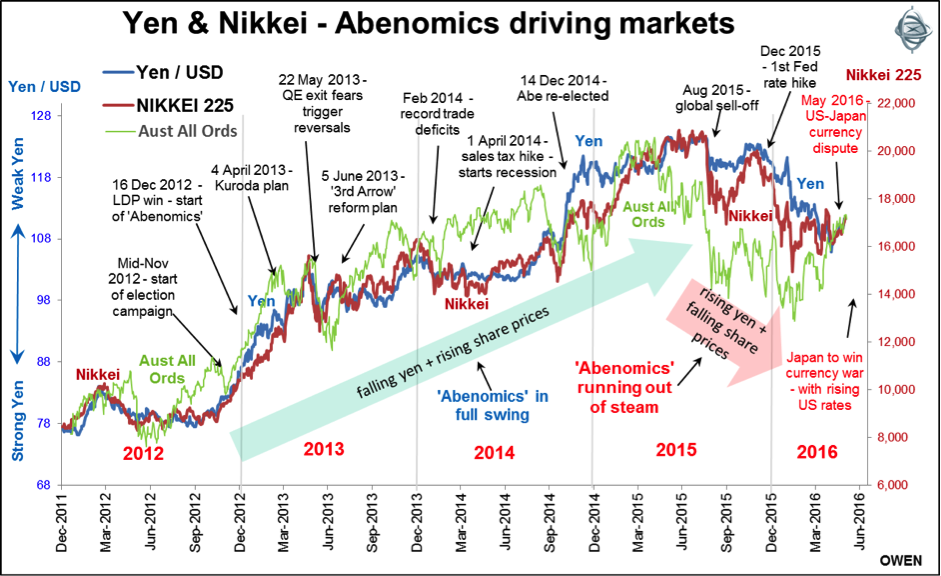
Then Abe-nomics ran out of steam in mid-2015 and things started to reverse: the yen rose and share prices fell back. Ultra-low and even negative interest rates and QE were losing their effect and structural reforms ground to a halt.
Impact on Australia
Why is this important for Australia? Japanese buying of foreign assets (driven by negative Japanese interest rates and a collapsing yen) has provided a major boost to the prices of Australian shares, bonds and property (listed and unlisted) since 2012. The above also shows how the Australian All Ordinaries Index has followed the path of Japanese stock prices and the yen during the period.
The Abe-nomics effect is likely to receive another boost (flowing through to Australian shares, listed property and bonds) in the coming year as the yen resumes its falls while the US dollar rises with US rate hikes.
Three factors are now in play.
The first is that the US Fed seems ready for more interest rate hikes. This expectation is driving up the US dollar once again after it receded in early 2016 while the Fed sat on its hands.
The second is the Japanese government and central bank appear to be preparing further stimulus actions after several months of inaction.
The third is geo-politics. With the US dollar rising again, the US is now openly opposing yen depreciation – a big switch in strategy since it had supported Japan’s depreciation efforts initially. The switch in US policy is due to the increasingly protectionist rhetoric from both Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton in the US election race.
We expect Japan to win the next phase of the currency war, which would see the US dollar rise, the yen fall and more Japanese money flowing out of Japan to buy foreign assets like Australian shares, property and bonds.
Rising global currency wars and protectionism means the RBA may need to cut rates even further to keep the AUD from rising as the US, Europe, Japan and China all compete to lower their exchange rates. Further rate cuts here would reduce interest rates on bank deposits and would also risk re-igniting the local housing bubble.
Ashley Owen (CFA, BA, LLB, LLM, Grad. Dip. App. Fin) has been an active investor since the mid-1980s, a senior executive of major global banking and finance groups, and currently advises investors and advisory groups in Australia and Asia. This article is general information only and does not consider the personal circumstances of any individual.