In 1974, the Whitlam Government was making its ill-fated moves to borrow USD4,000,000,000 from the surpluses of oil-exporting countries, and Australians quickly adopted the concept of billions to measure really big numbers. These days, we’re used to hearing things measured in trillions. A thousand billion. Last year’s US GDP was USD17 trillion and Australian superannuation assets have reached AUD1.75 trillion.
Plenty of liquidity
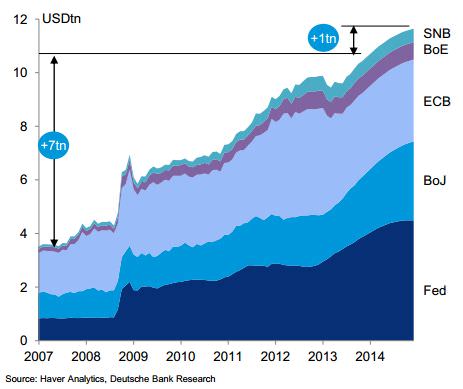
A recent report from Deutsche Bank caught my eye for its use of trillions to quantify the huge expansion in the balance sheets of central banks in the US, the Euro zone, Japan, UK and Switzerland. The five central banks “have delivered unprecedented monetary stimulus since the [global financial] crisis … Interest rates [have been] slashed to all-time lows [and] USD7 trillion in liquidity added since 2007 … These central banks will remain ultra-supportive, adding a further USD1 trillion of liquidity [in 2014]”.
Figure 1: USD8 trillion of additional liquidity, 2007-2014
What is 'liquidity'?
I should remind readers that the word ‘liquidity’, when used in discussions of financial markets, has several different meanings. It’s most often used to describe the ‘depth’ of a financial market: liquidity means that the buying or selling of a particular security doesn’t much affect the price at which it trades. Liquidity can also refer to the speed and ease with which a bank or insurance company can convert various assets into cash.
However, in discussions on monetary policy, liquidity refers to what a central bank is doing to the level of the money base. That is, the total of currency (notes and coin) on issue plus the level of deposits the commercial banks have with central bank (which can readily be converted into notes and coin). In turn, ‘liquidity creation’ (or ‘liquidity generation’) describes the expansion of the money base, or how much money is being printed.
A central bank creates liquidity when it buys bonds or other financial instruments, intervenes to keep the exchange rate down, or lends to banks or other financial institutions. In those circumstances, the central bank simultaneously acquires an asset (the bond, foreign exchange or loan) and increases its liabilities (the deposits that commercial banks hold with the central bank or the volume of currency on issue).
Central banks in developed economies have been doing ‘whatever it takes’ to increase spending and jobs and to avoid deflation; in the Euro zone, they’ve been keen also ‘to preserve the euro’.
No boost to business activity
To date, however, central banks haven’t succeeded in boosting business activity as much as they, and their governments, would like. That’s because, with many companies and households wanting to cut back on debt and with commercial banks taking a cautious view on lending, much of the additional liquidity isn’t circulating or giving rise to an expansion in credit; instead, it’s sitting around in idle balances. In the US, for example, commercial banks have USD2 trillion of excess reserves held on deposit with the Fed.
However, the massive creation of liquidity in recent years has greatly reduced the risks of another global recession and deflation. And in most developed economies it’s helped drive share prices and house prices higher.
The US Central Bank is expected to end its ‘quantitative easing’ (QE) by late 2014. Until recently, that programme was running at USD85 billion a month, but has since reduced. But that move – the ‘taper’ - will simply reduce the rate of build-up in liquidity. It will not result in the withdrawing of some of the massive increase in liquidity that’s already been generated. With the central banks of Europe and Japan apparently on course to move further along the paths of unconventional monetary policy, global liquidity is likely to rise strongly over the coming year. A recent move by the German constitutional court could complicate, and for a while delay, asset purchases by the European Central Bank, but the ECB will have no alternative to generating more liquidity if it is to preserve the euro.
Share markets in developed economies seem likely to benefit from the continuation of an ultra-easy setting in monetary policy by the major central banks. However, as average valuations of shares are so much higher than a year ago, the pace of liquidity-led gains is likely to be modest.
Anyone who misspent their youth studying economics would recall the concept of the velocity of circulation of money. Alas, there’s not much velocity at present. As and when confidence returns and money starts circulating again, central banks will find it hard to sufficiently reduce the volume of liquidity they’ve recently created.
Investors preparing for retirement need many years ahead to allow for the mounting risk of a powerful return of global inflation. Not yet, but in the medium term.
Don Stammer was for many years Director, Investment Strategy at Deutsche Bank Australia. He is currently a columnist for The Australian and an adviser to the Third Link Growth Fund, Altius Asset Management, Philo Capital and Centric Wealth. The views expressed are his alone.