A claim currently receiving renewed attention in the active versus passive investment debate is that the apparent outperformance of passive investment strategies is largely cyclical, and usually only takes place in the late stages of a bull market.
This article argues that while there may well be an element of cyclicality, it is minor in degree. What’s more, the sporadic periods of active outperformance don’t appear to provide much downside risk protection in bear markets and any such outperformance does not offset the much longer periods of active manager underperformance during bull market phases.
Active managers tend to do best in bear markets (but let’s not get carried away)
Financial research across the world has long noted that active equity investment managers, on average, fail to beat passive broad market investment benchmarks over time. Yet a wrinkle on this general observation is best represented in the graph below from a US-based active-investment manager, Baron Capital. It shows that active investment performance tends to be cyclical, especially during the downmarket in the early 2000s and again during the 2008 financial crisis, active managers on average tended to outperform.
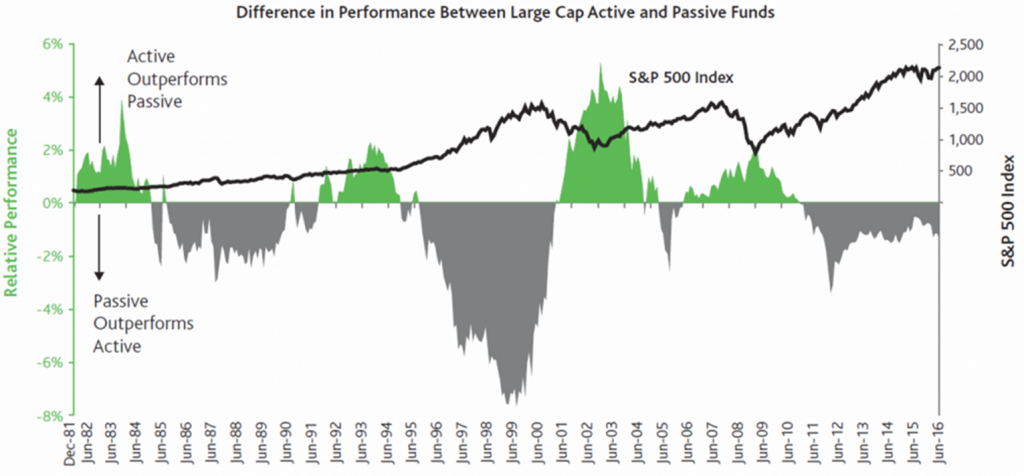
Source: Morningstar Direct, Baron Capital
The analysis is based on monthly rolling 3-year returns for the period 12/31/1981 to 6/30/2016. US OE Large includes all share classes in Morningstar’s US OE Large Growth, US OE Large Value, and US OE Large Blend categories. The performance of passive funds is calculated as the average 3-year performance of all index fund share classes in each category. The performance of active funds is calculated as the average 3-year performance of all non-index fund share classes in each category. Results for each category are then averaged and the differences between active funds’ averages and passive funds’ averages are calculated.
So far so good. At face value, this result seems to make intuitive sense: during strong bull market periods, popular large cap stocks with strong momentum may continue to perform well, even though an increasing number of active managers may feel they are overvalued and may reduce exposure to them. Passive indexing strategies which weight stocks according to their market capitalisation may tend to outperform more value-based active managers. When the bear market strikes, however, and once popular stocks fall out of favour, active managers then come into their own. Right?
Against this background, a generous theory could be that the recent extended period of active manager underperformance can be explained by the long bull market since the GFC. That is, the active manager underperformance is only cyclical, and will be corrected when the next bear market inevitably strikes. Sadly, the numbers don’t quite bear this out…
In bear markets, active managers don’t provide much downside risk protection
Even a cursory glance at the above chart should alert readers to one observation: the period of active manager outperformance (in green) tends to be milder and shorter than their periods of underperformance.
Indeed, also included in the research which produced the above chart was the analysis below, examining the degree of active manager outperformance in different stages of the past four US stock market cycles. Active managers tend to do best in bear market periods, with a majority of managers outperforming in each of the previous four bear periods. Yet at least over the past three market cycles, this degree of outperformance was more than fully offset by substantial underperformance during the preceding longer bull market periods. Active managers on average tended to underperform over the market cycle as a whole.
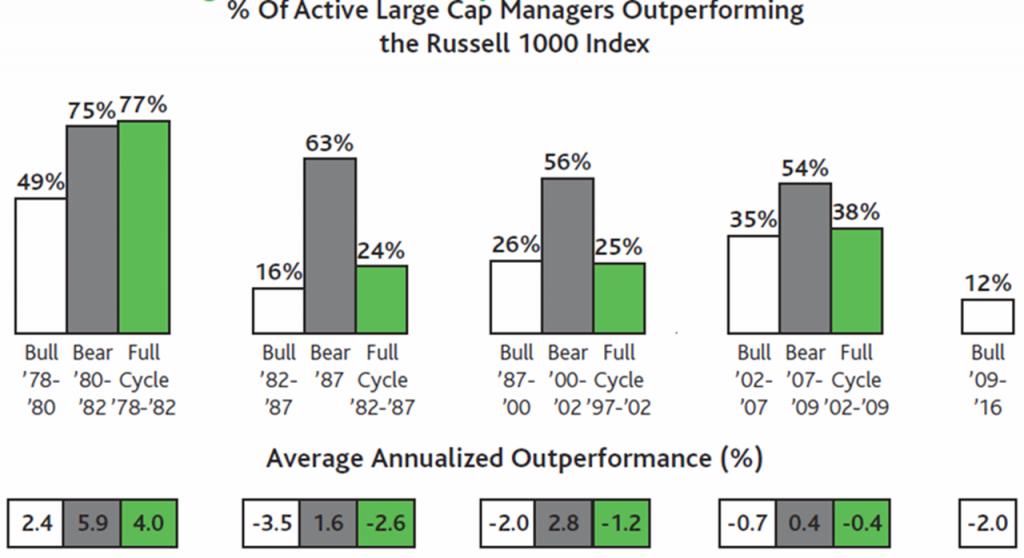
Source: Baron Capital
Not helping the active manager’s cause was the fact that the excess annualised return during the last three bear market periods appears, on average, to be quite modest, at not more than 3% p.a. If an investor’s active manager is down 27% in a bear market, however, it’s not much solace to know their manager nonetheless outperformed the market’s 30% decline.
It’s not surprising when active equity managers tend to have mandates requiring close to full investment in the market, with only limited ability to increase cash exposure. It’s also consistent with the difficulty most investors – professional or otherwise – have in timing market exposure.
Better ways to ‘index’ and get downside protection
One of the implied criticisms of passive investment in the above discussion is that it tends to chase performance. Supposedly, it increases the weight to strongly-performing stocks which are rising in market capitalisation, irrespective of their underlying value, and reducing the weight to poorly-performing stocks that might be better valued. This is really a criticism of market-cap passive index weighting, rather than passive investing per se.
Indeed, as seen in the charts below, while active managers on average haven’t beaten the market-cap weighted S&P 500 Index over time, an indexing strategy based on a company’s non-price measures of economic size has outperformed the S&P 500 Index over the past 10 years, and by consequence, the average performance of active managers.
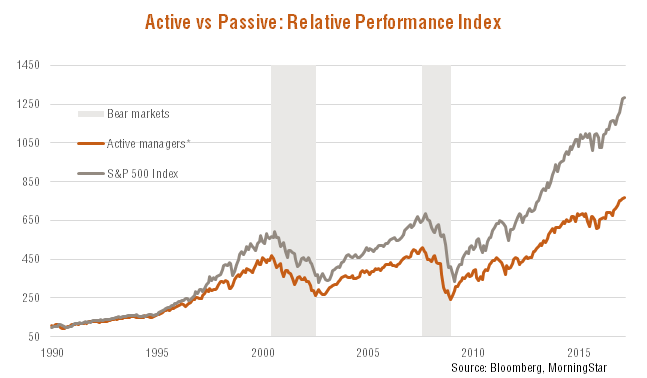
*Average active manager performance is defined as the equally weighted monthly performance of the median growth, value and blended large-cap US active manager in the Morningstar database.
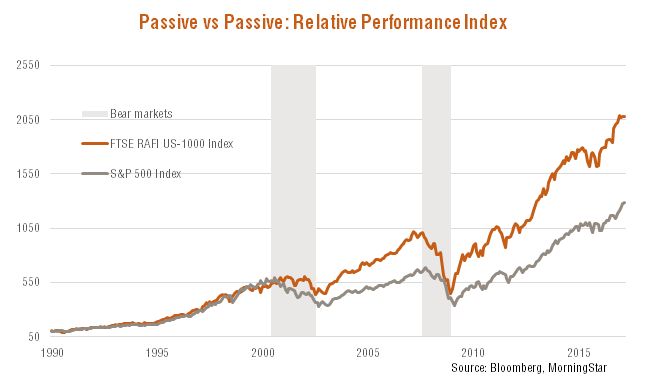
It is always important to ‘look beyond the headline’ and focus on the substance of an argument. There may well be more to it than meets the eye!
David Bassanese is Chief Economist at BetaShares. BetaShares is a sponsor of Cuffelinks, and offers risk-managed Exchange-Traded Funds listed on the ASX such as the ‘fundamentally-weighted’ BetaShares FTSE RAFI Australian 200 ETF (ASX Code: QOZ), and the BetaShares FTSE RAFI US 1000 ETF (ASX Code: QUS). Investors should also be aware that rules-based strategies exist which aim to provide a measure of protection in down markets, while still delivering reasonably low cost, diversified exposure to equities. Such a rules-based strategy forms part of the BetaShares Managed Risk Australian Share Fund (ASX:AUST) and the BetaShares Managed Risk Global Share Fund (ASX:WRLD). This article contains general information only and does not consider the investment circumstances of any individual.