‘Past performance is no guarantee of future performance.’ How many times have we heard that? The Australian Securities & Commission (ASIC) insists that fund managers and financial planners include it in practically every piece of communication they produce.
The Australian sharemarket is more than 20% up in this financial year, and there is much discussion between pundits on everything between an imminent crash, a ‘plateau’ and a brief correction before an onward march.
So it was with interest that I looked at a table sent to me by a fellow financial planner, Dejan Pekic of Newealth. It shows returns from different investment types (asset classes) for each calendar year since 1981. The data is considered robust over this period because before 1979 there were various proxies for the ‘Australian’ sharemarket index, which often excluded major companies. In the table below:
- the best performing asset class in a particular year is highlighted in green, and recessions are in orange
- ‘Property’ refers to Australian listed property trusts not residential property
- Fixed Interest refers to government and corporate bonds, not term deposits
- returns from International Shares are in Australian dollars, not hedged.
Asset Class Calendar Year Returns, 1981- 2012
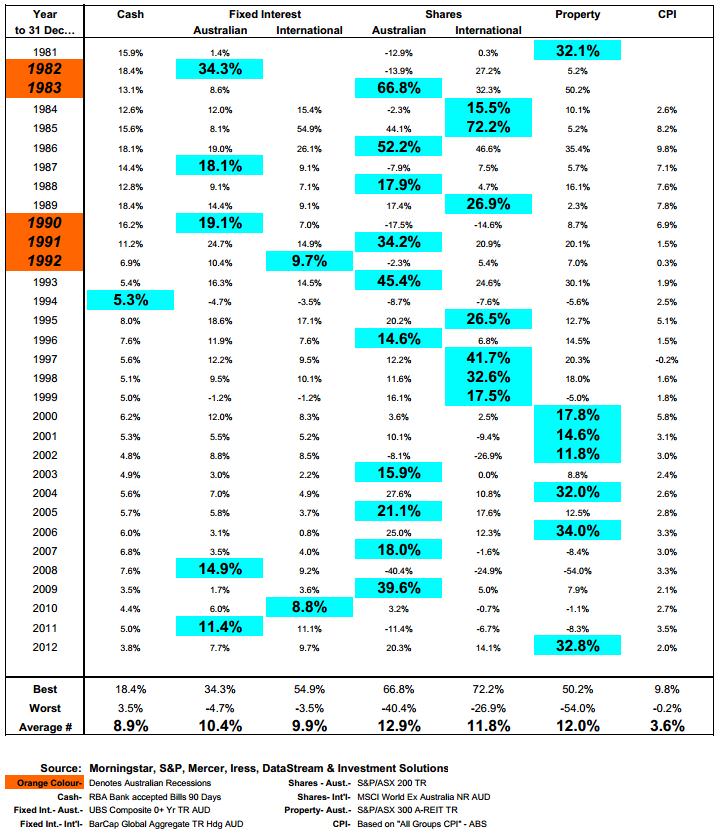
Sourced from Newealth Financial Services.
Here are a few observations:
- In 11 out of the 32 years, the sharemarket has risen by more than 20% in a calendar year. In fact, in more than half of these occasions the rise has been 34% or greater. So rises of 20%+ in a year are not unusual.
- Nine times out of ten, a negative year in the Australian share market has been followed by a positive year, and that positive year was more than 17%. This supports the notion of sticking to your guns after a bad year.
- Returns from international shares have been relatively poor compared with Australian shares for many years. International shares have not been the best performing asset class since 1999. But over the last 32 years as a whole, Australian shares have only delivered annual returns of 1.1% more than international shares. Exchange rates are a major factor.
- In almost 80% of the years, the difference in performance between Australian and international shares was greater than 10%. 25% of the time one was negative and the other was positive. This challenges the popular belief that returns from Australian shares and international shares are highly correlated.
- Cash has only been the best performer once, in 1994. If you had all your money in cash in that year you would have felt pretty good, because everything else went down. But if you had stayed in cash for the following years you would have missed the 20.2%, 14.6%, 12.2%, 11.6% and 16.1% returns delivered by Australian shares.
- However, in ‘real’ terms, cash returns have been pretty good over the past 32 years. The average annual return is 8.9% which is 5.3% more than inflation (CPI). This implies that cash is a good investment when inflation is high, which is contrary to what we are often told. Currently, we have a different situation, as interest rates are barely covering inflation.
- CPI has been below 3.6% for 20 out of the last 22 years. Many market commentators say that low inflation means low share market returns. However, in 15 of those years the Australian sharemarket delivered returns that were more than 10%, with the average return being 12%.
- Fixed interest has only delivered a loss once in 32 years, with average returns comfortably above inflation. However, interest rates have been declining for practically the whole time. This has been good for fixed interest returns because falling interest rates mean capital gains. The only time fixed interest delivered negative returns was in 1994 when interest rates went up.
- Listed property has been the best performing asset class in six of the last thirteen years. However, much like Pluto is no longer considered a planet because of its small size, I believe listed property should be considered a sector of the sharemarket. I am waiting for somebody to replace listed property with residential property in a chart like this. Then we can really have a discussion about performance and diversification.
Some will argue that the 1980s is no longer relevant because inflation and high interest rates have been well and truly beaten. But how far back should we go? According to AMP, which has analysed statistics from the Australian Bureau of Statistics and the Real Estate Institute of Australia, the average annual returns from cash, Australian bonds and Australian shares since 1926 are 5.7%, 7% and 11.4% respectively. Australian residential property has delivered 11.1%.
Each of you will have your own opinion, but the figures are what they are. So, whilst past performance is indeed no guarantee of future performance, it’s all we’ve got.