The dramatic changes to U.S. tariffs settings challenges the financial market’s Trump pro-growth market narrative which heralded the start of 2025. Instead, investors now face conditions which look likely to invoke a global economic slowdown, if not recession, with significant pressure on corporate earnings from higher costs together with unsettled consumer demand and production patterns.
Regardless of where Trump’s tariffs settle, the market is coming to terms with higher risk hurdles when assessing investments. Whilst we cannot be sure about absolute outcomes, in this environment we believe REITs are relatively well placed to produce competitive risk adjusted returns. As we will explain, income security generated by select real estate combined with the operating and capital strength of REITs underpin our belief.
The fundamentals underlying our optimism
We see the biggest threat to our constructive thesis on REITs relate to a scenario involving the onset of stagflation and acknowledge that a deep and extended period of economic contraction will increasingly weigh on real estate returns. We also can not dismiss the possibility of additional imposts on real estate as Trump seeks to find alternate sources of income to provide tax relief for businesses and ordinary citizens. Given Trump’s background, this latter risk would be somewhat surprising.
Our reasons for optimism are starting to play out. Whilst Global REITs have not been spared in the broad sell down of publicly market investments, as investors seek less economically sensitive areas of the market they have outperformed broad equities thus far in 2025. Thanks to underlying strong fundamentals, we believe there is scope for this trend to continue.
Figure 1: Global Equity Performance CYTD
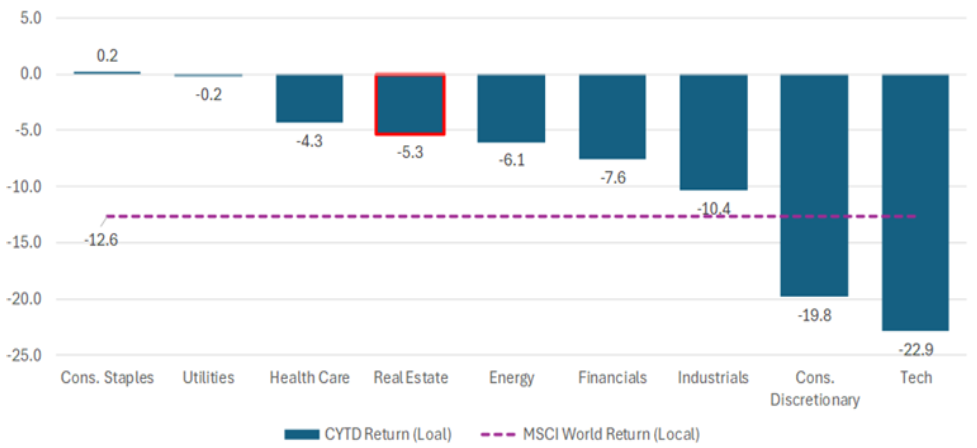
Source: MSCI World Index (Local Currency). 07 April 2025
Importantly, to date, bond yields have been relatively stable and there is room for central banks to reduce interest rates should there be clear evidence of a rapidly deteriorating economy and/or reduced consumer price inflation. That said, core inflation dynamics remain challenging, and central banks will be loath to repeat the mistakes of past stock market corrections such as that which occurred post the 1987 crash when emergency rate cuts fuelled higher inflation. Whilst REITs will not be totally immune, their earnings are less sensitive to slowing economic activity and increasing costs pressures.
Critically, real estate and REIT earnings are not directly affected by changes to tariffs.
From an operating expense perspective, REIT outgoings largely relate to property taxes, repairs and maintenance, property management and insurance. Hence, by and large, these are unaffected by tariffs.
In many underlying real estate categories, REIT revenue (rental) streams are relatively secure thanks to medium to long-term lease contracts, often three to 10 years in duration, which provide cashflow security. Where these lease structures are common, industrial and office property are perhaps the most vulnerable to a prolonged economic slowdown thanks to diminished tenant demand. We are significantly underweight REITs with office and warehouse exposures, in total representing less than 15% of the portfolio, with the U.S. being less than half this figure.
In other segments such as residential, self-storage, and hotels, income is often derived from short term lettings. In some of these instances, occupier demand is needs-based and hence income tends to be relatively resilient. Clearly hotels are the most economically sensitive to which we have minimal exposure. Of course, this income profile is subject to tenant credit. We would note that the largest single tenant underlying our REIT property portfolios generates less than 2% of total portfolio income [Astria Senior Living].
Furthermore, increased tariffs will put further upward pressure on building material replacement costs, making real estate development economics even more challenging unless rents rise meaningfully. Of course, tenant demand is critical but weaker demand will not be compounded by a growing supply overhang and in an environment where real estate vacancy rates are historically low.
For broader equities investors, we believe the picture is more challenging. Trump’s policies are likely to put pressure on corporate profits and margins as businesses will find it difficult to pass on the full cost of higher import prices to their customers. De-globalisation will create other challenges including sources of production, re shaping of supply chains and capital needs for businesses. We expect in this environment greater investor scrutiny on fundamental value and real cashflows from business models that have been over hyped and overpriced.
Figure 2: Relative EV/EBITDA spreads
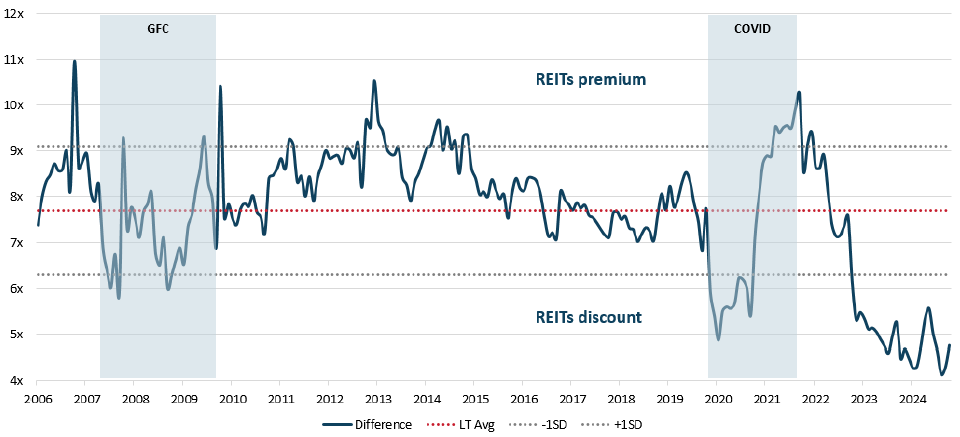
Source: Resolution Capital. Spreads calculated as EV/EBITDA difference between FTSE EPRA Nareit Developed Index and MSCI World Index. 28 February 2025
Crucially, we do not believe current REIT earnings multiples takes into account the key replacement cost dynamic. Based on this fundamental tangible quality, by our estimates, commercial real estate is currently trading at/below replacement costs with low new construction. Consequently, REITs multiples appear on the surface to be very undemanding versus broader equities. Hence, the sector could benefit from investors continuing to rotate from more economically sensitive sectors into more defensive cashflows. It is reasonable that investors will view real estate as being a relatively secure investment and generating meaningful income distributions (REIT legislation requires a substantial payout of after depreciation earnings).
From a capital perspective, the REIT sector is in a strong financial position. By and large, the sector doesn’t require meaningful additional debt or equity to meet any additional capital commitments, dividends are covered by operating cashflows and refi needs are manageable. Indeed, REIT capital structures are arguably stronger today than in any period entering an economic slowdown over the past 30 years. Most debt is structured with fixed interest rates generally for more than three years, cushioning earnings from short term market rate volatility.
Whilst an outcome of bottom-up analysis, towards late 2024 and into early 2025 we reduced our exposure to the U.S. REITs and are now meaningfully underweight the U.S. market for the first time since 2015. We have positioned the portfolio away from the more economically sensitive sectors and little development exposure. REIT capital structures are robust and at this stage we see no need to meaningfully increase cash levels. In addition, we will continue to focus on those REITs best placed to withstand more challenging tenant demand conditions.
Andrew Parsons is a Co-Founder and Chief Investment Officer at Resolution Capital, an affiliate manager of Pinnacle Investment Management. Pinnacle is a sponsor of Firstlinks. Resolution has launched the only active GREIT Fund in Australia (ASX:RCAP).
This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider any person’s objectives, financial situation or needs, and because of that, reliance should not be placed on this information as the basis for making an investment, financial or other decision.
For more articles and papers from Pinnacle Investment Management and affiliate managers, click here.