It has been six months since Donald Trump won the US presidential election. Contrary to the talk of doom and gloom from the usual line-up of shrill ‘experts’ in the media, share prices have done well since the election. The chart below shows the total returns from the major asset classes since 9 November 2016.
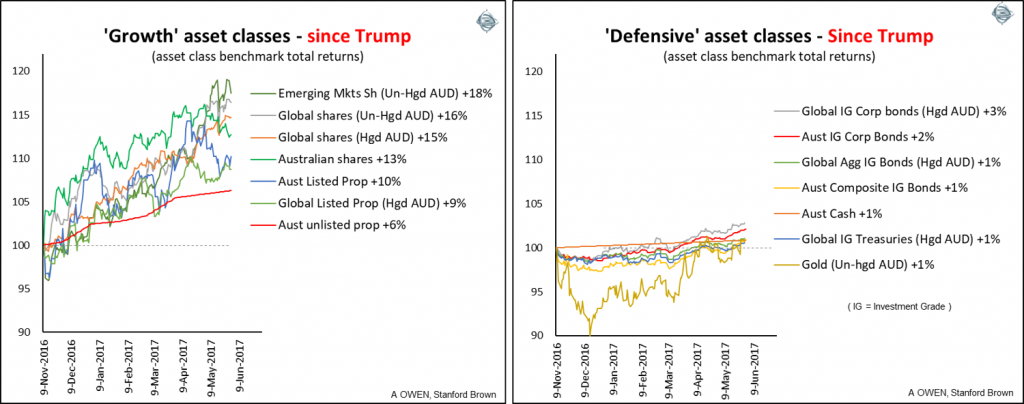
Click to enlarge
Global shares have risen well virtually across the board. Returns in hedged and un-hedged Aussie dollars have both been good as the AUD has remained little changed against most currencies. Japanese shares have been the stand-out, up 20%, and European markets have also seen double-digit returns, led by Germany. We remained committed to global shares in portfolios throughout the lead-up to the election and since. We also increased weightings of Australian shares shortly after the election and the market here has done well.
The Trump victory became clear only after the US market had closed on Tuesday 8 November, US time, but the Australian market was already open on our Wednesday 9th, so local investors here had to think for themselves. With no lead from the US, local investors panicked and sold shares down 2% across the board. But as soon as the US market opened strongly on its Wednesday 9th US time, local Aussie investors said: “Oops - we should have bought, not sold!”, and then our market jumped 3% on Thursday 10th. The local Aussie stock market rose with the rest of the world until the local banks retreated a little in May 2017 as fears of a housing bust set in.
On the other hand, the ‘defensive’ asset classes have done relatively poorly, but still positive. Within the defensive allocations, our portfolios have been skewed toward corporate bonds and floating rates, which have done better than government bonds. The worst of the scaremongers in November were advocating selling everything and retreating to gold, but gold sold off sharply after the election. We hold no gold in portfolios.
Of course, past returns provide no guarantees for the future, but it shows the value of keeping a cool head and sticking to a disciplined process. Markets have done well in the first six months under Trump but that does not mean this will continue. As always it pays to ignore the media noise and focus on the real drivers of markets over the long term.
Trump versus Nixon: impacts here
In recent weeks, many people have asked me about the possible impacts on markets of a Trump impeachment. Comparisons have been made to Nixon who resigned on 9 August 1974 to avoid being impeached over his involvement in, and cover-up of, the Watergate break-in on 17 March 1972 in the lead-up to the 1972 election.
The Nixon crisis in the US and the Whitlam crisis here both played out during the 1973-74 stock market crashes in the US and Australian markets. Here is a daily chart of the Australian All Ordinaries Index (green) and the Dow Jones Industrial Index of US shares (red) during 1972-75. I have re-based both to start at 100 at the start of 1972 to make the comparison easier. The chart also shows the main monetary policy indicators in both countries in that era – the yield on 10-year government bonds in Australia and the Fed’s discount rate in the US.
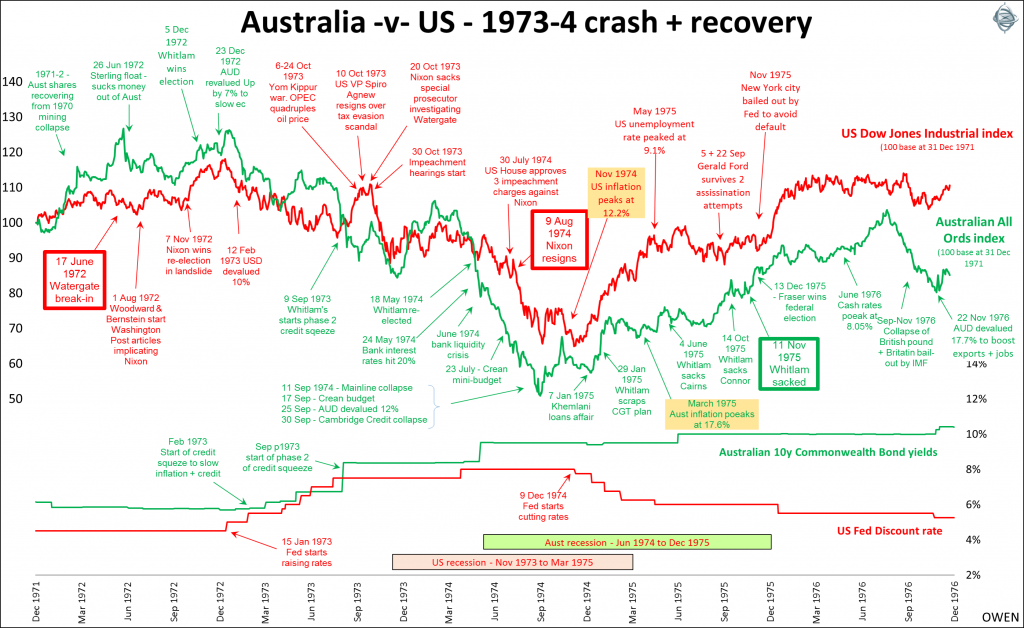
Click to enlarge
While the policy decisions of the Nixon and Whitlam administrations certainly influenced the direction of the crises, the tumultuous removals from office of Nixon in the US and Whitlam in Australia were not the main drivers of markets. The main issues were the battle against inflation (which peaked at 12.2% in the US and 17.6% in Australia), the trade-off with unemployment, and the severe credit squeezes in both countries. These factors triggered the deepest recessions and stock market sell-offs since the 1929 crash and the 1930s depression. Nixon and Whitlam contributed to the problems but the main causes of inflation in both countries lay in the sustained increases in government spending from the mid-1960s on social programmes and the Vietnam war, poor central bank responses to rising inflation and to the OPEC oil price hike, and worsening current account and currency imbalances.
Trump’s continued haphazard announcements, and possible moves to impeach him, are likely to rattle markets from time to time, but that is not the main game. Far more important issues include fiscal policy (government spending and debt), monetary policy responses to rising inflation (interest rates), company profits and cash-flows.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at privately-owned advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.