What you need to know about the 2020 US presidential elections
Daniel Morris and Mark Allan
The elections take place on Tuesday, 3 November 2020. Let’s first remind ourselves of the US political structure.
US Government 101: Congress
The United States Congress, the legislative arm of the US Government, consists of two bodies: the Senate (upper chamber) and the House of Representatives (lower chamber). Passing legislation requires the consent of both the House and Senate and the agreement of the President.
Today, Congress consists of 100 senators (two from each state) and 435 voting members of the House of Representatives. The number of representatives a state has is determined by its population.
On 3 November 2020, all 435 seats in the House of Representatives, 35 of the 100 seats in the Senate as well as the office of President of the United States will be contested. In addition, elections will be held for 13 state and territorial governorships, as well as a number of other state and local bodies.
The current situation
Democrats have held a majority in the House since the 2018 elections, while Republicans have controlled the Senate since the 2014 elections.
The Democrats enter the 2020 election with 232 of the 435 seats in the House to the Republicans’ 196, giving them a sizeable 37-seat advantage. The Republicans hold the Senate by a 53-47 margin.
Control of both the House and the Senate: a Democrat clean sweep?
To enact sweeping change, the next administration would need to have a working majority in both the House and the Senate. This is particularly true given the current divided and very partisan political climate in the US.
At time of writing, Democratic candidate Joe Biden leads President Trump by around 10% in national opinion polls. In addition, the Democrats are clear favourites to retain their majority in the House. It would be a huge surprise if they do not do so.
It is control of the US Senate that is most tightly fought over in this election.
The 2020 contest for the Senate: down to a few states
This year, the Republicans have to defend 23 of the seats up for election, compared to 12 for the Democrats.
Theoretically, to gain control of the Senate, the Democrats need to win a net four seats (or three if Joe Biden wins and Kamala Harris becomes Vice-President and chair of the Senate, with the ability to cast a tie-break vote).
In our view, it is likely that the race for control of the Senate will come down to key, or 'swing', states: Arizona, Colorado, Maine, North Carolina, South Carolina, Iowa, Georgia and Montana.
We agree with the consensus view that the Alabama Senate contest is the only likely opportunity for Republicans to reclaim a seat from a Democrat.
We (and the consensus) anticipate that the Republicans will win Alabama (in a special election contest in 2017, the Democrats won Alabama for the first time since 1992, defeating a scandal-ridden Republican candidate).
Economic policy
Although millions of people have already voted, there is still time for the race to change dramatically. However, absent a meaningful shift in public opinion, a clean sweep for the Democrats with Joe Biden in the White House and Democrats controlling both the House and Senate looks likely.
That outcome would open the way for substantial fiscal stimulus.
In our view, it is quite plausible that a Democratic clean sweep could lead to fiscal stimulus of as much as USD2.5 trillion in the next 12-18 months – that equates to around 10% of US GDP. By way of comparison, the tax cuts President Trump enacted in 2018 represented around USD1 trillion over five years.
Exhibit 1 below summarises what we see as the probable implications of Republican or Democrat control of the White House and Senate for US fiscal policy and the outlook for monetary policy after the elections.
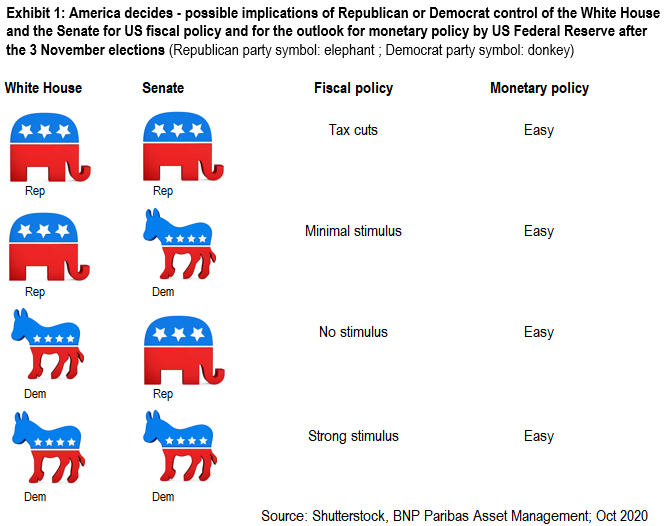
In a nutshell, the sort of very significant fiscal stimulus that a Democratic clean sweep could bring may increase growth, and possibly generate a little more inflation in the US.
Daniel Morris is Chief Market Strategist and Mark Allan is a Senior US Economist at BNP Paribas Asset Management. The information published does not constitute financial product advice, an offer to issue or recommendation to acquire any financial product. You will need to seek your own advice for any topic covered in the article.
This article was first published on 13 October 2020 on Investors’ Corner.
Five ways the US election could impact investments
John Ma and Jason Epstein
The stakes are high for a country that has been grappling with the COVID-19 pandemic, social unrest and an economic crisis.
Before the country heads to the polls, First Sentier Investors invited two of its US-based investment experts to discuss the potential impacts of the election.
John Ma, Head of Investments, North America, Unlisted Infrastructure and Jason Epstein, Senior Portfolio Manager, Co-Head of High Yield, from First Sentier Investments, shared their insights.
1. A ‘Blue Wave’ win could spark a progressive policy push
As polls are predicting a Democrat win is more likely, this outcome is mostly priced into markets already, Mr Epstein said. What’s more difficult to predict is the scale of such a win. If the Democrats gain a majority in the Senate, they will have more scope to make changes.
“A so-called Blue Wave, where Democrats take back the Senate, could lead to a more aggressive push of their policy priorities. Some of the policy areas already flagged in Biden’s campaign include tax rates, healthcare, infrastructure spending, climate change policy, education and housing.”
2. Stimulus funds will flow freely - regardless of the winner
It’s clear that boosting the flagging economy will be a priority for the new President – whoever it is.
Mr Epstein said, “There will be a tremendous level of fiscal and monetary stimulus, combined with the prospect of a new stimulus bill and the idea of a Fed ‘put’ for the foreseeable future.
“The real question is how sustainable that approach is. Will it continue to underpin markets, or is there a breaking point? There are also questions about if the US Dollar will retain its place as the leading reserve currency.”
3. China relations remain under pressure
In a break from past Democrat administrations, Biden has indicated he will maintain Trump’s tough stance on China.
“A tense relationship with China is likely to be the new normal, regardless of who’s President. Biden is looking to make the US competitive with China and to bring jobs back to US in areas such as automotive manufacturing. The goal is to have strong domestic production capabilities that reduce their reliance on China,” Mr Epstein said.
4. Infrastructure will remain a local affair
Mr Ma said it’s important to recognise that the infrastructure market is predominantly under state and municipal control, rather than federal.
“The White House has less direct ability to influence outcomes in the infrastructure sector. While funding can be allocated to the states at a national level, it’s the states and cities who mostly choose how to deploy the funding. As such, the election is unlikely to have a big impact on specific infrastructure projects.”
It is possible, however, that governments prioritise short-term job creation.
“In the wake of the 2008 recession, Federal stimulus funds were focused on ‘shovel-ready’ projects that would create jobs immediately. It was a missed opportunity for bigger, more ambitious projects. Hopefully we don’t see the same phenomenon play out this time,” Mr Ma said.
5. Democrats would give renewables a boost
One area of clear differentiation between Biden and Trump is the Democrats’ emphasis on renewable energy.
“The more progressive elements of the party put forward concepts like the Green New Deal during the primaries season, and this has informed Biden’s policies.
“It’s likely Biden would be a net positive for the renewable energy sector, which is already experiencing strong tailwinds. While power generation is controlled locally and regionally, a Democrat administration is likely to put an emphasis on clean energy through levers like tax credits,” Mr Ma said.
John Ma is Head of Investments, North America, Unlisted Infrastructure and Jason Epstein, is Senior Portfolio Manager, Co-Head of High Yield at First Sentier Investors, a sponsor of Firstlinks.
These views are general information and do not consider the circumstances of any individual.