Arguments over the vertical integration of wealth management across advice, administration and asset management continue as a political and economic issue. After poring over bank results recently and seeing how involved the banks are in the business of managing Australia’s investments, this article looks at the funds management landscape in Australia, and in particular the dominance by the largest players.
Influence of the major institutions
The wealth management businesses of the major banks (plus AMP) include funds management, life insurance, general insurance, investment administration platforms and financial advice. The businesses are attractive for the banks due to the government mandated growth from rising compulsory superannuation contributions and because wealth management earnings carry a low capital charge. This attraction has increased with the $19 billion of capital raised in 2015 to meet tougher capital adequacy rules.
Changes to capital requirements make funds management earnings more attractive and increase the cost of lending to business and home loans. When a bank makes a standard home loan with a 70% loan to value ratio (LVR), APRA requires that the bank holds approximately $2.25 in capital for every $100 lent. This rises to $5 for every $100 for a loan to a business due to a higher risk weighting. Mathematically, when a bank is required to quarantine more capital to conduct activities, their return on equity (ROE) declines. Faced with higher capital requirements from regulators globally, earnings from wealth management can boost the bank’s ROE.
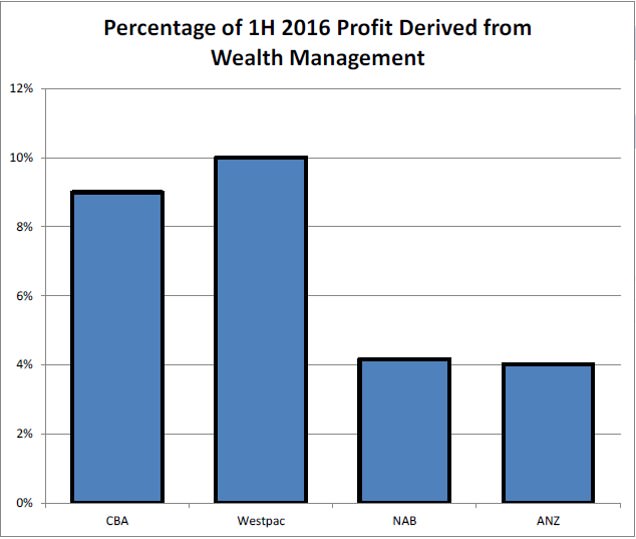
About 10% of bank profits come from wealth management
In the 2015 financial year, the four major trading banks in aggregate earned $30 billion, representing an increase of 5% on 2014. In 2015, approximately 10% of bank profits or $2.7 billion were attributable to wealth management, with CBA (Colonial First State) and Westpac (BT) gaining a higher percentage than the Melbourne-based banks. In the Aurora Dividend Income Fund, we have our exposure to wealth management indirectly via positions in the banks, rather than in listed wealth managers such as Perpetual or AMP. This results in buying $1 of wealth management earnings on a price to earnings (PE) of 13 times rather than 16 times!
Vertical integration clips the ticket at three stages
Essentially, the wealth management industry comprises a value chain of advice (financial advisers), portfolio administration (platforms) and manufacturing (funds management). The major financial institutions have captured a dominant market share in these three links via acquisitions and technology expenditure. From the below chart on the left, the four major banks plus AMP and IOOF have financial relationships with 60% of the financial planners in Australia. Their market share has been increasing with acquisitions (Count acquired by CBA for example) and heightened compliance requirements in favour of the large institutions over smaller practices.
Investment platforms are the ‘middle man’ in the process, connecting the fund manager to the adviser and providing administration services and tax reporting for a client’s portfolio of managed funds, shares and cash. Platforms generally charge around 0.3-0.6% of funds under management annually. Whilst this may not sound glamorous, it has been a lucrative path to capturing over 85% of this market.
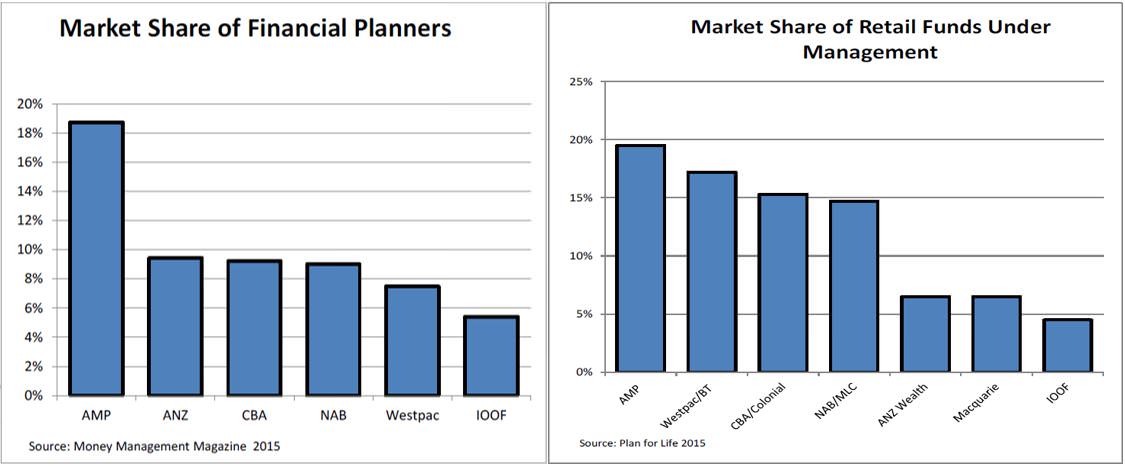
Finally, the major financial institutions have also been successful in actually managing the money. The above chart on the right demonstrates the dominance that the large institutions enjoy in ‘manufacturing’ the investment products or funds for sale to retail investors. Currently the major banks plus AMP manage almost 80% of the retail funds under management.
Negatives for the banks
Whilst this sounds like a solid way to supplement bank profits in an environment of relatively anaemic credit growth and rising bad debts, the ownership of wealth management businesses by the banks do pose some risks.
Aside from the volatility in investment returns, wealth management businesses have the potential to deliver adverse headlines. Over the last year, both CBA and Macquarie Bank have received ‘enforceable undertakings’ from ASIC and face political enquiries related to allegedly fraudulent behavior and bad financial advice from the banks financial planners.
Indeed, in 2015 CBA spent $522 million in advertising building its banking brands. A portion of the goodwill generated is no doubt dissipated by headlines detailing ASIC probes into the bank’s financial planning or insurance divisions. The banks are clearly concerned that negative activities occurring in wealth management do not spill over to damage their core banking brands that generate the bulk of their profits.
Our view as an investor and a boutique manager
The major financial players have not built these vertically integrated wealth platforms (advice, investment accounting and funds management) to see large amounts of value being ‘leaked’’ to service providers outside the network. This naturally creates strong incentives to recommend the house products over independent providers, or favour house products over external products with similar or even slightly superior characteristics.
As an investor in the major banks, we would prefer that they keep as much of the value in-house to boost payments to shareholders. However, as the fund manager of an independent boutique investment firm, I have a strong personal incentive to see funds being leaked out of the control of the major players.
Hugh Dive is Senior Portfolio Manager at Aurora Funds Management. This article is general information and does not address the personal circumstances of any individual.