Australia and the United States are similar in many ways. Both are former British colonies with relatively stable democracies, both have strong political, administrative, judicial and educational institutions, both have strong institutional protection of property rights and the rule of law, both have favourable demographics with relatively high immigration rates, and both have withstood invasions from foreigners (although indigenous natives in both countries would argue with this).
Remarkable long-term return similarities
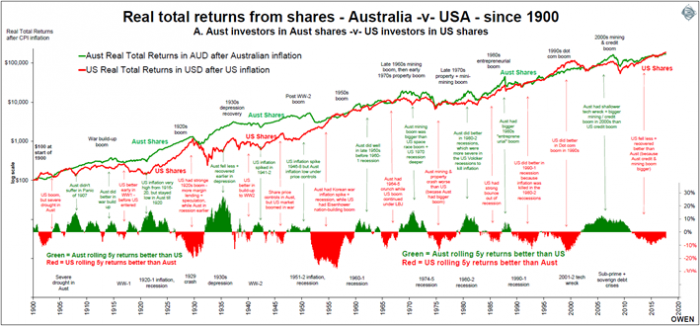
The stock markets in both countries have generated the same level of real total returns (including dividends, after inflation). Both have averaged 6.5% per year above inflation since 1900. US shares have returned 1% pa lower total returns, but has had 1% lower inflation, so the real total returns after inflation have been the same. The mix of capital growth and dividends is also different, with US shares paying lower dividends but enjoying higher capital growth as a result.
The chart shows real total return series for Australian shares (green line) and American shares (red) since 1900. Although both markets have generated the same returns overall and have broadly followed same boom and bust cycles, they take turns to have the bigger boom and then the bigger bust. The lower section shows the rolling 5-year difference between returns from the two markets. Green positive bars are when Australian shares are beating American shares, and red negative bars are when American shares are winning. The red negative bars in the lower right show that US shares are winning in the current cycle.
Click image to enlarge
Boom and bust cycles
The main reason US shares have beaten Australian shares in recent years is that the US had a milder 2003-2007 boom than we did, and so it had a milder sell-off (even though the trigger for the GFC was the US housing market and US bank shenanigans). Australia also had a credit bubble in 2003-2007 but we had a China commodities boom as well. We are still recovering from our bigger bust while US shares are leading the next boom, which will be known as the great 2010s smart phone boom.
This tit-for-tat game has been going on for more than a century. The US had a bigger 1920s boom and therefore a bigger 1929 crash and early 1930s bust. Australia had a bigger 1960s mining/aerospace boom and early 1970s property boom and we had a bigger 1973-4 bust. Australia had a bigger mid-1980s entrepreneurial boom and so had further to fall in the 1987 crash. The US had a bigger late-1990s ‘dot com’ boom and so had further to all in the 2001-2 ‘tech wreck’ bust.
The market with the bigger boom falls further in the bust that follows. The US is leading the current boom and US shares are more over-priced than Australian shares, so US shares will have further to fall in the next bust.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.