The wealth of Australia in the last official estimate by the ABS for FY2016 was $14.4 trillion, and net of foreign liabilities (equity and debt) was just over $11 trillion. This net wealth is split 83% household and 17% government.
Residential land and dwellings dominate wealth
It is our developed resources of land used for dwellings and commercial buildings, and the buildings and infrastructure on that land, that dominate with almost two-thirds of wealth. Interestingly, our natural resources of mining and timber account for a small 7% of the total wealth. Equipment and inventories add another 9% and intellectual property 2%. The balance of 15% is in the form of financial assets. The exhibits below tease out the composition.
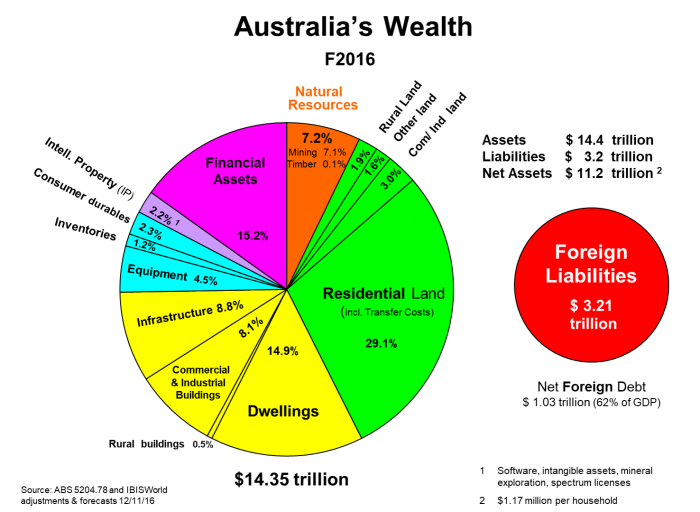
Australian wealth
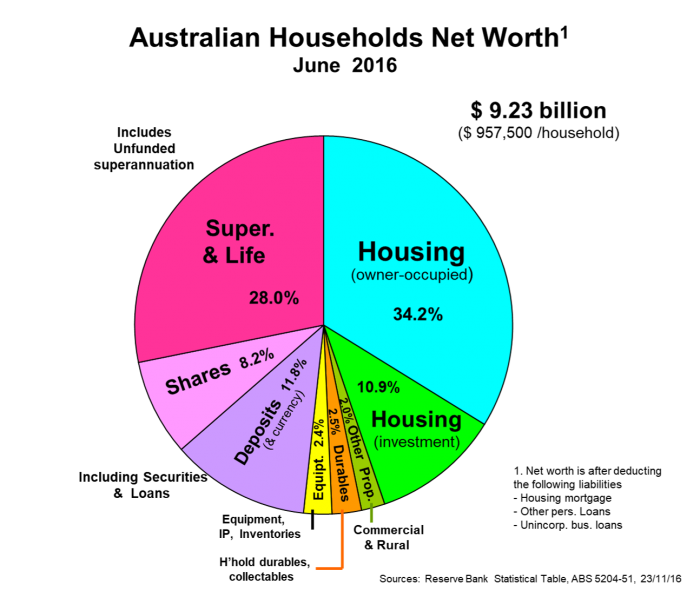
For households, average net worth sat at just under $1 million in FY2016, and will average $1 million by the end of 2017 calendar year. Thanks mainly to the rapid growth in superannuation, households are on the cusp of having financial assets at over half this average net worth, which is already a reality in the USA. Superannuation has accelerated the displacement of hard assets such as land, buildings, equipment and household durables such as vehicles, appliances and furniture.
The new wealth created every year is termed our gross domestic product (GDP), and it reached $1.7 trillion in calendar 2016, although we consume most of it in the form of consumable goods and services. We export around a fifth of it to balance our imports and invest around a quarter of the GDP in dwellings, buildings, equipment and intellectual property. Depreciation eats into such investment, new and old, but asset appreciation also takes place via land values and the growing value of businesses.
The exhibit below shows this new wealth creation in the year to March 2017.
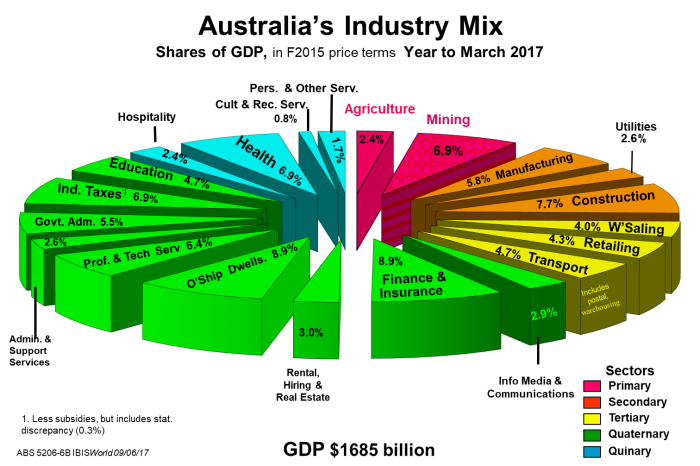
Touring the land beats the land itself
Gone are the days when most of our wealth was created on the land. Agriculture and Mining now account for less than 10% of our wealth each year. The value-added via processing is rightly credited to Manufacturing industry.
Ironically, more wealth is created these days by touring on the land (tourism by Australians and inbound tourists) at nearly $100 billion compared with Agriculture at a little over $70 billion.
Our secondary (industrial age) industries are a shadow of their former dominance. It has fallen from about 40% of GDP in the 1960s to 18% now. It is the quaternary (fourth) and quinary (fifth) service industries that are creating most of the wealth in our current Infotronics Age (1965-2040s). Health is now the nation’s largest industry when the health services, medical insurance, pharmaceutical manufacturing and pharmacists are taken into account.
Only manufacturing - under blow-torch pressure from mass-producers such as China, and a lack of uniqueness or economies-of-scale - has fallen in net new wealth creation. It is the service industries creating the vast bulk of new wealth.
How do the changes translate into jobs?
This is even more the case when it comes to jobs, as seen below. The goods sector (via only Construction) created 1 in 8 of the new jobs, but the goods sectors accounted for nearly all the jobs lost over the past 5 years.
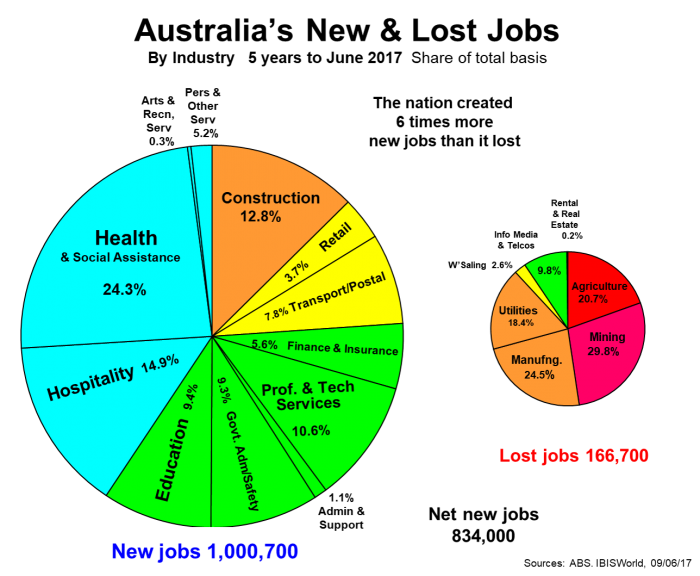
We are still creating new wealth, our net worth continues to grow and will pass $1 million per household as we enter 2018, and we are creating six times more jobs than we are losing over a 5-year period.
For all of the political shambles we put up with - worse in most other countries - our business sector continues to create this new wealth and jobs. Let’s thank the business sector for that.
Phil Ruthven is Founder of IBISWorld and is recognised as one of Australia’s foremost business strategists and futurists.