It’s coming to that time of year when equity market strategists and the financial media will start issuing their forecasts for the performance of the stock market in FY25. Airlie’s view is to ignore them. Their predictions (like most predictions) are usually wrong.
Consider the past few years. Had investors been presented with a list of all the challenges global markets could face over the past five years (in advance), many might have chosen to sit on the sidelines and reduce their exposure to equities.
The list below (while not exhaustive) is a reminder of some of these challenges:
- FY20 – COVID-19 pandemic shuts down many parts of the economy and sees cuts to interest rates globally.
- FY21 – COVID-19 crisis continues as states implement various degrees of lockdown. Similar disruptions globally morph into a supply-chain crisis.
- FY22 – Russia invades Ukraine and inflation fears emerge.
- FY23 – Central banks, including the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA), embark on an aggressive rate-tightening cycle.
- FY24 – Hamas and Israel conflict intensifies and inflation moderates but remains sticky and above central bank targets.
Despite all these events, global equity markets have risen. The S&P/ASX 200 Accumulation index (which includes dividends) has delivered a total return of 47% or 8% per annum [1].
In our view, the past five years have shown that buying and selling stocks based on a view of the market’s impending movements is a fool’s game.
In this article, I'll avoid predicting where the market is going to be in 12 months and instead focuses on three reasons for investors to be bullish on Australian equities in FY25 and three reasons to be bearish.
Bull case for Australian equities
1. Corporate balance sheets in good shape
Many Australian investors have lived in a period of declining and ultra-low interest rates. Before the RBA’s first interest-rate hike in May 2022, the public had not experienced an increase in interest rates since November 2010, and that cycle only saw the cash rate increase from 3% to 4.75%. To find a rate-hiking cycle of equivalent magnitude today, investors would have to go back more than 30 years.
The rise in interest rates over the last two years could be seen as a reminder for investors of the opportunity cost of capital and the value of conservative capital structures.
Our view is that when rates were low, debt was considered ‘free’ and helped prop up risky companies as investors chased greater returns in speculative companies, while other companies were encouraged to take on large amounts of debt to fund acquisitions and growth with no consequence of increasing financial risk. This era of ‘free money’ is over and balance sheets now matter.
And, corporate balance sheets across the ASX 200 in general look in good shape. The chart below shows the leverage ratio of the average industrial company in the ASX 200 today versus previous economic cycles. At less than 1.0x Net Debt/EBITDA, corporate balance sheets look healthy. They indicate that Australia’s largest companies could be well placed to handle any adverse bumps the economic cycle, competitors or internal issues may throw at them.
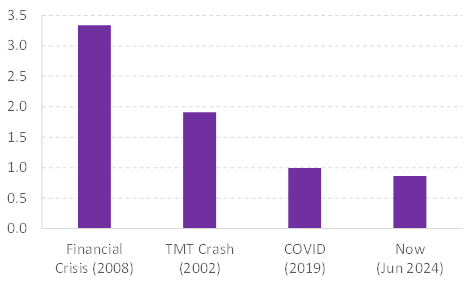
Source: MST Financial
2. Domestic profit pools often supported by a handful of players
In contrast to other global markets, the size of Australia’s population and its distance from the rest of the world has resulted in several domestic industry oligopolies with substantial barriers to entry. The smaller population in particular means industry profit pools often cannot support a third or fourth entrant. Some notable oligopolies include:
- The grocery sector, where two major supermarket chains account for about 65% of the market. Contrast this with the UK, where the top two grocers account for 43% of the market, and the US, where the four largest supermarket chains have a combined share of 34% [2].
- The airline sector, where our national carrier, Qantas Group (ASX:QAN) (including Jetstar), has a 62% share of domestic air travel [3]. This has possibly been enhanced following news that recent market airline entrant Bonza has gone into voluntary administration.
- The banking sector, where the four major banks account for over 70% of the home-loan market in Australia [4].
This concentration can potentially be a positive for investors in large-cap Australian equities in that they can put their money behind industry-leading companies that have a low risk of being disrupted by competition. Historically these businesses tend to have a track record of stable returns and market-share gains versus their smaller rivals.
3. Australia’s place in the world only getting better
When we look through a global lens, Australia has a lot going for it – a beautiful place to live, a safe, strong rule of law, and high-quality education.
Even the much-grumbled-about house prices still mean some people can buy a house and not a shoebox apartment in capital cities. Australia continues to attract people and capital, both providing a long-term tailwind for the economy.
This is best reflected in Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) data (see charts below) showing that compared to pre-COVID-19, an additional 1.35 million people are employed in the country (a 10% increase) [5]. This compares favourably to other developed economies like the UK, where the total labour force has increased by just 1% over the same period [6].
The growth in employed persons translates directly into spending and this has provided a tailwind for Australia’s consumer-facing sectors despite cost-of-living pressures. Total retail sales have increased by 30% over the last five years [7]. According to Airlie, the looming tax cuts for individual workers in Australia in FY25 are likely to bolster retail spending and support those companies relying on the domestic consumer.
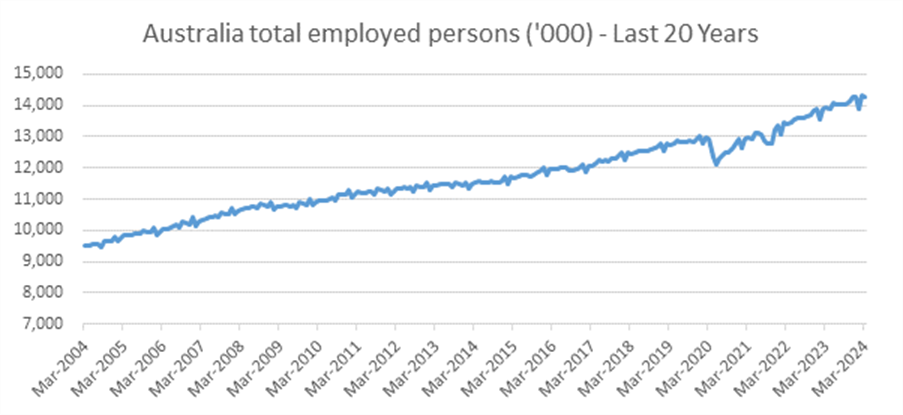
Source: ABS
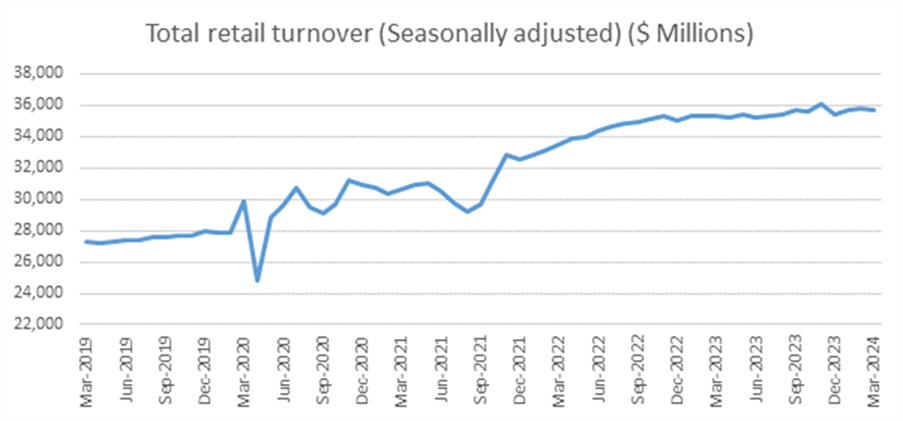
Source: ABS
The bear case for Australian equities
1. Valuations for publicly listed companies have re-rated higher
In our view, higher company valuations reduce the prospect of near-term upside for investors. The rally in equity markets over the past 12 months reflects a level of optimism about ‘peak’ interest rates and the need to see further evidence for the market to continue re-rating higher.
The ASX 200 is currently trading above its long-term median Price Earnings multiple of 14.6 times [8]. This suggests that companies in general are valued positively and it’s clearly not the ‘cheap’ market witnessed in March 2020 and July 2022 (see chart below).
Within this aggregate, however, there may still be individual businesses that look attractive, and investors could have to dig for mispriced opportunities.
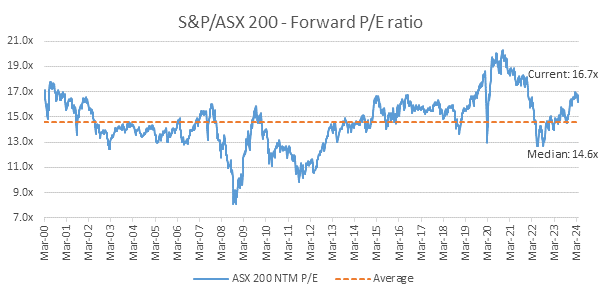
Source: FactSet
2. High cost of living is gaining political attention
As mentioned, concentrated domestic oligopolies can potentially be good for investors. But in an environment where consumers are under pressure, some oligopolies could come under threat from politicians.
For example, there have been recent accusations of profiteering levelled at the domestic supermarkets. It would not be a surprise if the government turned its attention to other concentrated sectors, so as to be seen to be tackling the cost-of-living crisis. Even if there is no immediate change to regulation of these sectors, Airlie has seen this kind of political pressure can hurt returns as companies respond by pulling back on pricing power.
3. Sticky inflation
Interest rates may well remain elevated, or worse – they may even increase in the coming year. The optimism embedded in sharemarket valuations is predicated on a narrative of peak rates. Any evidence of inflation persisting above the RBA’s target range of 2-3% may lead investors to reprice securities lower to reflect a higher cost of capital.
To date, the Australian economy has been strong with elevated migration and record-low unemployment supporting demand. And on the supply side, the cost of the energy transition and the restructuring of global trade (away from China) could continue to act as inflationary forces that may well be structural.
Conclusion
While I don't have a crystal ball for what 2025 will have in store for the Australian sharemarket, investing in companies with strong balance sheets, and that are market leaders with pricing power, should help drive returns over the long term. Attempting to profit from a view of the market’s ups and downs in what has otherwise been an upward journey is likely to detract from returns rather than add to them.
--------------------------------
[1] FactSet – ASX 200 total return 5 years to 3 May 2024
[2] Independent Review of the Food and Grocery Code of Conduct 2023-24 – Consultation Paper (February 2024)
[3] ACCC Report – Airline Competition in Australia (March 2023)
[4] Commonwealth Bank of Australia 1H24 Results Presentation
[5] ABS 6202 – Labour Force, Australia (Total employed persons – original) March 2024
[6] Office for National Statistics – Employment in the UK
[7] ABS 8501 – Retail Trade, Australia (Retail Turnover by Industry Group) March 2024
[8] FactSet at 10 May 2024
Vinay Ranjan is a Senior Equities Analyst at Magellan-owned, Airlie Funds Management. Magellan Asset Management is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article has been prepared for general information purposes only and must not be construed as investment advice or as an investment recommendation. This material does not consider your investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs.
For more articles and papers from Magellan, please click here.