China has proved a powerful partner in supporting the growth of Australian businesses, aided by our geographic proximity, political stability and governance-led business practices. We have a long and reliable history of high quality, reasonable cost goods and services manufacture which has led us to be ‘first-hand receivers’ of China’s attention when it comes to meeting the demands of its growing population.
Australian business sectors that have to date benefited from China’s attention have included the mining and resources sector, the tourism sector and most recently, those involved with the manufacture of health supplements and vitamins.
Changing Chinese demographics
Like many countries, China has an ageing population. According to an article, ‘How can China Care for its Ageing Population?’ distributed by the World Economic Forum, its population aged 65+ is forecast to grow to 167 million by 2020, accounting for 11.5% of the population or nearly double what it was in 1995. In addition, studies undertaken by the Wharton Business School state that China is now also facing an epidemic of chronic diseases and lifestyle issues (such as hypertension, stroke, diabetes and heart disease) that were typically associated with the ‘West’, mostly due to economic changes such as a growing middle class, rising GDP per capita and rising disposable income.
The cost of China’s evolving health and demographic trends has been enormous. It has been estimated that the country’s annual expenditure on health will grow at an average rate of 11.8% a year from 2014-2018, reaching a total spend of $892 billion by 2018. Yet according to a recent research paper issued by Deloitte, China’s healthcare spending, estimated at 5.4% of GDP in 2013, is still lower than other OECD countries, as shown in the chart below.
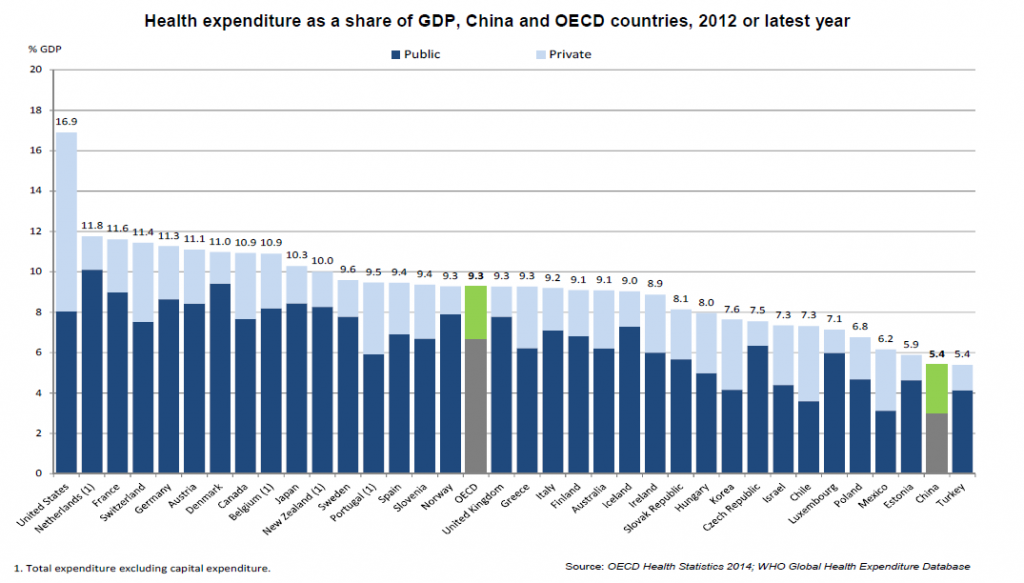
Growth and competition in healthcare
In response to the rising cost and need for healthcare services, the Chinese government recently announced several initiatives aimed at promoting growth and development in the health sector. According to research by Deloitte, ‘Projects that meet strict operational guidelines are expected to receive full government support, especially around land transfer, preferential financial and tax policies and related subsidies’. The research states that private and wholly owned foreign hospitals account for almost half of China’s total number of health care facilities and growth from this sector in China will bring the benefit of ‘leading medical technologies, advanced management, clinical practices and service models’. Additional service providers are considered good for competition, potentially leading to better pricing and satisfaction levels for patients. It may also help with raising the profile and use of private health insurance in the country, as commercial insurers develop plans to help consumers meet the rising cost of hospital care.
Of course, growth in the service and provision of healthcare services in the hospital and insurance areas in China will also promote growth in the supply chain such as in aged care, medical tourism and medical devices.
Australia’s recently agreed Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with China promises unprecedented access for our healthcare providers to expand their services into China. The benefits of the FTA to the sector were summarised in a recent article published in Business Spectator titled ‘The China FTA is just the tonic for Australia’s healthcare operators’, by Kim O’Connell and Suzy Madar.
The article outlined the key benefits as:
- For hospital providers, China now offers Australian businesses the opportunity to establish wholly foreign owned hospitals.
- Medical and dental service suppliers can also establish Australian majority-owned joint venture hospitals and clinics with Chinese partners, provided the majority of medical professionals are Chinese.
- In the aged care space, Australian providers may now establish wholly foreign-owned aged care facilities with tax incentives and fee waivers.
- For R&D service providers, Australian companies looking to conduct R&D in China will be permitted both to carry out and offer R&D services through Australian-owned subsidiaries based in China.
Those ASX listed companies set to benefit from the growth and development of the healthcare service sector in China and the introduction of the FTA include Cochlear Limited (COH), CSL Limited (CSL) and Ramsay Healthcare Limited (RHC).
Sebastian Evans is Chief Investment Officer and Managing Director of NAOS Asset Management. This information is general only and does not take into consideration the investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs of any reader. Readers should consider consulting a financial adviser before making any investment decision.