Earlier in 2021, energy markets were pre-occupied by the price of crude oil and what the OPEC + (Russia) cartel might do in terms of future production. The pandemic placed pressure on OPEC’s meeting schedules but this masked the real developing energy problem, especially in Europe: the looming shortage of natural gas.
This is now headline-grabbing, with the UK’s wholesale energy markets reaching record highs in recent weeks. Half of the UK’s electricity is generated in gas-fired plants.
But ageing nuclear power plants have been forced to undertake unplanned outages for maintenance and less windy conditions have increased demand for gas in the UK. A fire shutdown a high-voltage power cable bringing electricity from predominantly nuclear-powered France, further increasing demand for gas power.
At the same time, a very cold 2020-21 winter depleted gas stockpiles. The UK reportedly only has about seven days’ supply of gas in storage facilities. Overall, gas storage levels in Europe are very low at 70%, barely covering two months of consumption. In the previous two years gas storage levels have been over 90%. Gas storage capacity in itself may not have directly driven gas prices, but it is likely to be a factor in the overall energy equation.
There are 36 LNG import terminals across Europe with many of the largest ones in Spain. Another 27 import terminals are under construction.
Problems with gas supply
Europe’s gas supply has traditionally come from three sources:
- Imports from Russia via pipeline (Gazprom)
- Imports from Algeria via pipelines (State-owned Sonatrach)
- Indigenous Norwegian production, mainly from offshore (Equinor)
For whatever reasons, Russia is not increasing its gas supply to Western Europe. In Algeria, a breakdown in diplomatic relations with Morocco threatened the flow of gas in one of the two pipelines to Europe. Production is stagnating and a rapid domestic gas consumption growth increases pressure on export potential.
Norway provides about 25% of European gas demand. But Norway’s gas production is falling with easily-accessed gas fields being exhausted and less investment in the sector spurned by domestic energy policy that favours renewables.
Indeed, Europe (and the World) is experiencing declining investment in fossil fuels at the same time as there is increased dependency on intermittent sources of energy such as solar and wind. Magnifying Europe’s gas supply and demand equation, the UK had one of its least-windy summers since 1961, meaning wind power has been low.
High energy costs hit businesses
UK and European energy suppliers who have to buy gas at very high prices will suffer from shrinking margins. Many smaller operators have already collapsed. Government intervention is likely to offer some protection for consumers who are facing increased energy costs. Business, particularly heavy industry, will also face higher energy costs.
|
How much have European energy prices increased?
|
|
Source
|
Indicator
|
Q3-20
|
Q2-21E
|
YOY Change
|
|
Gas
|
Dutch TTF (€/MWh)
|
8.20
|
47.3
|
477%
|
|
Coal
|
Rotterdam($/tonne)
|
50.70
|
147.0
|
190%
|
|
Power
|
Germany baseload (€/MWh)
|
35.90
|
100.0
|
179%
|
|
CO2
|
EU ETS (€/tonne)
|
27.36
|
56.5
|
107%
|
Source: RC Global Funds Management
While the gas supply crunch is particularly acute in Europe with the TTF (Dutch import) benchmark also at record highs, there is strong demand and limited new supply globally.
The (global) gas grab
Industrial activity has rebounded as the world starts to emerge from the pandemic, with the global energy demand set to increase by some 4% in 2021. It is anticipated that the global gas demand will correspondingly increase, in part to meet this demand but also to replenish gas supplies before the onset of the next northern winter.
In Asia, which relies heavily on LNG imports, prices are also just shy of the record reached in January 2021. The JKM (Japan and Korea import benchmark) spot price may reach a fresh record again this coming (northern) winter. Currently there are many LNG carriers lining up to load in Qatar and Australia, the world’s two largest LNG exporters. Europe is fighting for every LNG cargo with equally-hungry Asian buyers.
Investment winners and losers
As with any supply/demand ‘crunch’ there are winners and losers. High energy-user industries such as those involved in the production of fertilizers and by extension, some in the food and drinks industries, will also face headwinds.
Some of the biggest winners are in fact those that don’t even produce any natural gas. They are the utilities that generate electric power using either hydro or nuclear, both of which are characterised by high upfront capital costs but low on-going operating costs. They benefit from higher power prices and have fairly fixed operating costs.
Examples of such companies include BKW Switzerland and Verbund Austria, which are mainly generating energy using hydropower taking advantage of the mountainous geography of these two countries.
LNG shipping companies who transport LNG based on spot prices are of course clear winners in the 2021 Energy Crunch. Companies like Nippon Yusen and Mitsui OSK are prime examples.
But the point is that a subtle shift in the circumstance could make picking winners and losers difficult. Remember this Energy Crunch had its genesis hidden behind an oil price headline. If some of the factors had been different – wind in the UK during the summer of 2021 was at historic averages, Russia did open the gas tap a little more, there was no pandemic – the winners and losers from a (share) investment perspective might have been different.
In any event, a particular investment approach, such as only investing in renewable energy or within certain ESG parameters, could influence returns.
A broader view of energy
Understanding the energy value chain helps a more informed view about potential energy investments. Sure, diversification is a well-trodden path but with energy it's more than just the value chain in a linear sense.
One of the key factors is a big investment universe for companies operating in essential industries. There is a much better investment selection potential when the interconnection of both the infrastructure and energy segments are considered. After all, infrastructure needs an energy source to work and energy needs infrastructure to allow it to be produced, converted, stored, distributed, and transmitted.
A holistic value chain reveals the broad investment universe for essential industries in the (related) infrastructure and energy business segments.
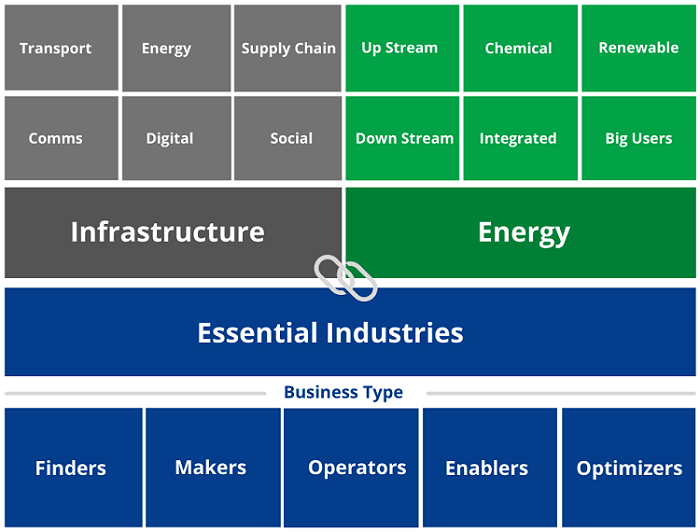
Source: RC Global Funds Management
This wider lens of viewing energy investment opportunity means investors are automatically tapping into global megatrends such as urbanisation, digital transformation and of course energy transformation. Importantly, potential investment is being done at an essential economic layer that is supported by both private and public spending.
Roy Chen is the Founder, CIO and MD of RC Global Funds Management The material in this article is general information only and does not consider any individual’s investment objectives.