In Part 1, we looked at the record of Labor versus Liberal governments in running surpluses or deficits. Both sides have run very few government surpluses during their respective years since Federation.
In Part 2, we looked at the record of Labor versus Liberal governments in running up (and occasionally paying off) government debt. We saw that the current level of Commonwealth government debt (relative to national income) is modest, and is lower than almost any other time since World War 1. It is also lower than almost all other countries today.
Part 3 looks at what government deficits mean for share markets.
As investors we are not concerned here with debates about whether deficits are inherently good or bad, nor about inter-generational equity between current and future taxpayers, etc. We are primarily interested in the returns from shares in different fiscal conditions.
Chart 1 shows the annual Federal government balance plotted against real total returns from shares (including re-invested dividends and after CPI inflation). These are for years ending in June so they line up with the government’s fiscal years. Labor government years are shown in red and right-leaning government years (including Liberal) are shown in blue.
Chart 1: Federal government surplus/deficit versus real total returns from shares since Federation
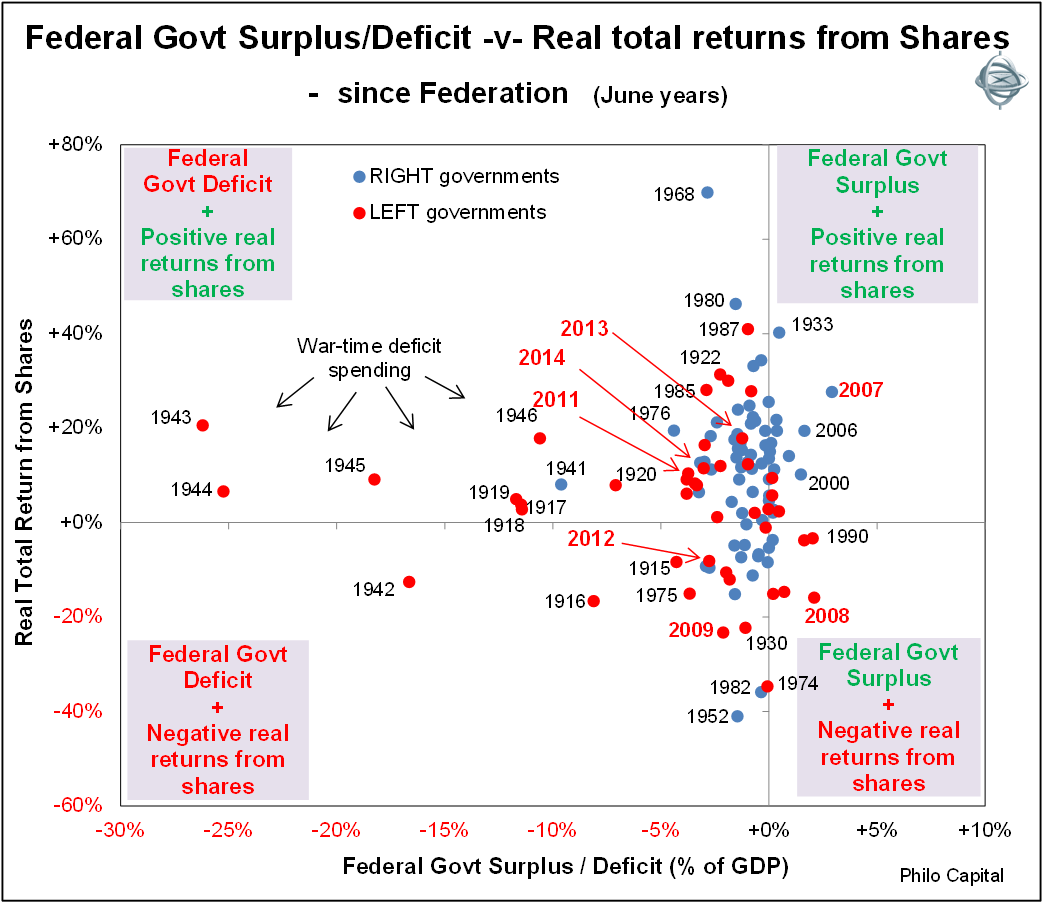
Clearly the war-time years at the left of the chart dominate the overall picture, with very large deficits but also good stock market returns in most years (although returns during World War 2 were somewhat affected by war-time limits on share price movements). World War 2 was particularly good for business in Australia, despite the government’s measures to control prices and limit profiteering. Chart 2 shows the same story but for post-war years only.
Chart 2: Federal government surplus/deficit -v- real total returns from shares post 1946
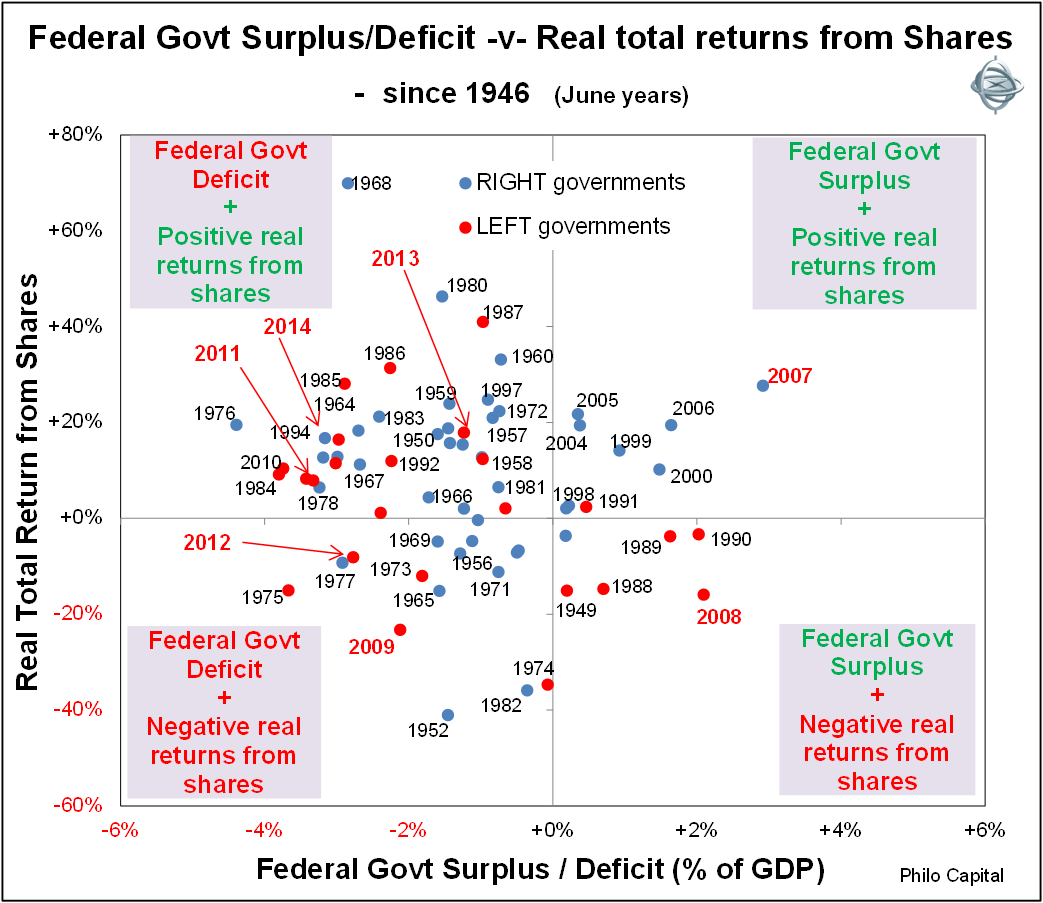
Deficits are good for stock markets
There has been a mildly negative correlation or inverse relationship between government balances and stock market returns. Most of the high return years from shares were government deficit years (top left section). This includes 2011 and 2013 and the likely result in 2014 (remember all years are June years in this paper).
Deficits are generally good for shareholders and surpluses are generally bad for shareholders. In the post-war era the median real total return from shares was 10.8% pa in the deficit years but only 2.4% pa in the surplus years, which is a very significant difference. This is shown in Chart 3.
Chart 3: Real returns from shares -v- Government surplus/deficit - post-1946
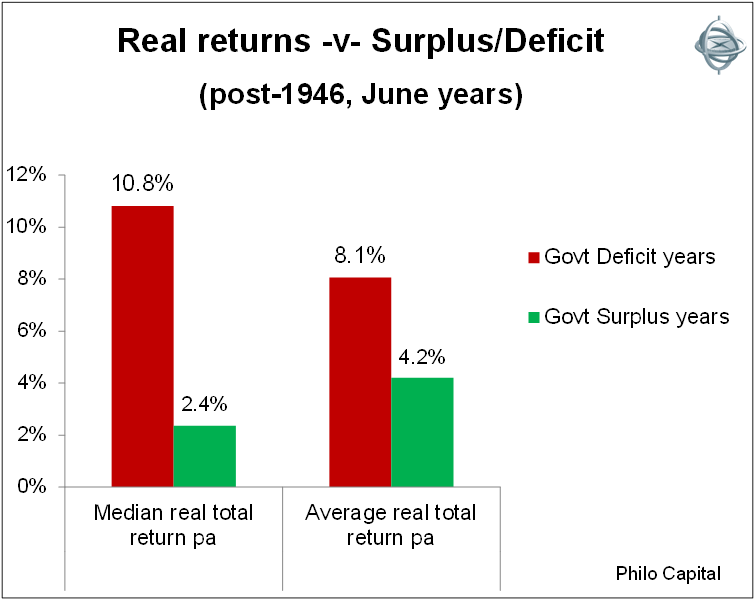
There are two main reasons for this. The first is that deficits come about by governments spending more money (and/or taxing less), and much of the additional cash ends up in company coffers, either directly via contracting to the government, or indirectly via household spending.
The second reason is one of timing. Deficits tend to be high in mid-late recessions (when tax revenues are down and welfare spending is up), and this is when shares generally do best, rebounding out of the middle of recessions. This was the case in 1954, 1972, 1983, 1992 and 2010 (and in the pre-war years: 1922, 1923 and 1932).
Tax revenues and welfare payments tend to lag economic activity, both on the way into recessions and in the recoveries on the way out. On the other hand, stock markets tend to lead economic activity. As a result of these leads and lags, stock markets tend to do well in government deficit years, and tend to do poorly in government surplus years.
There have been very few years when government surpluses accompanied negative returns from shares (bottom right section). The most obvious instance was 2008, when tax revenues from the boom were still rolling in but shares were already falling in the GFC.
Some conclusions
History provides useful lessons, and some conclusions are:
- Government deficit years have generally been good years for stock market returns. 2013-2014 will be a big deficit year and shares are heading for another good year to June 2014.
- Government surpluses have generally been bad for shareholders, with significantly lower returns from shares compared to returns in deficit years.
- The differences in returns between surplus and deficit years have been large and significant, regardless of which side of politics was in power at the time.
Ashley Owen is Joint CEO of Philo Capital Advisers and a director and adviser to the Third Link Growth Fund.