[Editor: the following is an extract from Bell Potter's latest quarterly report on the latest trends in LICs and LITs.]
Paying for the beta
The emergence of trading discounts amongst closed-ended funds has become a challenge for investors and managers alike, with the combination of market rallies and interest rate volatility fueling the growth of trading discounts to historic wide levels for many Listed Investment Companies (LICs). Whilst trading activity for LICs have been volatile, investors look to the relationship between returns from the LIC and the benchmark in determining the dislocation from NTA.
The relationship between LIC and Listed Investment Trust (LIT) returns and the market can be captured through ‘beta’, being a useful measure in understanding the riskiness of an investment. A beta of 1 reflects returns which are just as volatile as the market, with a value greater than 1 indicating greater volatility relative to the market portfolio. The relationship between LIC/LIT beta and its corresponding trading premium or discount over the last three years, is depicted in Figure 1, noting many domestic listed strategies exhibit risk-return characteristics close to their respective benchmarks.
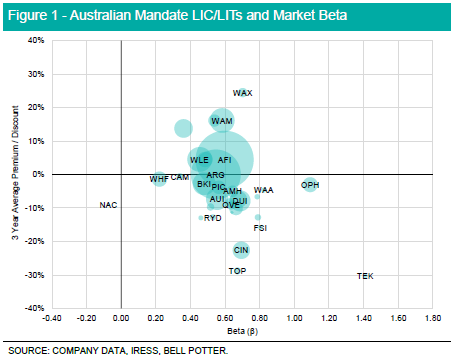
Amongst LICs with a domestic equity mandate, investors continue to preference funds with a benchmark like risk return relationship, highlighted by the majority of LICs capturing a market beta of between 0.5 to 0.8, with larger market capitalisation listed products trading near NTA. Smaller and more concentrated portfolios demonstrate dislocations from the market beta and NTA. This is headlined by the Australian Foundation Investment Company (AFI) and Argo Investments (ARG) which report a 3-year average beta of ~0.6, signifying a reduction in market risk compared to their respective benchmarks.
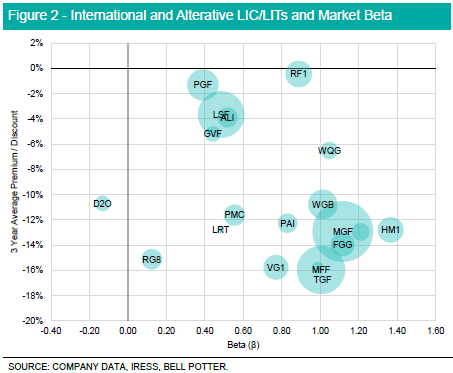
A similar relationship can be inferred amongst international and alternative mandated listed closed ended funds, with the average trading discount for LIC/ LITs closing as beta rises towards 1. Most listed products with this mandate trade on a beta of less than 1, reflecting a return profile which is less volatile than the underlying index. Divergence from NTA is more prevalent in listed products with international and alternative mandates, with markets unable to close trading discounts irrespective of historical return performance. The Regal Investment Fund (RF1) best captures market volatility whilst trading near NTA, reflected by an average beta of 0.89 and underpinned by strong performance in the LITs small company and global alpha strategies over the last 12 months.
The relationship between historical market discounts and beta indicates markets are better able to price index replicating strategies, with trading discounts becoming the result of divergence from the market portfolio. This relationship is best demonstrated with Australian equity mandated LIC/LITs, whilst International and Alternative mandates have less of a defined relationship. Outside of this the flow of additional capital towards exchange traded funds (or ‘ETFs’) has coincided with the recent emergence of trading discounts, with the sector reporting a FUM CAGR of circa 35%. Whist ETFs remain a popular alternative in capturing market returns, similar exposure exists in the LIC/LIT sector given multiple products hold broad market mandates, whilst exhibiting risk-return characteristics similar to the market portfolio, notwithstanding the impact of trading discounts, dividends and manager risk in overall returns.
It's all the same to me
Diversification is key in looking at LICs as investors want to minimize the degree of correlation in returns between assets in order to reduce overall portfolio volatility. Correlation is the degree in which two assets move together, captured by a value between -1 and 1. The higher the correlation between two assets, the closer they move in line with each other, with a value of 1 capturing perfect positive correlation, and a value of -1 capturing perfect negative correlation. In assessing the LIC/LIT market, assets which report a high correlation offer lower diversification benefits when held together in a portfolio, compared to assets which exhibit lower correlation.
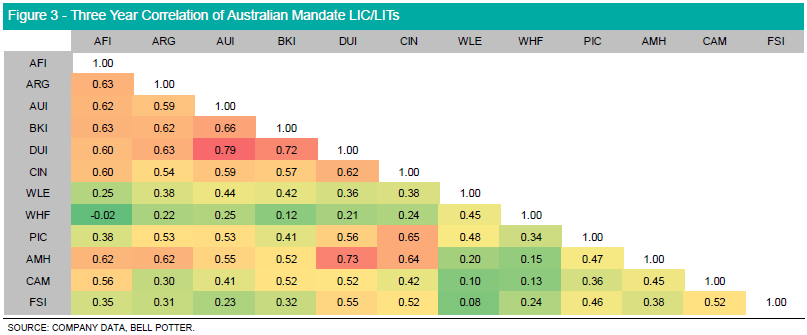
Amongst LIC/LITs with Australian equity mandates, Whitefield Industrials (WHF), Clime Capital (CAM) and Flagship Investments (FSI) exhibit a weak positive correlation against other listed products. The strongest positive correlation is held between Australian United Investment (AUI) and Diversified United Investment (DUI) given both companies share similar investment philosophies. Furthermore, LICs which hold a large cap only mandate report a strong positive correlation given there is often high overlap between underlying portfolio investments.
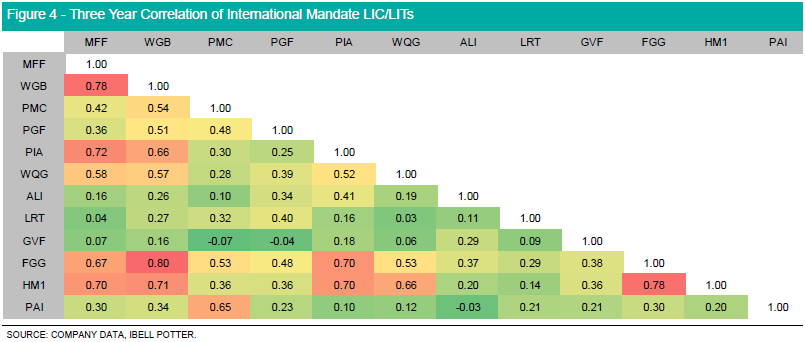
Looking at LIC/LITs with International equity mandates, the Global Value Fund (GVF) exhibits low historical correlation, given returns are driven by the managers discount capture strategy. Together with GVF, both Argo Infrastructure Limited (ALI) and Lowell Resources Trust (LRT) report a low correlation with their peers given their sector specific exposures. Contrastingly, both MFF Capital (MFF) and WAM Global (WGB) demonstrate a return high correlation given both LICs hold similar thematic and geographic allocations in their respective portfolios.
Capital raisings
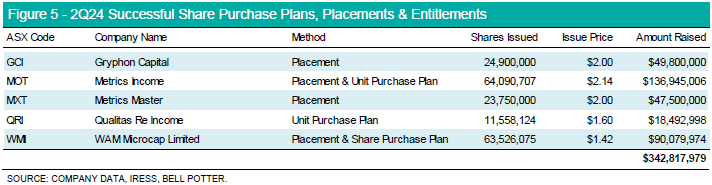
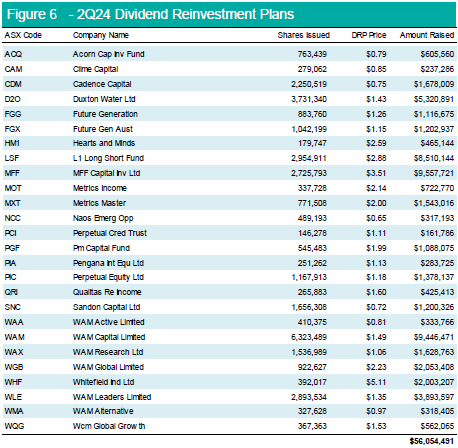
Strong market conditions provided a backdrop for LICs and LITs to raise incremental capital. A total of $398.87m was raised via the secondary market through Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRPs), Stock Options and Placements.
The majority of additional capital stemmed from fixed income LIT managers on the back of stronger demand from the market, given LITs under this mandate trade at a weighted average premium of 1.48% versus the sector at a 7.33% discount. Managers have taken the opportunity to offer the ability to subscribe to additional units in the trust at NTA, allowing investors to capture value during a period of trading at a premium to NAV. The increased appetite for alternative income strategies comes during an elevated interest rate environment, coupled with shifting appetite from traditional lenders in participating in commercial lending.
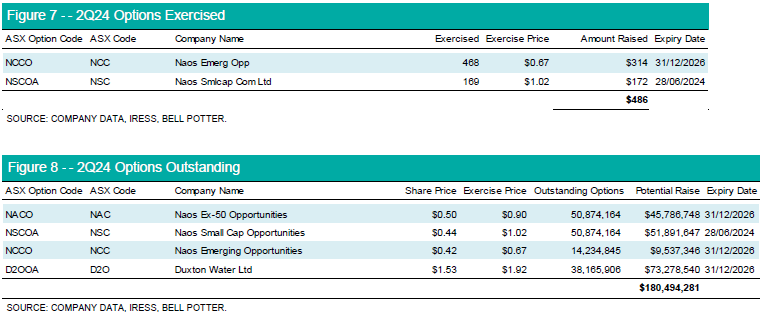
Option exercises were a negligible source of additional capital with most trading deeply out of the money at circa 20-50%.
Kion Sapountzis is an Investment Analyst at Bell Potter Securities. This information contains general information only and has been prepared without taking into account your objectives, financial situation or needs.