Time travel is a skill that would dramatically transform the world of the investor. Sadly, despite all the technological advances of the past two decades, the ability to go back or forward in time remains the realm of science fiction novels, not a killer app on an investor’s smartphone. While time travel may still be the domain of TV and film producers, the passage of time is a real-world test for investment ideas even if - as we are constantly reminded - history is not a great predictor of future returns.
What has changed over 20 years?
Twenty years ago, Australia was a country of 18 million people with a median age of 37 and the median weekly household income was $637 while the cash rate was set at 7.5%. The fledgling superannuation system had accumulated assets of $262 billion some four years after the super guarantee contribution had been introduced.
In 1996 a new, more modest undertaking was getting started - it was the year Vanguard established its Australian business which was its first outside the US. It seems an appropriate time to look back and see how the underlying investment principles that Vanguard has used in guidance to clients has stood up to the test of two decades.
The market has changed markedly. Of the top 10 companies by market capitalisation on the Australian share market in 1996, half have either dropped out of the top 10 or are no longer on the ASX.
With help from actuarial firm Rice Warner, we decided to look at the past 20 years through the time capsule of three different investors in 1996 – a 40-year-old, a 20-year-old and a newborn baby – and test how our investment principles have stood up to 20 years of significant geo-political shocks, stunning market rises and dramatic declines that included a global financial crisis.

All our investment strategies are underpinned by four core principles:
- Goals: Create clear and appropriate investment goals
- Balance: Develop a suitable asset allocation using broadly diversified funds
- Cost: Use low-cost, transparent investment options
- Discipline: Keep perspective and long-term discipline
Outcomes for our three investors over two decades
One of the first lessons is that investors have been rewarded for taking extra risk.
An investor who invested $10,000 at the start of 1996 in cash would have seen the nominal value grow to $26,800. Someone who had invested in the Australian sharemarket index would have seen the portfolio value grow to $51,400. The US sharemarket index was just slightly behind at $48,100 while Australian bonds grew to $37,600.
For our three investors, Rice Warner was asked to model the superannuation outcomes. Remember back in 1996, super was really just getting started, so our 40-year-old did not get the benefit of a full career under the super guarantee nor the higher rate we have today.
The growth in the super system has clearly been one of the major developments in the Australian financial landscape in the past 20 years with it now being the second largest financial asset in average Australian households and the system growing into a savings pool of more than $2 trillion.
Our 40-year-old in 1996 is now turning 60 in 2016 and with retirement firmly in sight, Rice Warner project their super balance at retirement (assuming compulsory Superannuation Guarantee only contributions, average wages and a 7.5% gross return on investments) to be $217,000 in today’s dollars. That is projected to last until they are 74-years-old.
For the person turning 20 in 1996, and effectively just starting out in their working life, who is now 40 in 2016, the projected retirement balance is $395,000 when they reach retirement age. This money is expected to last until they are 83-years-old.
For the baby in our investor trio who is now 20, the projected super account balance accumulated during their working life is $456,000 – more than double what the 40-year-old is likely to get. It should last until they are 87.
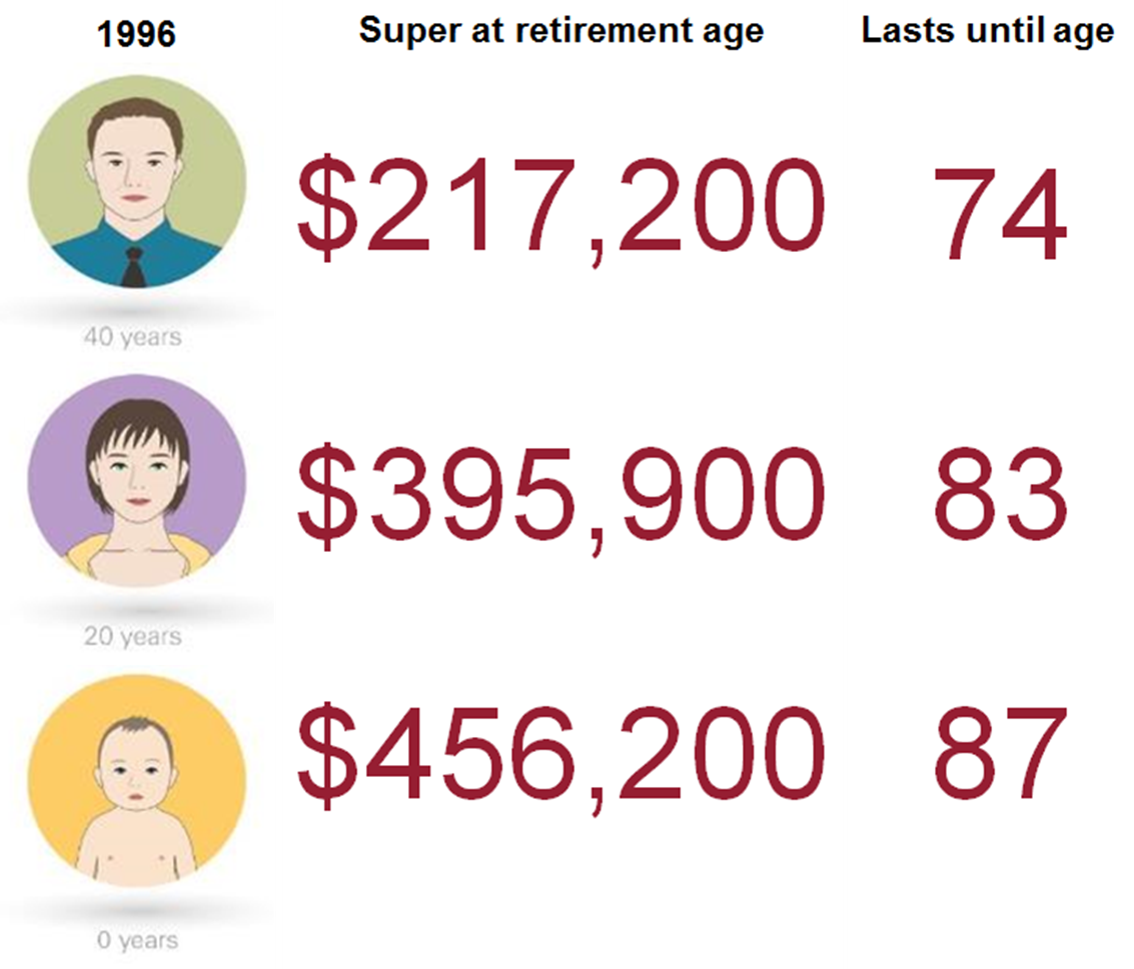
Source: Rice Warner. Assumes default super with no additional concessional contributions.
Based on the ASFA comfortable retirement standard, the baby of 1996 could reasonably expect her super to last 13 years longer than their older baby boomer counterpart.
Higher contribution rates and a long-time period to allow compounding to work is driving these outcomes but it is interesting to reflect that even after more than 20 years, our super system is not yet at maturity. The challenge remains for those in the older age bracket to be able to contribute enough to fund their retirement lifestyle.
Robin Bowerman is Principal, Market Strategy and Communications at Vanguard Australia. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.