For those believing the price you pay for an investment is an important determinant of future returns, life isn’t comfortable.
Momentum and stories rule as ever more capital seeks to squeeze through the eye of the needle. As Robert Armstrong detailed in a recent Financial Times article, recent months have seen an alarming narrowing in equity market returns.
“All of the gains in the market - and more – are from companies touched by AI. The S&P 500 as a whole is up more than 4 per cent. The non-AI 484 is down 2 per cent.” The top 10% of companies in the US now represent the highest proportion of market value in the index since the 1930s.”
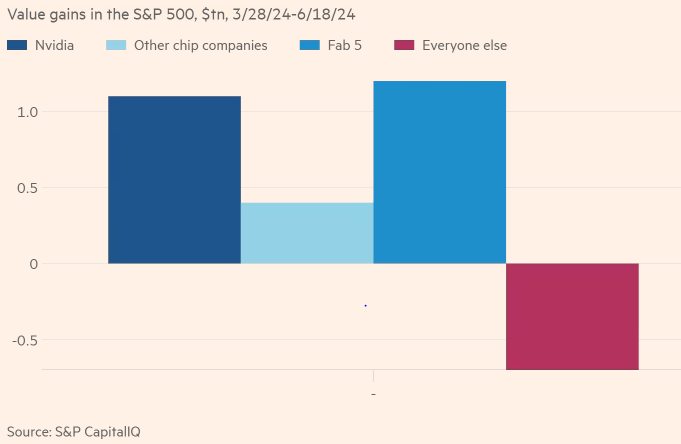
Source: FT
Narrowing stock markets are normally a bad sign. For those believing these valuations will be justified by future profits, they must necessarily be associated with narrower economies and/or increasing profit margins from already very high levels (which means a lower share for wages).
The narrowing of markets in the US has largely been due to AI and tech mania taking hold in the past year. In Australia, the process has been more gradual since the savaging of large resource companies in the 2014-2016 period.
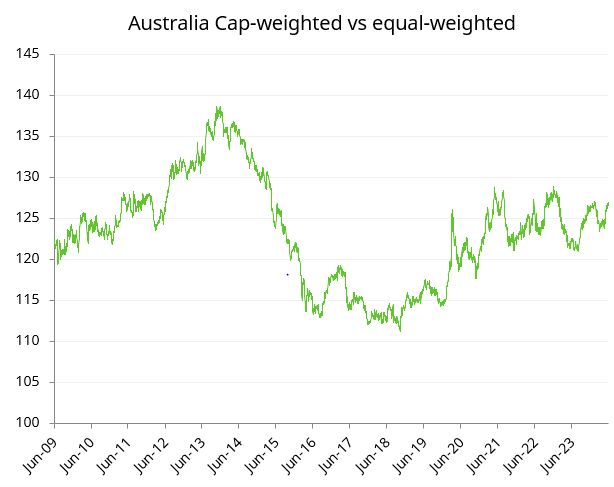
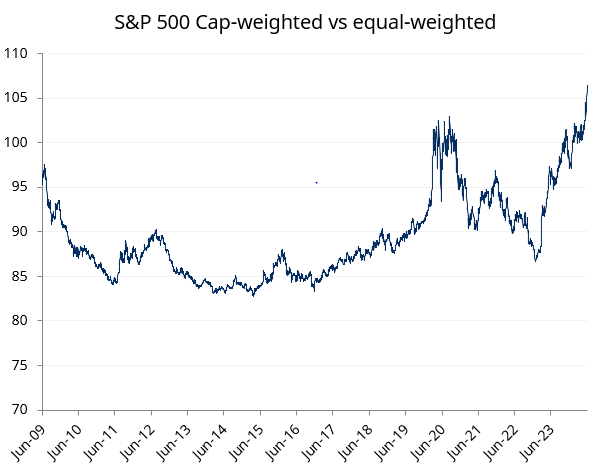
Source: Schroders, Datastream
Determining the reasons for this collapsing breadth is tricky. The ongoing supremacy of passive and systematic investment is almost certainly a factor. Yet the narrowing of underlying economies also seems to play a reasonable part.
As productivity gains evaporate and the services economy becomes ever more important, money illusion, confidence and asset prices have elevated as levers to hold modern economies together.
Technology may provide some exciting prospects, but construction, retail and services are the employment engines of the economy. And recent feedback from retailers, developers and anyone exposed to consumers is consistent - activity is slowing sharply.
Some of the most worrying trends, particularly domestically, are in housing. The costs of a speculation scheme fuelled by long-run debt and immigration are becoming more evident. Across almost all of the western world, the number of houses completed relative to population is falling towards historic lows.
Land prices, regulatory costs, labour availability and generally rising construction costs are combining with more normal levels of interest rates to challenge housing affordability everywhere. When no-one can afford houses, developers stop building them. Despite government assertions, a solution that doesn’t involve falling property prices looks increasingly implausible.
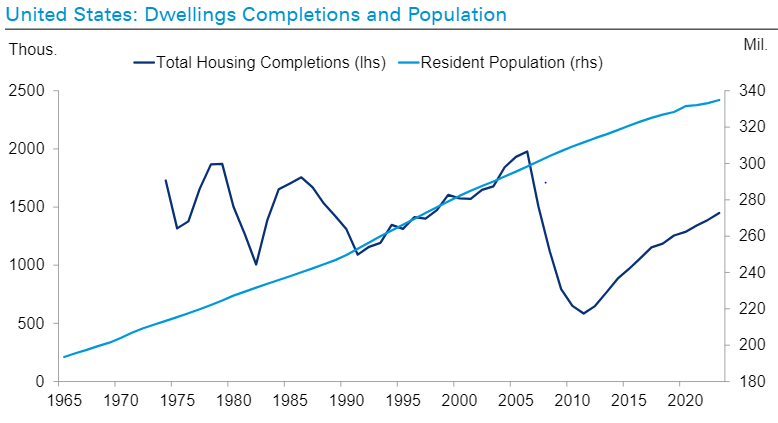
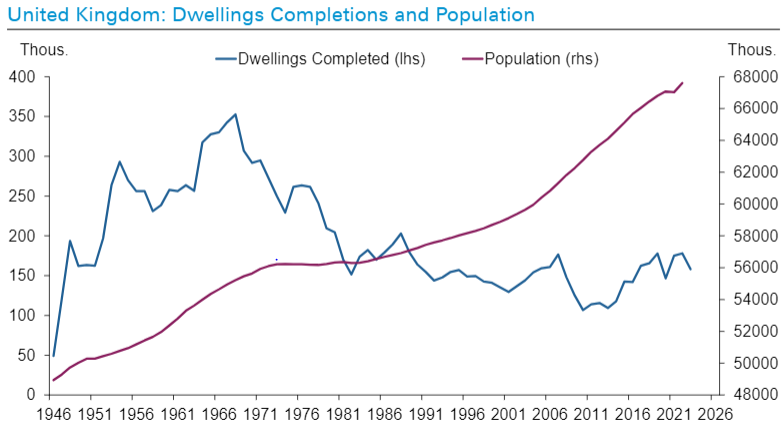
Source: Deutsche Bank, Haver Analytics, ONB, US Census Bureau
Australian Building Approvals, Commencements and Completions
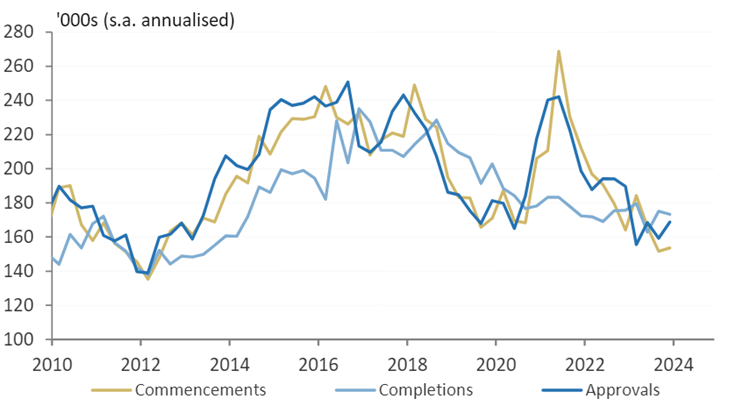
Source: Morgan Stanley
The strong performance of banks over recent months sits at odds with this reality. While the resource market, a barometer of real economic activity globally, has deteriorated, the barometer of the financial economy is off to the races.
CBA, one of the most expensive banks globally, continues to confound us and many other market observers. Disproportionately owned by passive and retail shareholders, CBA is making a significant contribution to Australia’s deteriorating market breadth as its valuation (rather than profits) edges ever higher.
Investors continue to wager on the value of the financial economy being able to separate from the profits of the economy which it is designed to facilitate. We feel differently.
Numbers versus narrative
For those of us waiting for some rationality to return to equity market valuation, the Guzman Y Gomez (GYG) IPO was not a day for high fives all round.
Capturing the imagination of investors remains a far more appealing way of creating market value than the hard yards of making money. While applauding the job GYG management have done getting the business to its current position, our role as investors is to determine a reasonable business valuation.
In an era in which high margins, growth, and avoiding capital commitment are the holy grail, franchisor and franchisee structures have unsurprisingly boomed in popularity. These arrangements can centralise functions and split the earnings of a retail operation between different parties, however, the sales and profit per store will always dictate the envelope of total profit and value available to split.
GYG currently has a little under 200 stores and a little over $750 million in network sales. Stores are currently exceptionally profitable versus most comparable businesses, making margins of nearly 20% on average sales of $4-$5 million (per the chart below).
GYG Sales Per Store
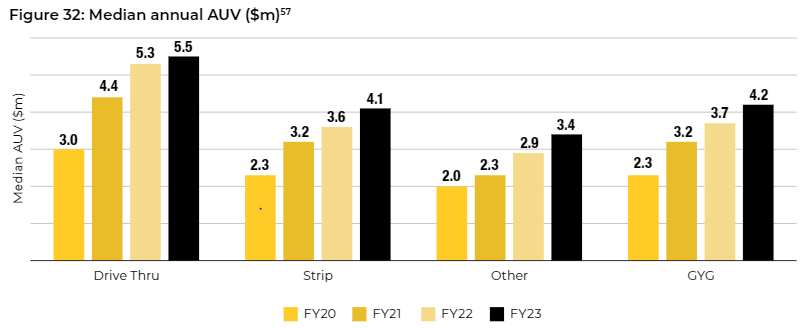
This exceptional profitability allows the franchisor to take around $0.5 million per store while leaving a similar amount for the franchisee (on an investment of <$2 million). Assuming one is prepared to assume this high level of profitability is sustainable (a very brave assumption), 10x EBIT for a mature store might allow a value per store of around $10 million, split fairly evenly between franchisor and franchisee, with the latter funding the $2 million store cost.
On this basis, the 62 corporate restaurants and 123 franchise stores would be expected to deliver around $120 million EBIT ($1 million for each corporate store and $0.5 million for each franchised store) and would justify around $1.2 billion of value on a mature store basis (ignoring all other costs).
In reality, around $1 billion of this value is absorbed in running costs, with GYG pro forma EBIT of around $12 million for 2024 and <$20 million for 2025. This rudimentary maths leaves the business delivering earnings which only justify $200-$300 million of value currently, meaning the remaining $2.7-$2.8 billion of the current $3 billion equity valuation is the ‘blue sky’ of store rollout.
While anything is possible, shareholders appear to be planning on a lot of people eating a lot more burritos. Investing is about assessing the odds. From our perspective the odds here look exceedingly poor.
The Metcash annual result offered the opportunity to compare a retail valuation at the other end of the spectrum. For a total equity valuation of less than $4 billion (within spitting distance of GYG), Metcash reported operating profit and cashflow of a little under $500 million (around 25 times that of GYG for 1.3x times the price).
Providing wholesale supply services (together with some store ownership) to nearly 1,300 supermarkets, 3,300 liquor stores and 600+ hardware stores, high levels of growth in stores may be behind Metcash. The good news for shareholders is the profits have already arrived.
Interestingly, Metcash is also the 100% owner of the Totals Tools franchise (and through joint ventures, the majority owner of more than 50 stores). A store network of 118 stores produces network sales of around $1.1 billion ($10 million per store and store margins well above 10%), giving rise to a similar value per store to GYG if one accepts these metrics are sustainable.
The $82 million of EBIT (only $34 million of costs is unallocated across the total business) is already well ahead of levels delivered by GYG. As Metcash shareholders we may be biased, but we find the extent to which valuations of apparently similar earnings streams are accorded wildly divergent valuations mind boggling.
In perhaps another similar example, we have watched shares in Pro Medicus rise inexorably (up another 38.1% over the past quarter), to reach a market value of almost $15 billion. This $15 billion buys forecast revenues for 2024 of around $160 million and operating profit of a little over $100 million at extraordinary margins. Perhaps we’re old fashioned, but nearly 100 times revenue and 150 times operating profit seems like a lot.
Sonic Healthcare, one of the larger pathology and radiology operators globally, has forecast revenue of around $8.9 billion and operating profit of a little over $800 million. These metrics buy an equity valuation some $2 billion less than Pro Medicus.
We are extremely positive on the future for pathology and radiology. As the dominant tools in preventative healthcare (diagnosing and treating problems early, rather than waiting until vastly higher cost medical intervention is required), we struggle to understand why the split of health spending looks anything like the chart below.
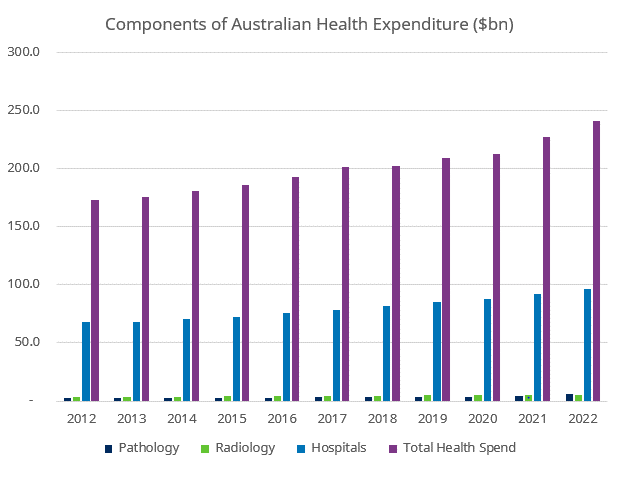
Source: Schroders, ABS
Loosening the purse strings and encouraging more preventative testing in order to reduce spending on extremely costly intervention seems like a no-brainer for both productivity and quality of life for the population. In addition, we see it as one of the more promising applications for AI.
Sonic Healthcare has one of the most extensive data sets of pathology and radiology results together with stakes or full ownership in technology businesses such as Harrison AI (across both pathology (Franklin AI) and radiology (Annalise AI)), Pathology Watch in dermatological pathology and in technology for GP’s.
In addition, you get actual pathology and radiology operations which may be pesky for technology loving shareholders yet are somewhat useful in providing the services which help diagnose and cure people.
As a core part of operations, most companies need to carefully consider how much of their technology operations they are prepared to outsource. The business development path of using attractively priced subscription-based technology to establish a market position and then leverage that position into ongoing price increases, which strip any productivity gains from the customer, is now well-trodden.
Companies that are effectively internalising important elements of technology seem far more appealing to us than pure technology companies expected to gorge on the blood of unsuspecting hosts long into the future.
Martin Conlon is Head of Australian Equities at Schroders, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article does not contain and should not be taken as containing any financial product advice or financial product recommendations. It does not take into consideration your personal objectives, financial situation or needs.
This article is an excerpt from Martin’s July 2024 market commentary ‘Threading the eye of the needle’. You can read the full version here.
For more articles and papers from Schroders, click here.