A new year is an opportunity both to reflect and to look forward, but I will not attempt to forecast particular outcomes. The last year was a stark reminder of how foolish predictions can look 12 months later, so I'll cover some more general themes.
What went wrong in 2022?
The main culprit was inflation and more importantly how persistent inflation proved to be after central banks initially believed that it would be transitory. This forced the banks to shift to the most aggressive tightening cycle since the 1980s in an attempt to restore price stability.
The picture was further complicated by the war in Ukraine and ongoing supply chain blockages thanks to China's zero-Covid policy.
In response, the Fed increased the Fed Funds rate by 4.25% over the year and was still warning that it had more to do as recently as its last meeting in December, with officials looking to raise rates further this year to between 5% and 5.5%.
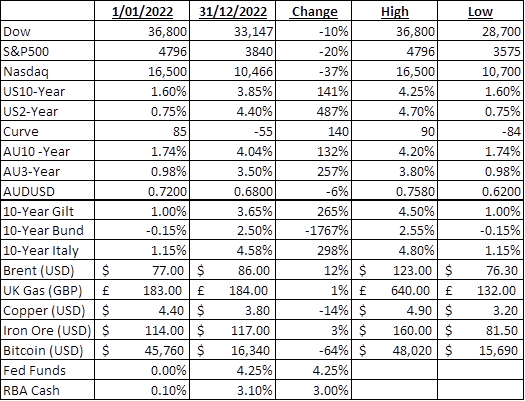
To highlight the impact this all had on markets, below is a table showing the markets I tend to watch the closest and the gains or losses that they experienced from the start of 2022 to the end of the year.
These are my numbers so might be a little different from the ‘official’ record, but they are still consistent with the underlying trend.
The outlook for this year
What does the next 12 months have the potential to look like?
The burning question at this stage is will the US economy enter into a recession and how will the Fed respond.
In a recent Wall Street Journal survey, two-thirds of economists at the 23 major financial institutions that directly deal with the Fed predicted a US recession this year with an increase in the unemployment rate to above 5% from its current historical low of 3.7%.
What became clear towards the end of last year was that the market was starting to bet that the Fed was being too negative in its outlook and that it was close to the end of its tightening cycle. It may be in a position to invoke the much anticipated ‘pivot’ by mid-year with the Fed cutting rates towards the end of 2023, which is in contrast with the Fed’s mantra of 'higher for longer'. The very tight jobs market in the US has been a major obstacle in the Fed’s fight against inflation.
The reality, and it is a similar story locally, is that consumers are still happy to keep spending despite the rapid rate increases and until there is a change to this behaviour it is going to stymie central bank’s ability to win the fight.
Record Christmas spending further underlines the challenge and is adding to inflationary pressures, compounded by governments that continue to undermine central banks by adding fiscal stimulus in the form of subsidies as well as talking up wages.
As has been a theme of mine for a while now, consumer behaviour is not changed by warnings alone. This could well be a generational phenomenon with many never having lived through the brunt of a recession and the shock this can have on asset prices and rising unemployment. They know only a prosperous period of economic growth which ironically has been perpetuated by central bank policy that is undermining their battle now.
As such, if the dramatic rate increase from last year does start to bite hard in the first half of this year, then we are close to the top of this cycle. However, if that level of pain is insufficient to alter behaviour, then rates must go higher.
Given Australia's exposure to the risk of ‘mortgage stress’ and the much-talked about cliff we are approaching as massive number of fixed mortgages switch to higher floating rates, maybe we are closer to the top than other economies.
However, this has been known for a while and mortgage holders should already have started to adjust their spending to reflect this. But maybe not.
Central banks warnings continue
In summary, for the year ahead, central banks and the market are in somewhat of a disagreement as to how high and for how long interest rates will remain elevated. Central banks continue to warn that they are 'not for turning' until they are confident that price stability has been restored. The outlook is further clouded by the war in Ukraine as well as the Chinese doing a 180-degree flip and letting Covid rip and this will have an impact on global growth.
Therefore, I am not confident we are close to a bottom in US equities although bonds should have a better year as markets sweat on the Fed pivot.
Tim Larkworthy is a Director - Fixed Income Sales at Fixed Income Solutions. The views expressed herein are the personal views of the author and in no way reflect the views of the BGC Group. Individuals should make investment decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of their own financial position and in consultation with their own financial advisors. No liability whatsoever shall accrue to the author or the BGC Group as a result of individuals or entities making investment decisions based wholly or partly on this material.