If you’re a long-term investor, ironically term deposits are one of your riskier assets. Investors have the potential to receive a higher cash flow from growth assets such as Australian property and shares. In times like the present, a focus on the income an investment provides is important. With interest rates set to remain low or fall further, bank deposit rates – already at their lowest in Australia since the 1950s – are likely to remain low or go lower.
(Shane and Paul provide more views in the video linked at the end of the article).
Beyond day to day cash requirements, the key for investors currently in cash or term deposits is to work out what is most important to them: absolute certainty regarding the capital value of their investment or obtaining access to a higher, more stable income flow at the cost of volatility in the value of their investment. In this, there are several alternative investments to cash.
Alternatives to term deposits for income return (yield)
The chart below shows the yield on a range of Australian investments. Yields on global investments tend to be lower.
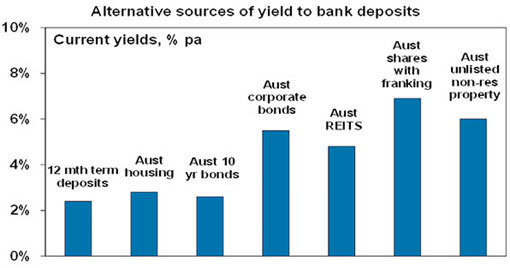 Source: Bloomberg, AMP Capital
Source: Bloomberg, AMP Capital
All of these yields have fallen over the last few years, but many alternatives offer more attractive yields than term deposits:
- Australian Government 10-year bond yields are now around 2.5%. This will be the return an investor will get if they hold these bonds to maturity. They can generate a higher return if yields continue to fall, but they are already very low. Global bond yields are lower, averaging around 1%.
- After the house price boom of the past 20 years, the rental yield on capital city houses is just 2.8% and on apartments is around 4.2% and even lower after costs.
- Corporate debt is an option for those who want higher yields than term deposits but don’t want the volatility of shares. For Australian corporates, investment grade yields are around 6.5% or less and lower quality corporate yields are higher. Sub investment grade corporate bond yields in the US are yielding around 9% as worries partly about loans to energy companies have pushed them higher.
- Following the turmoil of the GFC, Australian real estate investment trusts (A-REITs) have refocused on their core business of managing buildings, collecting rents and passing it on to their investors, with lower gearing. While their distribution yields have declined as rental growth has not kept up with total returns of 15% over the last five years, they are still reasonable at 4.8%.
- Unlisted commercial property also offers attractive yields, around 6% for a high-quality well diversified mix of buildings, but higher for smaller lower quality property. And it doesn’t suffer from the overvaluation of residential property.
- Unlisted infrastructure offers yields of around 5%, underpinned by investments such as toll roads and utilities where demand is relatively stable.
- Australian shares also fare well in the yield stakes. The grossed up dividend yield on Australian shares at around 6.9% is well above term deposit rates meaning shares actually provide a higher income than bank deposits. In fact, the gap is now back to levels seen during the GFC.
Key issues for investors to consider
All of the alternatives come with a risk of volatility in the value of the underlying investment. In the case of shares the key for an investor is to work out whether they want a stable value for their investment in which case bank deposits win hands down or a higher and more stable income flow in which case Australian shares win hands down.
More broadly, in searching for a higher yield investors need to keep their eyes open. It’s critical to focus on opportunities that have a track record of delivering reliable earnings and distribution growth and are not based on significant leverage. In other words, make sure the yields are sustainable. On this front it might be reasonable to avoid relying on some Australian resources stocks where current dividends look unsustainable unless there is a rapid recovery in commodity prices.
Shane Oliver is Chief Economist and Head of Investment Strategy at AMP Capital and Paul Clitheroe is Executive Director at ipac. This article contains general information only and does not consider the individual circumstances of any investor.