Great question. (Wish I had asked it 5, 10 or 15 years ago.) Near-term – say, to pick a random date, until 20 January 2025 – momentum may stay with the US trade. But beyond that US equities look rich, their EPS advantage may narrow, rising bond yields may crimp returns, and the next cycle – which isn’t here yet – should favour other markets. I’m not convinced Trump can offset these headwinds.
Who’s not bullish the US? Exhibit 1 – nicked from Torsten Slok – shows the share of US consumers expecting higher equity prices is now at an all-time high. The AAII survey is also high (not at a record). So is Mike Hartnett’s BoA fund manager survey. I don’t know when this will peak. The bulls can project their hopes and dreams on the President-elect until inauguration day (20 January 2025).
Exhibit 1: Everyone (almost) expects higher equity prices
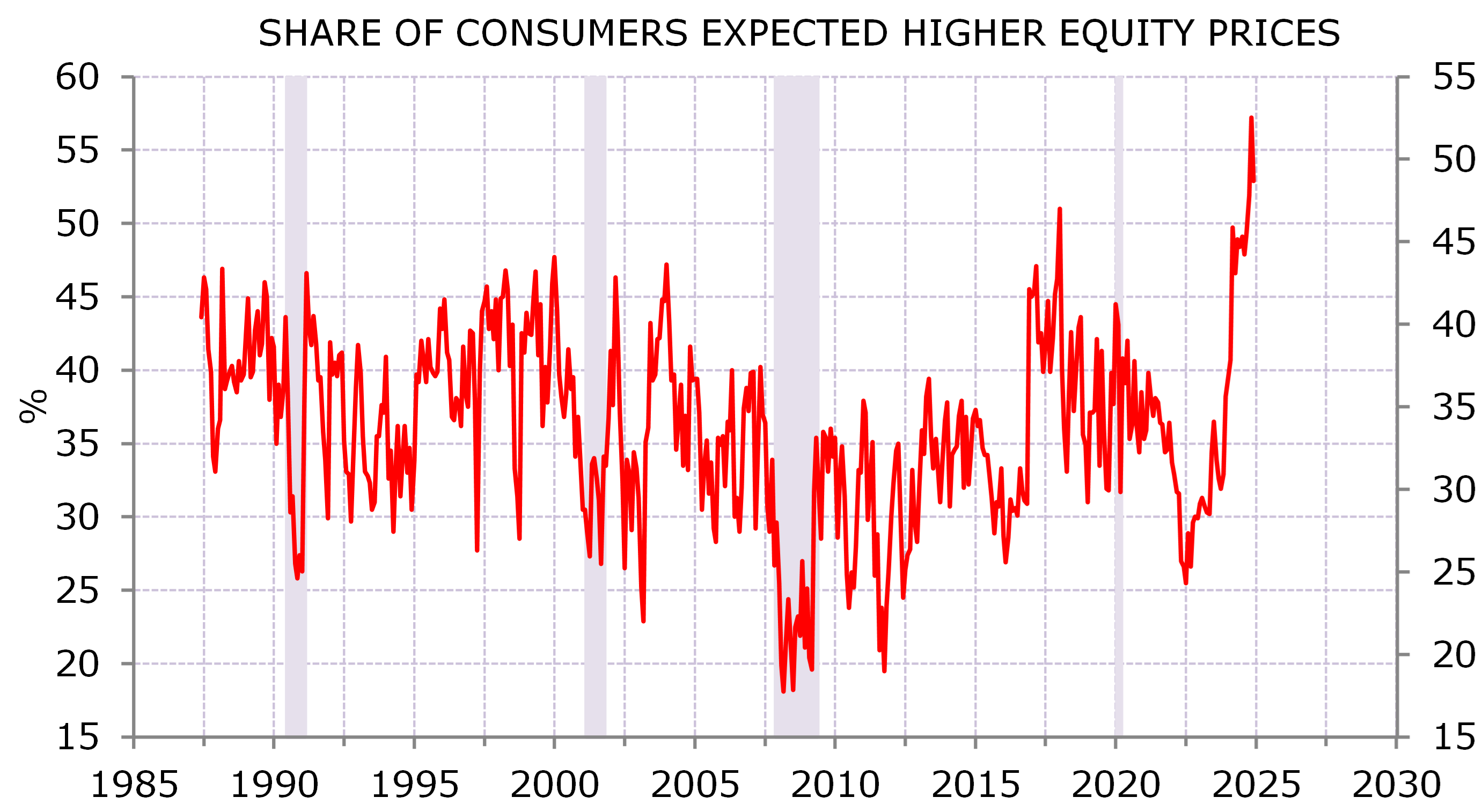
Source: Conference Board, NBER; Minack Advisors (thanks Torsten Slok)
The key to US exceptionalism has been earnings out-performance. Since 2016 EPS-driven out-performance has been enhanced by the US market rerating versus other markets (Exhibit 2).
Exhibit 2: Earnings drove most (not all) US exceptionalism
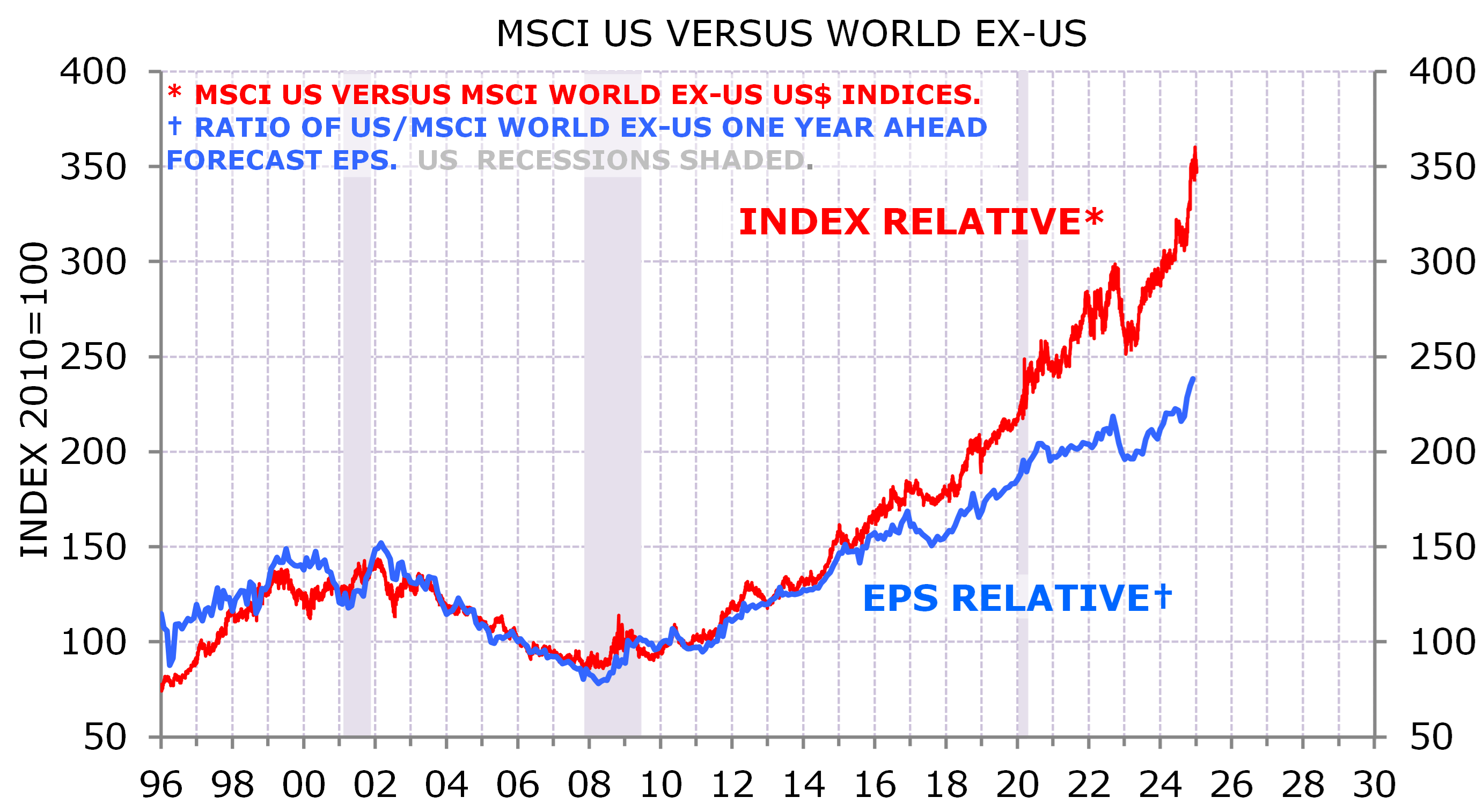
Source: MSCI, IBES/DataStream, NBER; Minack Advisors
That rerating coincided with a widening gap between US and non-US long-run EPS forecasts. The gap between expected US and non-US long-run EPS growth is now at 8%, a record, excluding 4 months in the GFC (Exhibit 3).
Exhibit 3: US exceptionalism is for the long run
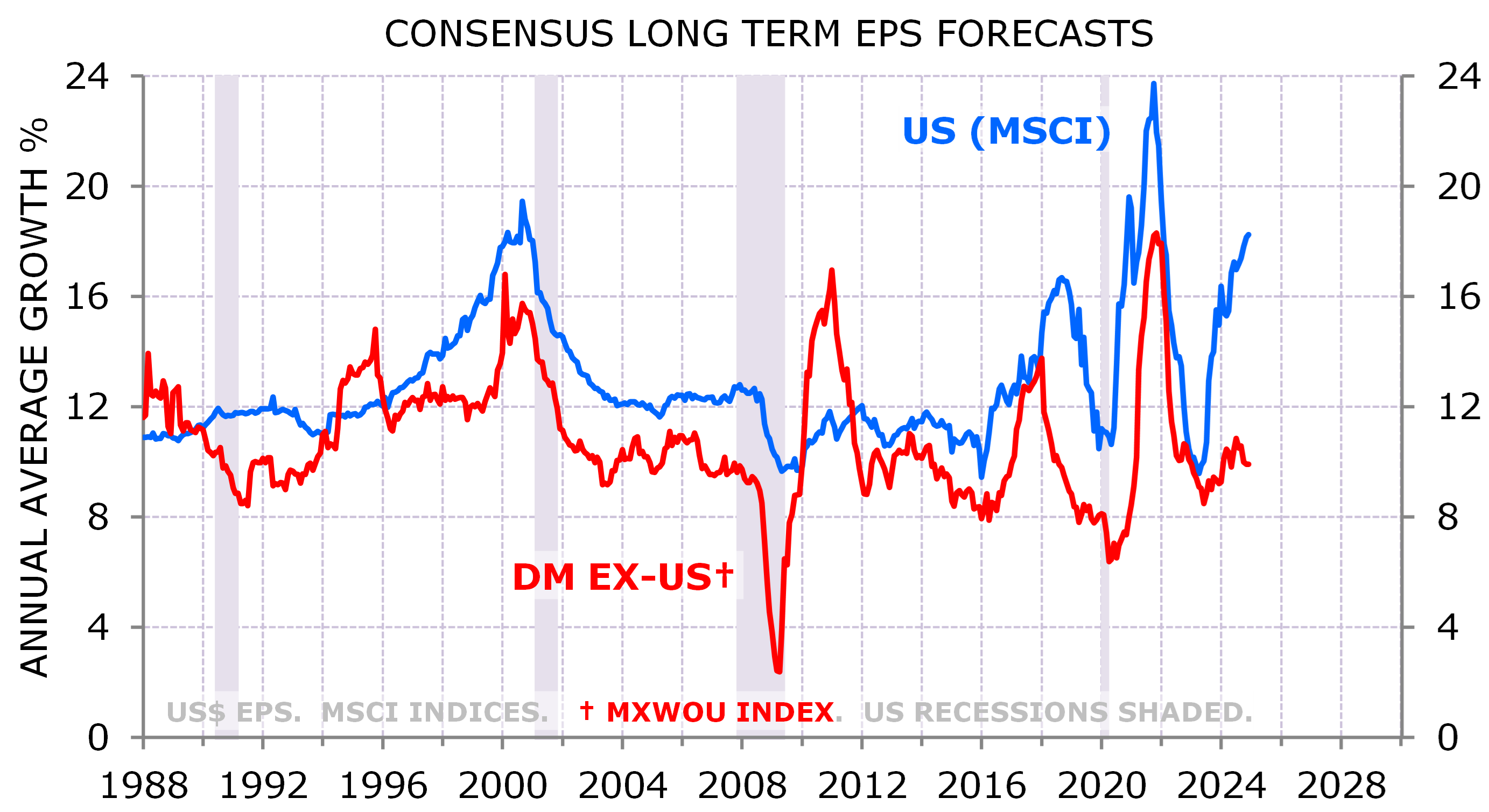
Source: MSCI, IBES/DataStream, NBER; Minack Advisors
I doubt that US EPS growth will outpace the rest of the world’s by that much. Even if it does, that superior EPS growth is now in the price. Exhibit 4 shows prospective PE ratios based on long-run (5 years ahead) EPS level. The US market has re-rated relative to other developed markets even after taking into account its faster long-run EPS growth.
Exhibit 4: US is expensive even with exceptional EPS
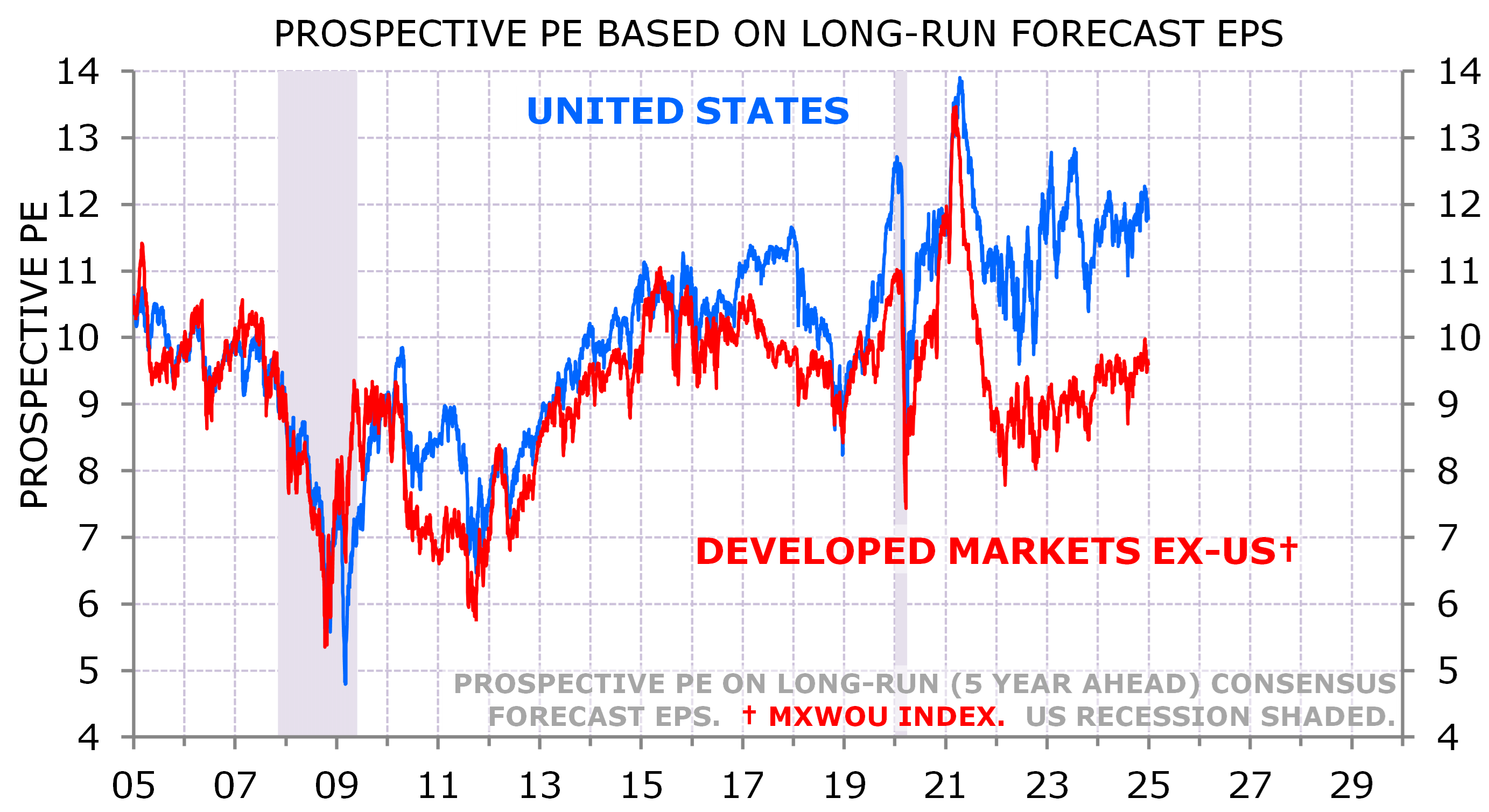
Source: MSCI, IBES/DataStream, NBER; Minack Advisors
The US market is expensive relative to its own history, relative to other markets and relative to other assets. The prospective earnings yield is now in line with the 10-year Treasury yield (Exhibit 5). I expect 10-year yields to breach 5% in 2025. At some stage rising long-end yields will be a headwind for equity valuations in the US.
Exhibit 5: Exceptional valuation at risk from bond yields
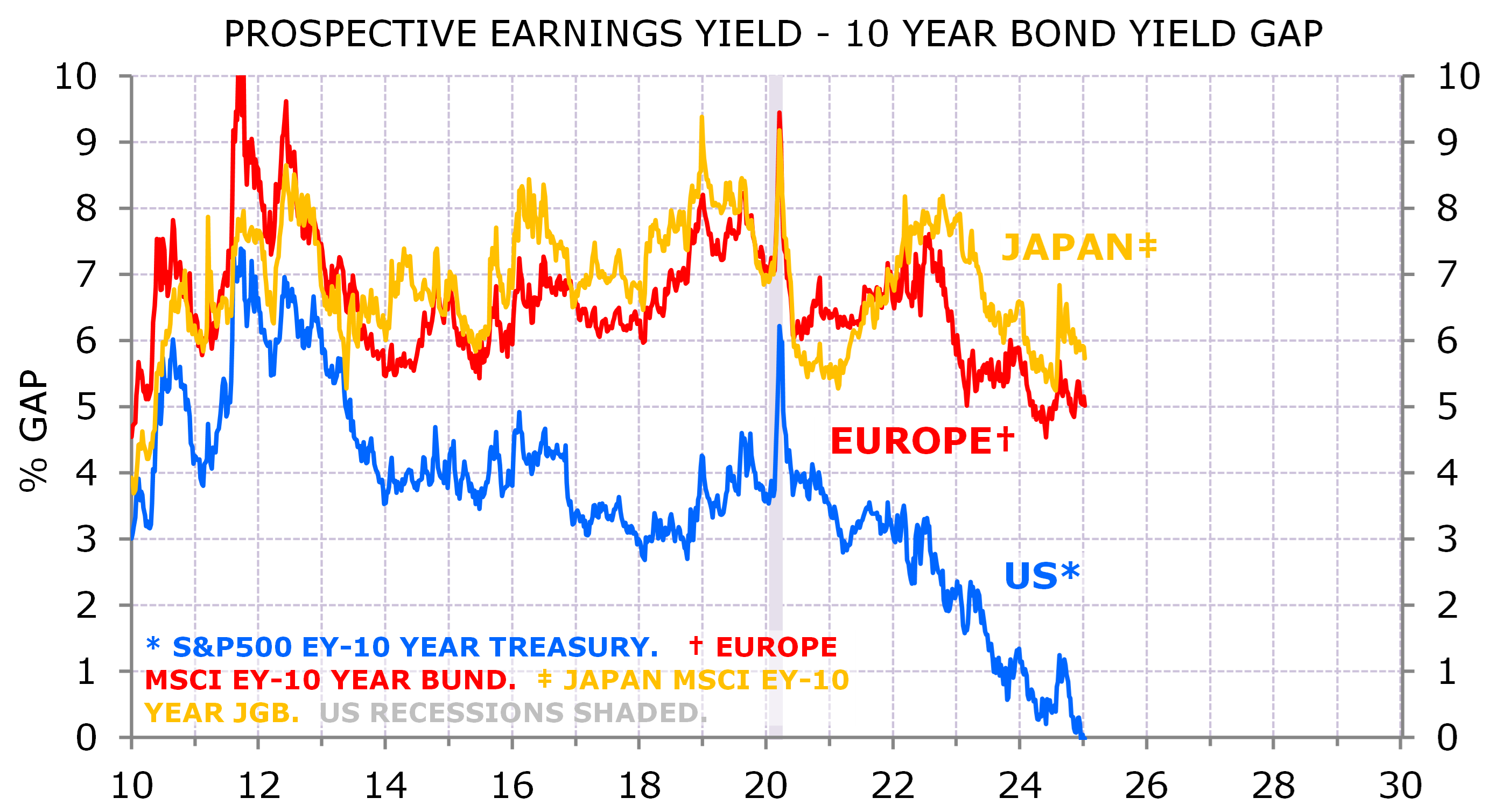
Source: MSCI, IBES/DataStream, Bloomberg, NBER; Minack Advisors
The post-GFC cycle saw unusually strong US EPS growth and unusually weak EPS growth outside the US. Why will that change? The principal reason why ex-US EPS has been so weak since the GFC is that earnings had ballooned to unsustainable levels before the GFC. EPS in US$ terms quadrupled between 2002 and 2008. That EPS bubble bursting kept EPS weak for several years. However, rest of world EPS is now back on its pre-bubble trend and has resumed normal growth through the past few years (Exhibit 6).
Exhibit 6: The rest of the world back on EPS growth trend
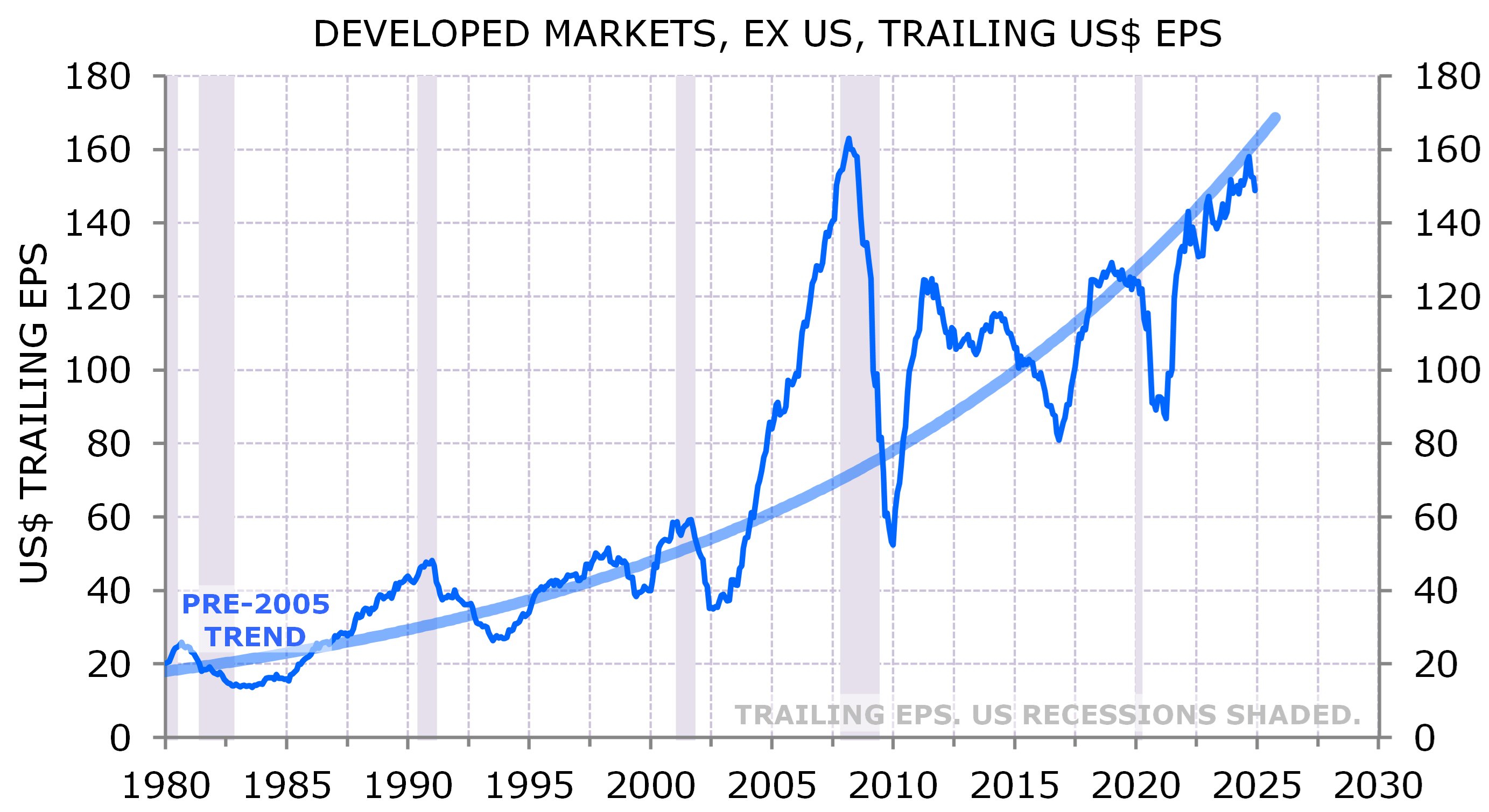
Source: MSCI, NBER; Minack Advisors
US EPS has grown at an above-average pace since the GFC: 4% real over the past decade versus a long run average of 1.75%. Most of that exceptional growth – and most of the recent US EPS out-performance versus other markets – is due to the Magnificent 7 (Exhibit 7). I don’t analyse single names, so I don’t have a strong view on how long the Magnificent 7 can maintain EPS growth at recent rates. At some stage the law of large numbers will have to kick in. But several clients have commented that 2025 will be the ‘show me the money’ year where investors will want companies to show the payoff for the massive investment in artificial intelligence. If the returns aren’t there, valuations could fall.
Exhibit 7: Mag 7 explains most of US EPS exceptionalism
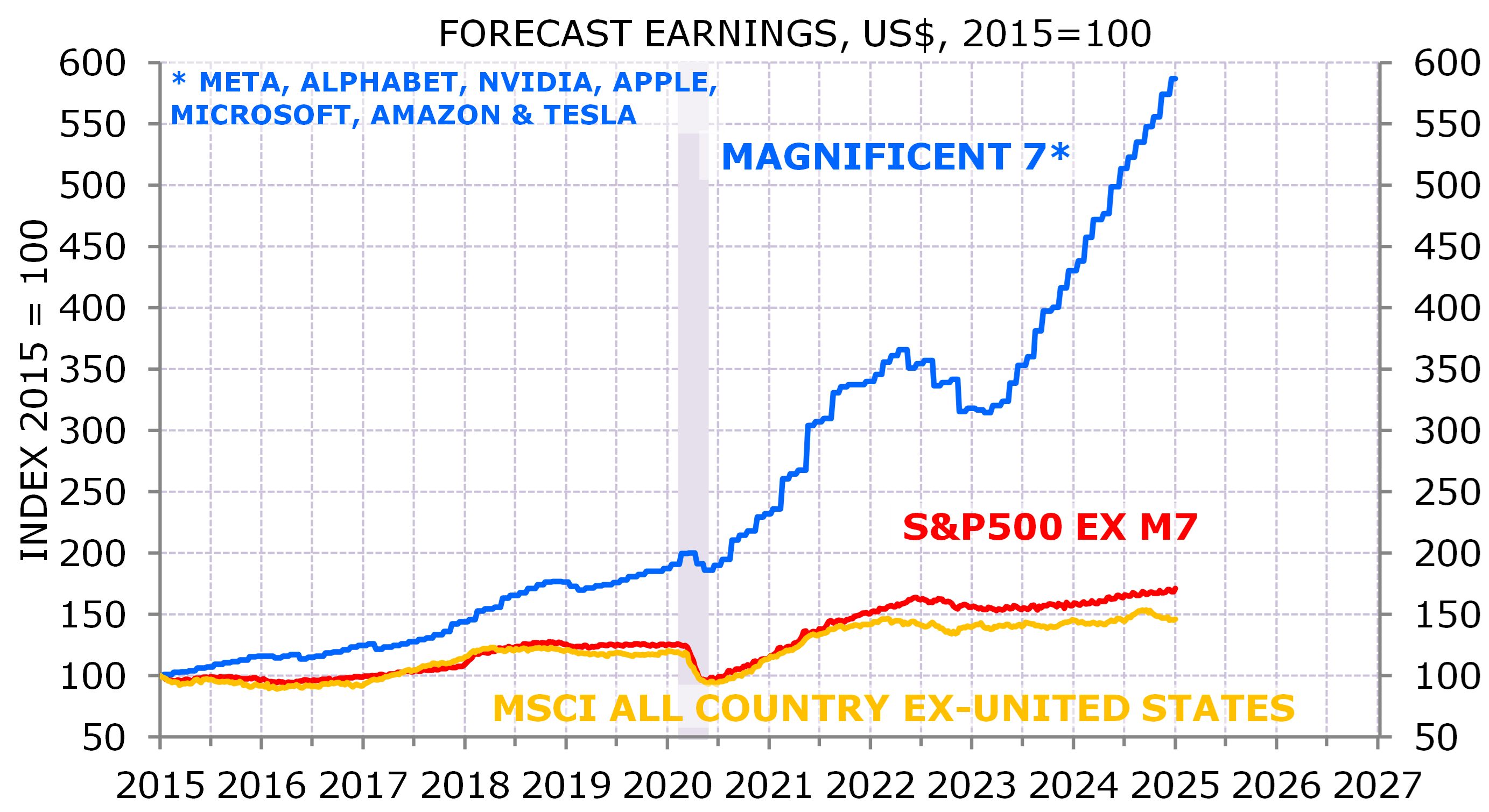
Source: Bloomberg, IBES/DataStream, MSCI, NBER; Minack Advisors
Much of the recent EPS out-performance of the S&P493 versus the rest of the world has been driven by diverging macro growth rates (Exhibit 8). However, I expect the growth gap between the US and the rest of the world to narrow in 2025.
Exhibit 8: This was not the year for RoW recovery
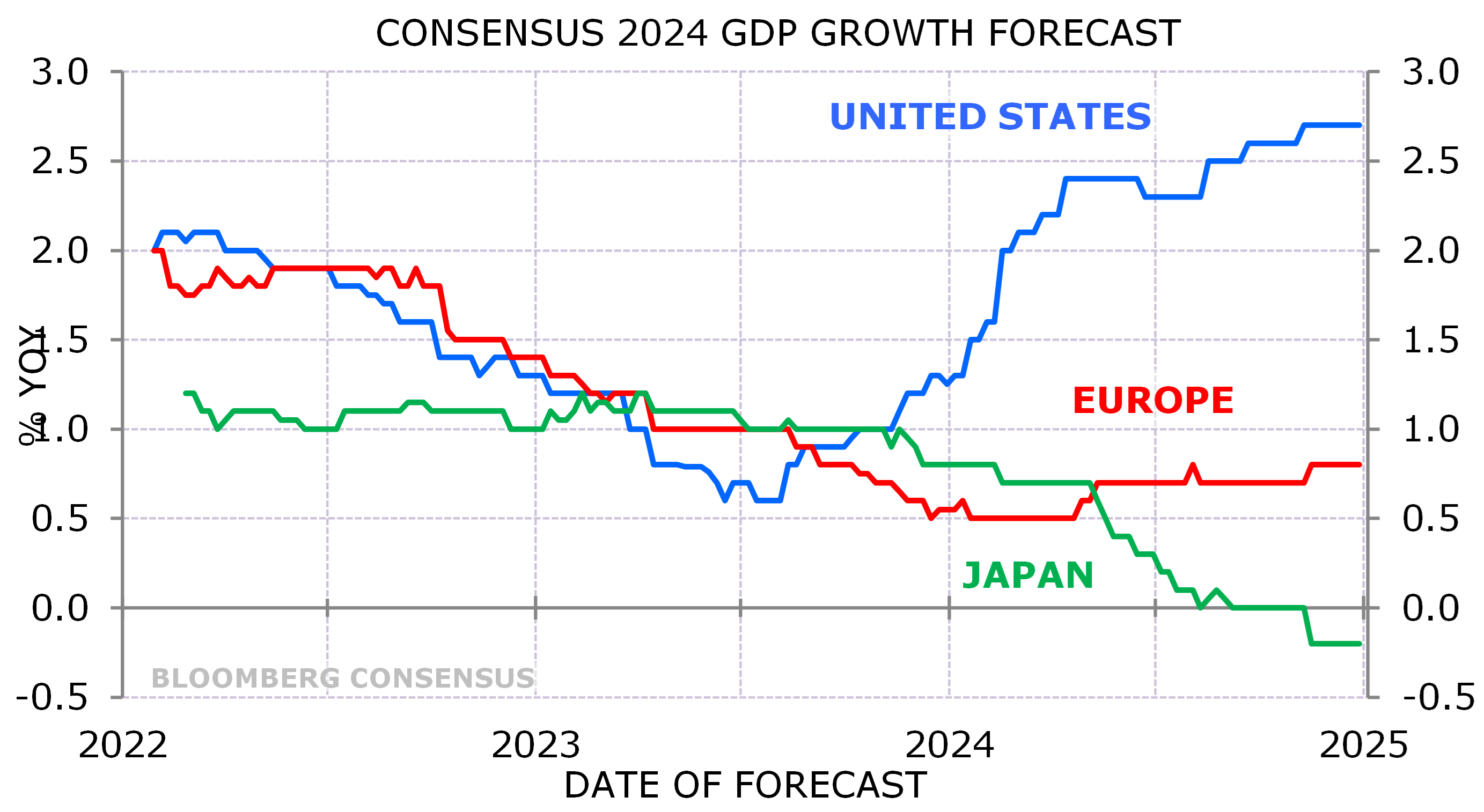
Source: Bloomberg, NBER; Minack Advisors
Mr Trump’s election has turbocharged US outperformance. While there may be a few sectors that benefit from specific policies, it’s not clear to me that Trump locks in sustained US equity outperformance. The cycle gap between the US and non-US markets should narrow next year. The prospect of higher long-end yields is a greater threat to the expensive US market. Mag 7 performance will be tested if AI underwhelms. And everyone is so bullish the US, who’s not already in?
Gerard Minack founded Minack Advisors in 2013 and has a wealth of experience as a macro strategist.
This article contains material based upon publicly available information, obtained from sources considered reliable, and is not soliciting any action based upon it. Opinions expressed are current as of the date of publication. All forecasts and statements about the future, even if presented as fact, should be treated as judgments, and neither Minack Advisors Pty Ltd nor its partners can be held responsible for any failure of those judgments to prove accurate. Minack Advisors Pty Ltd is regulated by ASIC, authorised representative number 443937.