Biotechnology and pharmaceuticals are probably the most seductive and exciting sectors of the market to invest in. Not only can investors have the warm and fuzzy feeling that they are helping humanity (an emotion not readily generated by buying shares in Westpac or BHP), but when drugs or devices are developed and successfully adopted, it can be very profitable. Furthermore healthcare as a sector exhibits little correlation with Chinese growth, the health of the domestic economy or US interest rates and has some powerful demographic tailwinds.
It can be volatile, too. Recently, for example, Sirtex (STX) announced that trials of its eagerly awaited SIRFLOX liver cancer treatment had failed to show a statistically significant increase in survival in patients with liver cancer, though the company noted that liver cancer ultimately has a 90% level of morbidity. The announcement of this news wiped $1 billion off Sirtex’s market cap as the stock fell 55%.
For reference the difference between biotech and pharmaceutical companies is that biotechs like CSL use microorganisms or biologicals to perform a process, whereas pharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer employ a chemical-based synthetic process to develop small-molecule drugs.
Fat profit margins
Most large corporations require substantial and continuing capital investments to maintain the quality of their assets. The major banks are required not only to set aside capital to back their lending, but have consistent expenditure on information technology (IT); for example the Commonwealth Bank spends over $1.2 billion per year on IT services. As the other banks match this expenditure, it does not result in any improvement in profit margins. Similarly, manufacturing companies such as Bluescope produce cardboard boxes and steel from capital equipment that can readily be bought by their competitors. This results in minimal barriers to entry beyond a company’s cost of capital and thus gives low single digit profit margins and growth in line with GDP.
Conversely biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies can enjoy both high growth and high profit margins when a treatment they own and develop is successful and is adopted. For example in 2009 when Sirtex gained traction with their targeted liver cancer treatment SIR-Spheres, the company saw an annual revenue increase of 72% and profits increase from $1.2 million to $18.2 million. Demand for new and potentially life-saving treatments is relatively price inelastic. Furthermore patents and the time and effort required to obtain regulatory approvals for new drugs provide strong barriers to entry for other companies looking to produce competing products.
At the larger end of town in 2014 Pfizer, Hoffmann-La Roche, AbbVie, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and CSL all generated profit margins in excess of 20%. Conversely global car makers delivered a profit margin of only 3% and steelmakers -4%. For many drugs, the marginal costs of producing these drugs is small. The best selling drug of all-time is Pfizer’s cholesterol drug Lipitor that generated US$123 billion in sales from 1998 until its patent expired in 2011.
Pitfalls
As the Sirtex announcement showed, the sector can be a challenging place for retail and professional investors alike. Aside from determining whether a company’s drugs will be successful, investors also require that the product be adopted by physicians and often that it be included on a government’s list of approved and subsidised treatments such as Australia’s Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS). In 2014, Australian taxpayers spent $9.1 billion on the PBS and listing every medicine on the PBS would quickly make the scheme unsustainable. For example, there is a good chance that an expensive new drug might not be listed on the PBS if it is deemed to only provide a marginal benefit over existing alternatives. Governments globally are looking to curtail healthcare spending that has been consistently growing at a multiple of tax revenue growth.
What to look for before investing
- Security of patents. What is the life of the new and existing patents? After Lipitor’s cholesterol patent rolled off, the cost of the treatment dropped from US$500 per month to US$50. The impact of this was an 81% reduction in sales in the US for Pfizer. Investors should be aware whether competitors have similar treatments undergoing approval or if another entity is disputing a company’s patents.
- Approval status. Where is a company’s treatments in being registered for clinical use with the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration)? FDA approval is a requirement for sale in the most profitable healthcare market in the world. Companies with at least one product in end-stage trials are safer investments than those just beginning the investigative phases of development. I have seen many companies issue exciting prospectuses and raise capital based on the results of their treatment on mice, with minimal further developments many years later. On average it takes 12 years and over US$350 million to get a new drug from the laboratory onto the pharmacy shelf, with a 3% success rate for drugs to move from pre-clinical trials to full approval.
- Financial strength and cash reserves. Whilst this point is germane to investing in all companies, the length and cost of the approval process for a drug is greater and more uncertain than for a new gold miner or retailer. If the company is required to make multiple dilutionary share issues just to keep in the game, its attractiveness as a potential investment declines.
- Diversity of the company’s pipeline. The number of investors that have made huge gains in one tiny biotech are dramatically outweighed by those that have seen share prices crater after a company’s only drug failed to win FDA approval. CSL shrugged off the failure of a competitor’s parallel trial of a plasma-derived product used to treat Alzheimer’s, as it had a range of other treatments both in the market and in clinical trials.
- Size of the addressable market. Whilst investing in companies treating niche ailments can be profitable, the addressable market is far greater in areas such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, heart disease, diabetes, neurological disorders and immunological diseases. Furthermore companies operating in these areas are more likely to attract a takeover bid from the big pharma companies looking to restock their pipelines.
Complex sector
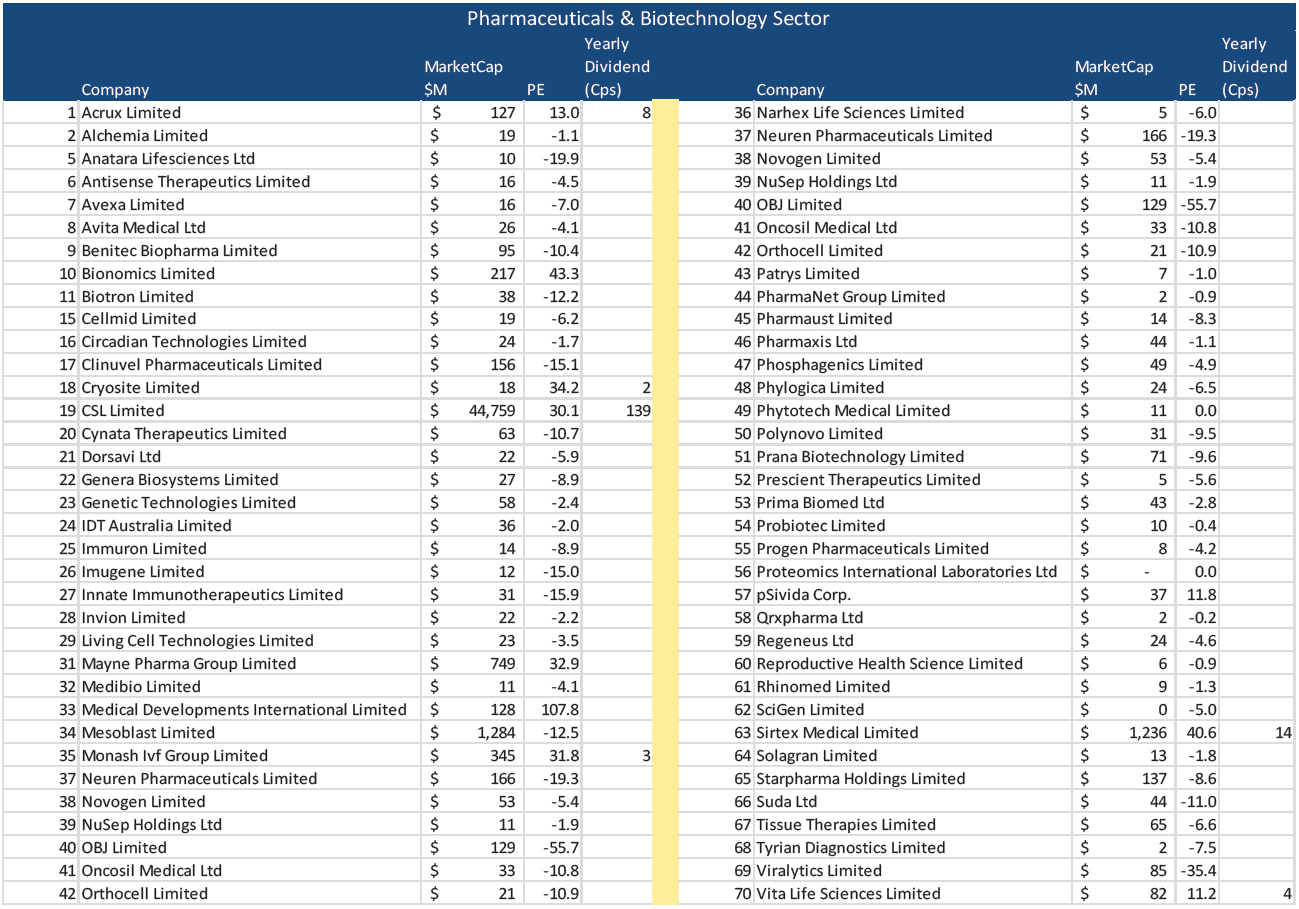
Looking across the biotech and pharma sectors in the table below, there are 70 companies listed on the ASX, but only six pay a dividend and out of the 70 only 14 are profitable! Furthermore the pharmaceuticals and biotechnology sector encompasses a wide range of companies specialising in very niche areas. Even where an investor possesses a strong understanding of a particular area of medicine such as liver cancer, this knowledge may be of little use in evaluating CSL’s blood plasma treatments. Conversely when investors are analysing the prospects for Boral, insight can be gained from examining competitor CSR’s building products division and speaking with their management team.
 Source: IRESS
Source: IRESS
Hugh Dive is a Senior Fund Manager for Aurora Funds Management Limited. This article is general information and does not address the personal needs of any individual.