The Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard observed that, “Life can only be understood backward, but it must be lived forward.” With the benefit of hindsight, events of the past often seem rational, even inevitable, yet the present is always fraught with uncertainty. This could also be said about investing.
Today’s investment climate could be summed up as cautious and noticeably bereft of conviction. While global equity markets have more than doubled from GFC lows, investors remain concerned about central bank policies, currencies and commodities, among other issues.
Even so, our company’s conviction in value investing is strengthening as we try to “understand the market backwards”.
What is value investing?
Value investing is a strategy where stocks are selected that trade for less than their intrinsic values. Value investors seek out stocks they believe the market has undervalued. These differ from growth stocks, which are companies whose earnings are expected to grow at an above-average rate relative to the market.
Value investors believe the market overreacts to good and bad news, resulting in stock price movements that do not correspond with a company's long-term fundamentals, giving an opportunity to profit when the price is deflated.
Valuation gap is extreme
Value stocks remain historically cheap relative to growth stocks. In fact, the valuation gap between value and growth stocks on a Price to Book value (P/BV) is at an extreme not seen for some time (see chart below).
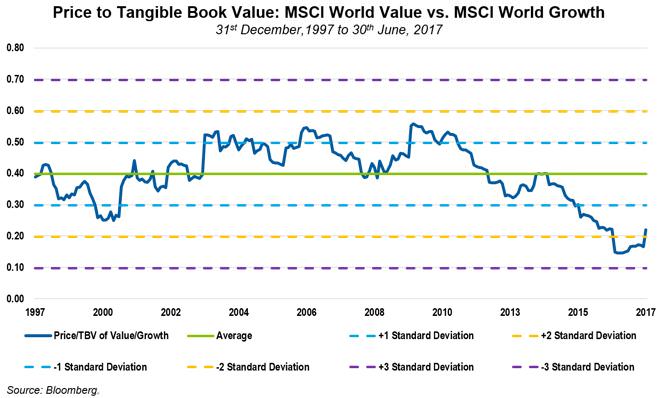
Investors would have to go back to the height of the ‘dotcom bubble’ in 2000 to find such extremes. Back then, interest in tech stocks was enormous, based on their perceived growth potential. Today, it is the consumer staples sector that is attracting market focus as investors look for growth stocks that offer the perception of safety and stability in an uncertain environment.
Value on the rebound
One of the stronger catalysts for a value revival is rising interest rates. In the past, value cycles have occurred when rising interest rates have corresponded with a strengthening economy, although some argue it is the stronger economy and inflationary pressures that were the real drivers of the value revival. Today, however, global economic growth is moderate and deflationary pressures persist.
While value can be pro-cyclically correlated to the economy, this isn’t always the case. For example, investors waiting for an improving economic cycle would have missed the value upturn in 2000. Investors fleeing value in anticipation of economic weakness would have missed value’s outperformance during the recession of 1981-82. In each of these instances, we believe stocks simply became too cheap and a reversion to the mean prompted a value rally.
Rather than economic growth, we consider valuation of stocks a far more accurate predictor of future returns and a value recovery. When it comes to value, today’s valuation starting point is distinctly compelling.
Value moving beyond 'the usual suspects'
Since the GFC, value stocks have been primarily concentrated in either the resource sectors such as energy and materials or rate-sensitive sectors such as financials. For many, being a value investor has therefore meant taking on commodity risk or interest rate risk.
Recently, however, value has proliferated beyond just a few deep cyclical sectors to across the broad market. For example, value is just as cheap today within pharmaceuticals and biotechs as it is within financials and energy, as shown in the chart below.
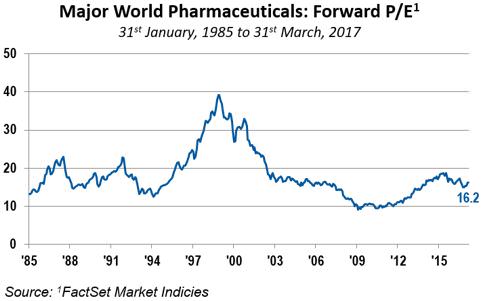
The long-term trends for pharma and biotechs are encouraging given the ageing world population and increased wealth in emerging markets. Regulatory reform and drug pricing are clouds hanging over the industry but will not impact all companies in the same way. The best way to deal with a tough price environment is to innovate. We are invested in companies working on drugs for immune-oncology, gene therapy and Alzheimer’s which have huge potential. Current concern and uncertainty is allowing us to buy new stocks at what we believe to be a discount, and this is where the advantage of having a long-term horizon and patience comes in.
Long term view helps pick a bargain
Uncertainty is a fact of life and the road ahead is rarely obvious. One way to deal with uncertainty is taking a longer-term investment horizon. Many of the macro and political variables that drive markets in the short term are unforecastable with any reliable degree of certainty. However, long term valuations move reliably through cycles, as do economic variables like commodity prices and interest rates. Quantifying the potential impact of different scenarios on each of our holdings’ prospects and earnings and contrasting them with the company’s valuation allows us to judge whether we have identified a value bargain.
Peter Wilmshurst is Portfolio Manager of Templeton Global Growth Fund Ltd (ASX:TGG) plus a number of Templeton Global Equity Group's global portfolios. This article is general information and does not consider the needs of any individual.