We are in the midst of a one-in-100-year pandemic and unemployment has reached levels not seen since the Great Depression. And while market observers continue to either marvel or scratch their heads at the surge in global equity prices, some truly unexpected real estate metrics continue to emerge.
First, it was widely expected by many economists and observers that the local residential market was poised to crash by up to 30%. However, to date, the data is not playing out as expected.
A pandemic and one million people unemployed, so house prices are … going up?
While it’s early days, some of the best real-time data we have – in this instance, preliminary auction clearance rates – suggest house prices are not (yet) falling in a meaningful way. In fact, despite the naysayers, a strong case can be made that by the time we reach the fourth quarter this year, residential prices in some of our main cities will in fact be rising.
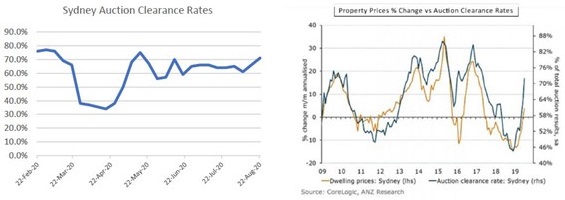
Source: Domain, CoreLogic, ANZ Research, Quay Global Investors
Of course, auction clearance rates are not a perfect measure. But nevertheless, over the long term there is a steady relationship between clearance rates and residential price movements. For instance, since the end of the lockdown in Sydney, clearance rates have generally oscillated around 60%, a situation suggesting a flat-to-rising market. CoreLogic reports that in the four weeks to 20 September across all capital cities, new listings increased and auction clearance rates were rising.
It appears to be happening elsewhere too
Australia is not alone in these unexpected metrics. The incredible resilience of our domestic residential real estate market is consistent with observations from other parts of the world too. In the UK, for instance, house prices are accelerating at their fastest pace since BREXIT.
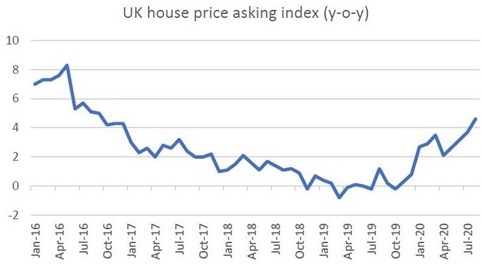
Source: Bloomberg, Quay Global Investors
And in the US, despite the sharp rise in mortgage delinquency rates, prospective home buyer activity (as measured by foot traffic) is at its highest level since 1994, matching the recent surge that has been seen in existing home sales.
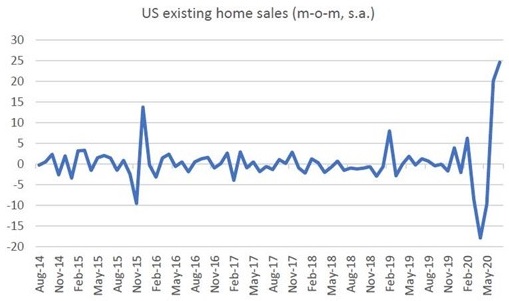
Source: US Bureau of Economics, Quay Global Investors
Retail also doing well
Residential property metrics are not an outlier. Another economic indicator that appears to defy the current economic narrative has been retail sales.
In Australia, ABS retail sales for July showed retail sales were up a significant 12% year-on-year. This bounce is more than just a catch-up from the April slump. On a rolling 12-month basis, we estimate Australian retail sales are now up 3.7% compared to the previous corresponding period.
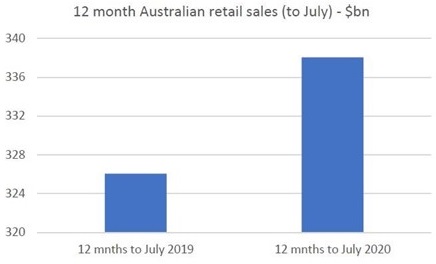
Source: ABS, Quay Global Investors
In fact, Australians have spent an additional $12 billion in the 12 months to July 2020 compared to the 12 months to July 2019.
While much has been made of the strength of the online shopping business models during this period, this retail activity is not all online either. During the recent Scentre group earnings call, it was noted that portfolio in-store retail sales during July were actually above those of July 2019, including Victoria (which went into lockdown on 9 July).
Overseas retail experience
We can observe similar data trends in retail sales in the US. While it is not quite as strong as Australia, total retail sales are nevertheless higher on a rolling 12-month basis.
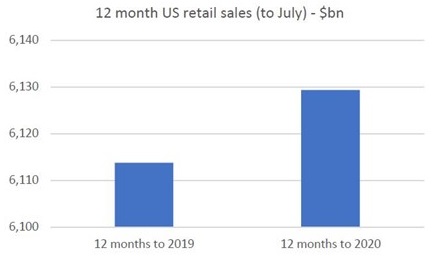
Source: US Census Bureau, Quay Global Investors
The US is not alone. In Germany, for instance, retail sales for the six months to June are 0.8% higher than the previous six months.
So, what’s happening to explain the rise of residential and retail?
Explaining the data via sectoral balances
It would be easy to suggest the observed data in residential and retail is a result of a ‘sugar high’ from fiscal stimulus – and indeed, that could be part of the story. As well, many consumers have been denied certain spending ‘avenues’ in 2020, most obviously air travel, entertainment and eating out. It may well be that the additional dollars are simply being spent elsewhere.
But we think there is more to it than that.
For the best part of 10 years, the common narrative has been that the Aussie consumer is ‘dead’. Weak wage growth coupled with very high levels of household debt has constrained the consumer. And the data certainly supported this argument.
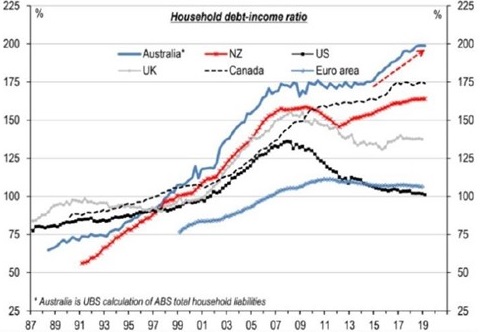
Source: ABS, Bloomberg, UBS
But the massive fiscal response to the lockdown from most governments will go a long way to repairing household balance sheets, freeing up the way forward for increased consumer spending.
Regular readers of our articles will know from the sectoral balances’ framework, that government financial deficits equal non-government financial surpluses. (The non-government sector includes businesses, households and the foreign account – aka the current account deficit.)
The US GFC experience
Below is a chart of the sectoral balances in the US in response to the financial crisis in 2008-09, clearly showing the significant increase in net financial assets (cash and bonds) accruing to the domestic private sector as a result of the Obama-driven American Recovery Act. This was a major reason why the US avoided repeating a second Depression.
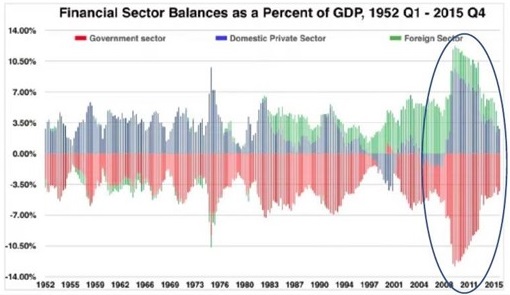
Source: Tipping Point North South
What is interesting about this chart (and Australia is similar) is the American Recovery Act deficit measured $831 billion. The current CARES act is closer to four times the size, at $3.5 trillion.
Similarly, in 2009 the Australian government stimulus to the financial crisis was $45 billion, or 4.5% of GDP. Today’s response is closer to $150 billion.
Even after allowing for 10 years of inflation, the sheer scale of government spending now is multiple times that undertaken during the GFC.
The bottom line is that household balance sheets (and corporate profits) are receiving a significant boost from net government spending. And until governments reverse course and start generating surpluses (which we do not envisage any time soon), these net financial assets will continue to reside in the private sector, permanently repairing balance sheets and setting up households for the next cycle, as the household savings ratio from the national accounts confirms.
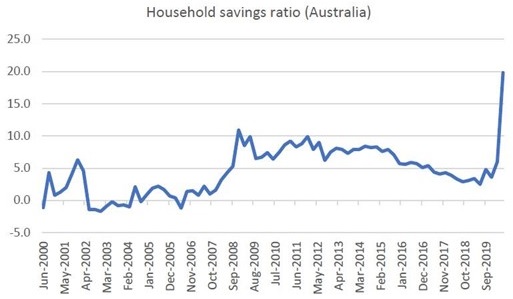
Source: ABS, Quay Global Investors
Conclusion: the power of public spending
This has been a very unpredictable economic cycle. Despite a one-in-100-year pandemic and near-depression levels of unemployment, residential property prices and retail sales are not following the widely expected doomsday script. While the recent data could of course be temporary, we think it is also helpful to view the recovery and other leading indicators from a sectoral balances’ framework.
Much in the same way that many financial commentators overestimated the power of central banks during the last decade (see our Investment Perspectives article which suggests the Federal Reserve does not influence long-term stock market returns), we believe there is an equal risk they will underestimate the power of the public purse now.
Chris Bedingfield is Principal and Portfolio Manager at Quay Global Investors. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.