Yields on Australian 10 year government bonds are now higher than yields on 10 year government bonds of Italy and Spain, the largest of the European ‘PIIGS’ (Portugal, Italy, Ireland, Greece, Spain), with their crippling debts, lower credit ratings and real possibility of Greek-style default/restructure. How can this be?
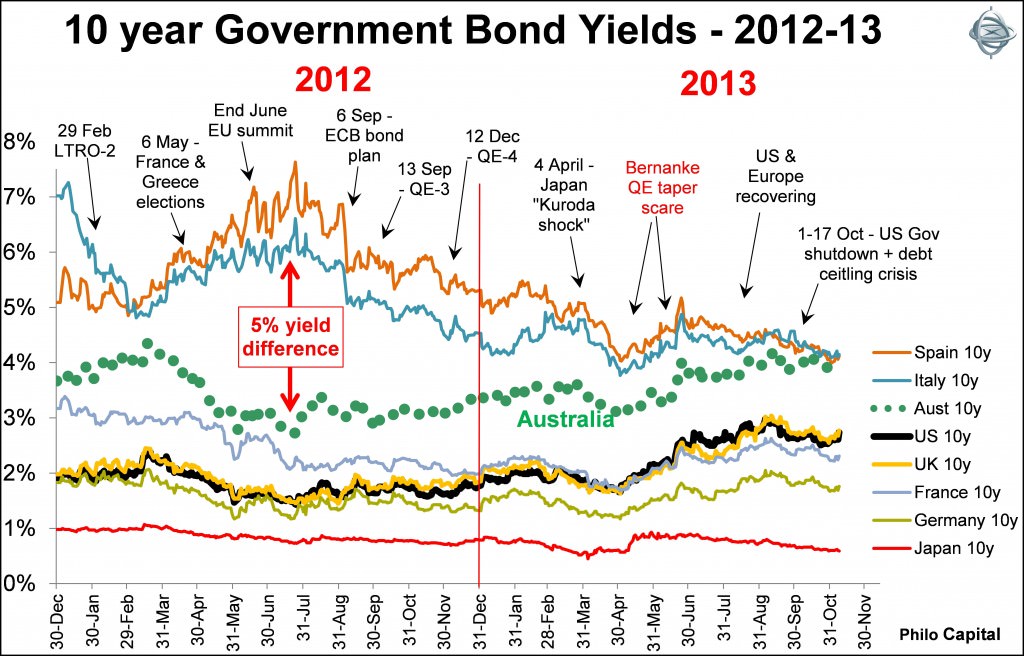
The chart shows yields on 10 year government bonds for Australia and the major markets since the start of 2012. The 5% yield spread between Australia and Spain in the middle of 2012 has now been reduced to nil.
Yields required by bond investors reflect a number of things, including:
- credit risk (expected loss through default or restructure of principal and/or interest)
- inflation risk (expected loss of real value through inflation during the term of the bond) or
- expectations of future interest rates (which largely reflect expectations of future inflation and future monetary policy shifts that may be made to counter inflation).
Yields are also being depressed by the flood of cheap central bank money sloshing around the world, but that is a common factor affecting all assets globally, including Australian bonds.
Aside from credit risk, bond yields should rise as economic growth and inflation rates rise, and yields should fall as economic growth and inflation rates fall. But Australian yields have been rising over the past year while the local economy slows, and PIIGS yields have been falling while Europe slowly recovers.
PIIGS yields are declining mainly because the perceived risk of default has declined due to progress on bank bailout and support mechanisms since the 2012 Greek crisis. In the absence of inflationary pressures, yields have little or no inflation premium built into them.
Australia is highly unlikely to default on its bonds any time soon (although it has in the past), but yields on Australian government bonds are still relatively high in order to compensate investors for potential losses:
- for local Australian bondholders, it is the loss of real value through domestic inflation
- for foreign holders of Australian bonds, it is compensation for future currency losses through likely declines in the Australian dollar over time due to our higher relative inflation.
Inflation may not be as dramatic or sudden as a headline-grabbing default, but it is just as damaging to real returns for investors.
Ashley Owen is Joint Chief Executive Officer of Philo Capital Advisers and a director and adviser to Third Link Growth Fund.