Last autumn we suggested that the global economy would likely face a slowdown in 2023 and that equity investors should eventually consider shifting toward a defensive stance. While this year’s solid returns may appear to belie our view, we are sticking with our call that a dose of caution is merited. In fact, the concentrated nature of 2023’s equities gains – being almost exclusively driven by multiple expansion within a handful of mega-cap technology and internet companies – hides what we consider to be signs of increasing vulnerability within the equities universe.
Exhibit 1: 2023 S&P 500 Index® earnings revisions and price-earnings multiple expansion
This year’s equities returns have been driven by expanding valuation multiples of a few mega-cap – mostly tech and Internet – names, and while this category’s 2023 earnings expectations have held up better than those of the broader market, its multiple expansion likely masks gathering clouds for equities.
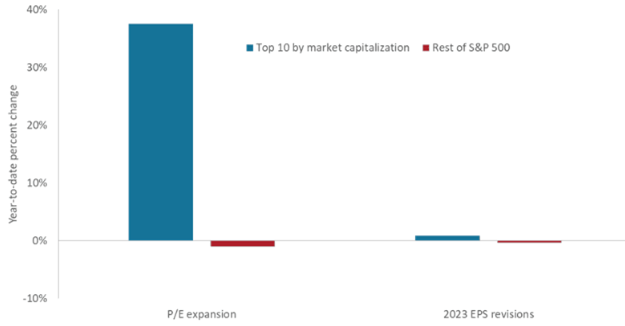
Source: Bloomberg, as of 31 May 2023.
We continue to expect that exceptionally tighter monetary policy will constrict economic activity and, with it, companies’ ability to grow earnings. It’s irrelevant whether the U.S. or other jurisdictions meet the textbook definition of recession; the trend is for economic growth to slide toward zero and for earnings revisions to continue their downward path. The early-year banking sector tumult only fortifies our view as tighter credit conditions should amplify the impact of restrictive policy. Some have characterized bank failures as idiosyncratic, but we consider them the natural consequence of monetary tightening as higher rates tend to break things – and what typically break first are the most fragile business models.
Economic dominoes
Since the Fed’s initial interest rate hike in March 2022, the phrase “long and variable lags” has found prominence in the investment vernacular. Typically, one would expect the economy to slow within 12 to 18 months of that first hike. Guess where we are now?
Central banks rely upon the blunt instrument of rate hikes to quell inflation because it works. In a nod to Milton Friedman, who posited that inflation is always a monetary phenomenon, higher interest rates drain liquidity from the economy, starving inflation of its feedstock. The upshot is a higher cost of capital, less economic activity, and ultimately weaker earnings. We are already seeing evidence of this progression. Only a few months after the Fed’s first post-pandemic rate hike, annualized quarterly broad money growth in the U.S. had dipped into negative territory. By March 2023, it registered -9.4%.
Exhibit 2: Fed funds rate and change in broad U.S. money supply
The U.S. money supply tends to react fairly quickly to a tightening cycle’s initial rate increase, with the current decline being magnified by the Fed’s balance sheet reduction program.
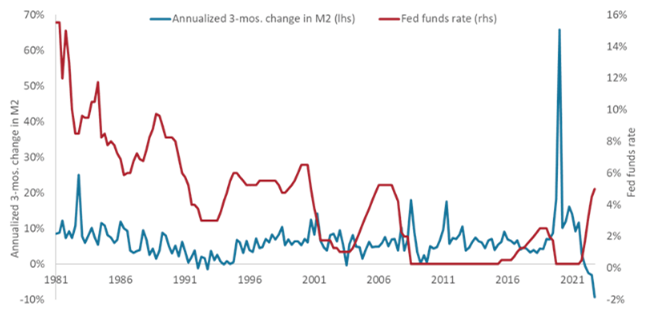
Source: Bloomberg, as of 31 May 2023. M2 is a measure of broader money that includes currency held by the public and other categories, such as checking deposits and money market accounts, that can be quickly converted to cash.
Even after 15 months of tightening, the global economy is proving resilient. Our view is that history’s most anticipated recession is still on track, albeit slightly delayed. Several factors have contributed to this, including the magnitude of the liquidity created during the pandemic and a puzzlingly tight U.S. labor market.
Not to be overlooked, however, is that the market is out of practice in navigating a garden-variety recession, with the two most recent downturns being sparked by a gargantuan housing bubble and a global pandemic. One must look back to 2001 for the most recent example of an interest-rate, capacity overhang-driven recession. That episode illustrated that – unlike the rapid contraction caused by historic events – monetary tightening takes time. With rate hikes possibly not done in the U.S. and likely to continue in other regions, investors need to recognize that sooner or later the inevitable economic outcomes caused by reduced liquidity cannot be avoided.
Rumbling through markets
Earnings expectations have begun to react to a diminishing money supply but – similar to economic growth – at a pace slower than anticipated. By mid-May, full-year 2023 earnings estimates for the S&P 500 Index and MSCI World Index had fallen 12% and 8%, respectively. Given the expectation of additional rate hikes, along with tightening credit conditions, we expect earnings forecasts to slide further.
Equities’ resilience in the face of monetary tightening has the hallmark of a tendency that we often see during this stage of the cycle: complacency. Feeding this behavior is the year-to-date multiple expansion registered by Big Tech and internet stocks. To a degree, this is a reversal of last year’s equity losses, which were driven by the multiple compression of secular growth stocks in the wake of a higher discount rate. Economic weakness typically favors growth stocks as investors seek out earnings growth where they can find it, but the current dominance of mega-cap tech in equities indices lends a veneer of stability while hiding festering weakness underneath.
We believe that the disconnect between aggregate multiple expansion and a slowing economy will come to a head once investors stop pricing in the recovery to a recession that has yet to occur. A capitulation in earnings expectations – completing what could be up to a 20% decline, peak to trough – would also likely ignite a wave of multiple compression as investors shed risk. Putting numbers behind these scenarios, another 10% decline in earnings coupled with a 10% compression in price-earnings (P/E) ratios add up to a bear market.
Staying invested, but defensive
A quick succession of trough earnings and trough multiples also represents opportunity for long-term investors. As we stated in December, while we expect an earnings recession, we believe that the U.S. and global economy are on sufficiently solid footing to avoid a deep and prolonged downturn. Rather, we believe the economy is facing a mid- to late-cycle adjustment, characterized by flat to modestly negative growth. Importantly, after 2022’s rise in rates, the Fed and other central banks now have room to reverse course and ease monetary policy should a worse-than-expected economic scenario unfold.
Under such circumstances, it is our view that this is a time to stay invested but do so by maintaining a defensive stance until greater clarity emerges on the next stage of the cycle. The preferred destination to ride out this uncertainty is quality stocks, as their sound balance sheets and steady cash flows should insulate them from unforeseen downside risk. Stocks with these characteristics also provide investors the potential to participate in any market gains should economic growth exceed expectations. In keeping with the pandemic-era trend, many of the largest tech and internet stocks also meet these defensive criteria. Conversely, exposure to highly cyclical sectors and overleveraged companies should be minimized.
Exhibit 3: Equity factor peak-to-trough returns in recent recessions
Quality tends to outperform in market downturns, and while value lost less than sagging markets in 2022 and growth has led the way in 2023, we believe quality stocks will have the opportunity to prove most resilient as the effects of monetary tightening continue to bite.
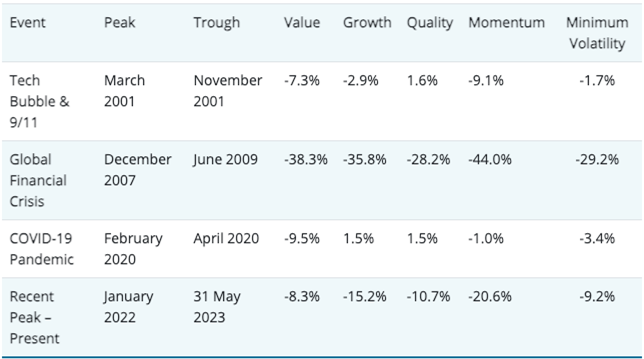
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, Janus Henderson Investors. Peak to trough returns measured on factor-based components of the MSCI World Index
Given the plodding pace of this stage of the cycle, we are not yet at the point where we would advise investors to look through to the other side and position portfolios for recovery. There will come a time for increasing exposure to small caps and cyclical sectors like energy, but until then, quality and defence remain the most prudent tactics.
When facing a slowdown, it’s important to remember that the profit machine of global equities is not broken. Yet, earnings will always remain susceptible to the inevitable economic cycles. Investors need to maintain a long-term view and consult their playbooks on how to navigate economic cycles in a non-zero-percent interest-rate world.
Matt Peron is Director of Research and a Portfolio Manager at Janus Henderson Investors.