Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, we have checked the latest memos to clients written by Howard Marks, Co-Chairman of multibillion-dollar asset manager, Oaktree Capital.
Marks recalls the recovery from the 23 March low resulted in the biggest three-day gain in more than 80 years, which built into a rise of 45% by 8 June. In fact, after Marks' note was published, Wall Street closed its best quarter since 1987, so it is timely to review his anatomy of a rally.
How can the market recover when the economy is much worse than before?
Prior to the pandemic, says Marks, an all-time high had been achieved when the economy was strong and the outlook good. Yet the market has recovered close to that level when economic conditions are much worse. He lists the reasons for the optimism as:
- Investor confidence in the Fed and Treasury to bring about an economic recovery by doing 'whatever it takes'.
- Some improvements in the number of COVID-19 cases and deaths, especially no shortages of hospital beds and optimism on vaccines and treatments.
- The market’s ability to look beyond the crisis, supported by improving economic statistics, to a recovery in GDP and corporate earnings in 2021.
Investors became convinced that the Fed would ensure markets continued to rise, with seemingly little concern for debt levels. The Fed did not even require strong creditworthiness in corporate bonds purchased. With ultra-low rates, the discounted present value of future cash flows rises. Low returns start to look relatively attractive, argues Marks.
He has been asking his team: can the Fed keep buying debt forever?
When bullish market moves began in late March, investors who have little regard for value, such as index funds, ETFs and other automatic traders, perpetuated whatever is set motion. Then behaviours such as FOMO replace the previous greed. He adds his voice to the impact of new retail investors:
“Retail investors are said to have contributed substantially to the stock market’s rise, and certainly to its most irrational aspects … large numbers of call options have been bought in recent days, and it was reported that small investors accounted for much of the volume. Developments like these suggest the influence of speculative fever and the absence of careful analysis. There’s a widely held theory that government benefit checks have been behind some of the retail investors’ purchases. And that makes sense: in the last three months, there’ve been no games for sports bettors to wager on, and the stock market was the only casino that was open.”
He acknowledges his usual cautious approach generates many opposites to the points made above (as described in his previous memos), but it depends what weight the markets gives to each at a point in time.
How to make sense of what is happening
Marks says it is futile to expect the stock market to operate with a universally accepted and reliable way to value companies without bouts of optimism or pessimism. The market can swing quickly between ‘flawless’ and ‘hopeless’.
“But the most optimistic psychology is always applied when things are thought to be going well, compounding and exaggerating the positives, and the most depressed psychology is applied when things are going poorly, compounding the negatives. This guarantees that extreme highs and lows will always be the eventual result in cycles, not the exception.”
He appeals to a few time-honoured standards in the three stages of a rally:
- the first stage, when only a few unusually perceptive people believe improvement is possible
- the second stage, when most investors realise that improvement is actually taking place, and
- the third stage, when everyone concludes everything will get better forever.
Around 23 March was the first stage, when few people focussed on economic improvement. Stage two happened quickly and we went straight to stage three. It feels to him that the market is too focused on the positives.
“I had good company in being sceptical of the May/June gains. On May 12, with the S&P 500 up a startling 28% from the March 23 low, Stan Druckenmiller, one of the greatest investors of all time, said, 'The risk-reward for equity is maybe as bad as I’ve seen in my career.' The next day, David Tepper, another investing great, said it was 'maybe the second-most overvalued stock market I’ve ever seen. I would say ’99 was more overvalued.'"
And after these two spoke, the market continued to run. So his bottom line is similar to his last few memos, that investors are not compensated for risk:
“the fundamental outlook may be positive on balance, but with listed security prices where they are, the odds aren’t in investors’ favour.”
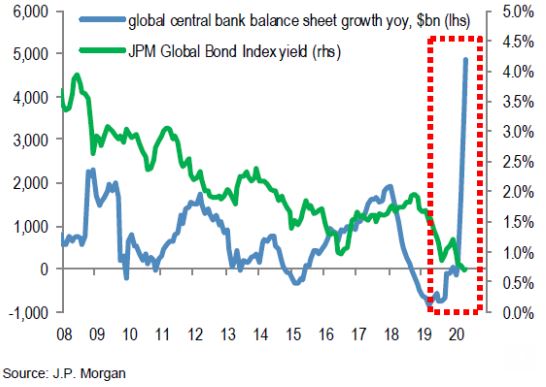
Footnote (not from the Marks article). This chart from JP Morgan shows the rapid growth of major central bank balance sheets as they print money, and how their bond purchases have pushed down global bond rates.
Graham Hand is Managing Editor of Firstlinks. Howard Marks is Co-Chairman of multibillion-dollar asset manager, Oaktree Capital, and here is the full text of his latest memo. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.