Han Fantong, an accountant, beat almost 60 other bidders to buy a three-bedroom home in Melbourne in November 2015 for $930,000. He had an advantage – full funding from his parents back in China. Han, 32, an Australian permanent resident, bought the house on 688 square meters of land in Ringwood East, about 30 kilometres east of Melbourne’s business district, after a five-month search. His parents sold a 23-year-old two-bedroom apartment in Beijing for 8.1 million yuan ($1.65 million) to help pay for the property, he said by phone.
“It comes as a tradition in China to buy a home for a son to establish a family,” said Han who lives in the house with his 29-year-old wife Chen Junyang. “Without my parents, it would still be difficult for us to bear the large mortgage loans.”
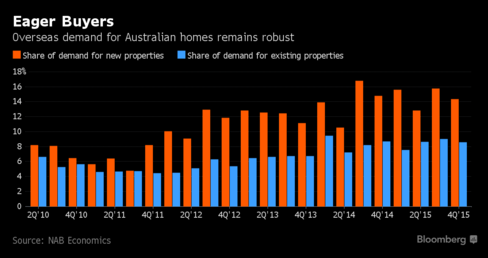
Han is among scores of buyers who with the backing of relatives in China are underpinning a housing market in Australia that’s coming off the boil. More than half the buyers of Chinese origin are supported financially by relatives residing in the world’s second-largest economy, according to McGrath Ltd, Australia’s only listed real estate agency. The firm’s China desk has assisted in sales worth A$140 million since it was established in September 2013.
Increasing demand
Such demand, whether from permanent residents or overseas buyers, has triggered community concern that locals are being priced out of Australia’s housing market. The government has responded to the unease with tighter scrutiny of foreign investment that critics say may deter much-needed offshore capital.
“Chinese buying in Sydney and Melbourne has stepped up from say where it was five years ago, but publicity around that has created a perception which has run ahead of reality,” said Shane Oliver, chief economist at AMP Capital in Sydney. “The Chinese demand – both from mainland China and Chinese Australians – is propping up the housing market and boosting construction.”
Leo Yu, 31, an Australian citizen, last year bought a two-bedroom apartment in the inner-Sydney suburb of Surry Hills, known for its cafes and restaurants, with the help of his parents from Qingdao. They gave him $73,000, part of it from China, toward a 20% deposit on the unit, which cost $835,000. The rest of the money was through a bank loan. Yu, an accountant, is renting out the property.
“The property can protect my parent’s money from inflation and foreign-exchange risk,” he said. “One day when they come to Australia for family reunion, I can sell the property to repay the deposit so that they can buy their own retirement home."
Hot market
Purchases by foreigners, many with a connection to China, helped drive an almost 55% jump in home prices across Australia’s capital cities in the past seven years as mortgage rates dropped to five-decade lows. The median Sydney home price reached a record $800,000 in October, according to research firm CoreLogic Inc. data. It has since fallen after a regulatory clampdown led to a slowdown in mortgages to landlords and the first increase in borrowing costs in five years.
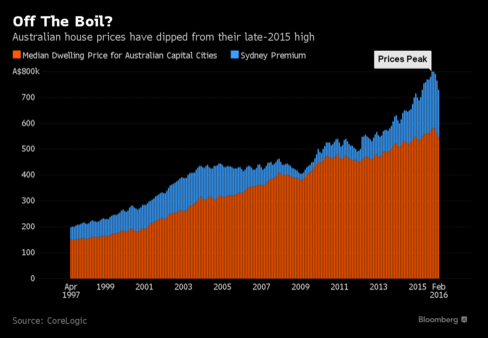
Global financial market turmoil after China unexpectedly devalued the yuan last August, sending the benchmark Shanghai Composite Index more than 40% lower from a June peak, doesn’t seem to have put a dent in demand.
And channels to get money out of China, where top-tier city home prices have been surging, remain open, even amid a crackdown by Beijing on capital outflows. As Bloomberg reported in November, Chinese nationals can break down cash into small amounts to avoid official scrutiny, and enlist friends, relatives and even employees to send out the money on their behalf.
Capital outflow restrictions are expected to be short-term and while they may have some impact on overseas investments, there are still enough buyers in China who can afford overseas properties, G.T. Hu, the chief executive officer of the Australian unit of Country Garden Holdings Co., said in an interview Thursday.
“It didn’t feel to us that the stock rout in China impacted the market in Sydney,” said Luo Xiaohua, general manager of Shanghai-based property developer Greenland Group’s investment arm in Australia. “We feel the market is stable and the demand is relatively strong.”
The firm, which entered Australia in 2013, has sold $1 billion worth of apartments across three projects in Sydney, and is working on another two developments in the city and one in Melbourne, Luo said.
Home open
Five out of the seven properties sold earlier this year by First National Real Estate in Lindfield – a suburb about 13 kilometres north of Sydney’s business district – were to buyers of Chinese origin, according to Lan Zhang, a director at the firm.
“Chinese origin buyers who are either permanent residents or citizens are among the biggest group of people who visit our open homes,” she said. The buyers were able to exchange contracts within a few days of agreeing on a deal, suggesting financing was not an issue, she said.
Overseas buyers are largely limited by Australian law to new homes and need approval from the Foreign Investment Review Board. Temporary residents can buy new or existing properties with the board’s approval, but must sell them when they leave the country. Amid community concern, Australia announced a crackdown on unlawful home purchases last year, and has forced sales of 27 properties, worth more than $76 million.
Authorities in Canada have also been grappling with the issue. The National Bank of Canada estimates that Chinese buyers made up about one-third of purchases last year in Vancouver, and the government has set aside money to find ways of tracking foreign homebuyers.
House with garden
Demand in Australia is so strong that online real estate listing firm Domain Group has, since late 2013, published a glossy weekly in Chinese which it distributes at 400 points across Sydney and Melbourne. The site is looking at more ways to connect with Chinese Australians as it expects demand from the community to only increase, according to its Chief Economist Andrew Wilson.
About one in two buyers who show up at auctions in Ringwood East in Melbourne are Chinese, according to Han, who has no siblings as a result of China’s one-child policy that created a generation of so-called “little emperors.” He said his home purchase was a “good trade”.
“Houses here are still a lot cheaper, larger and better quality than those tiny apartments in Beijing,” he said. “I would never imagine living in an American-style house with a garden in Beijing.”
Narayanan Somasundaram is Bloomberg’s Australian Financial Services Correspondent. This article was first published by Bloomberg and is reproduced with permission. This article is general information only.